Abstract
Death by drowning is a major cause of unnatural death worldwide. It is therefore important to conduct forensic examination of immersed bodies following drowning, in order to determine the diagnosis of drowning, because no specific methods have been established thus far. Therefore, we performed a series of rat experiments to compare autopsy findings between seawater and fresh water drowning cases, which included the presence of pleural effusion and histologic findings of the lung. The results showed that the volume of pleural effusion increased in the seawater drowning group compared to the fresh water drowning group, and the total weight of lung was affected by the type of drowning medium and postmortem interval. However, histologic findings of the lung showed no significant difference between the 2 types of drowning mediums.
REFERENCES
2. van Beeck EF, Branche CM, Szpilman D, et al. A new definition of drowning: towards documentation and prevention of a global public health problem. Bull World Health Organ. 2005; 83:853–6.
3. Davis JH. Autopsy findings in victims of drowning. Modell JH, editor. The Pathology and Treatment of Drownings and Near-Drowning. Illinois: Charles C Thomas Publisher;1971. p.p. 74–82.
5. Idris AH, Berg RA, Bierens J, et al. Recommended guidelines for uniform reporting data from drowning: the “Utstein style”. Resusciatation. 2003; 59:45–57.
6. Kringsholm B, Filskov A, Kock K. Autopsied cases of drowning in Denmark 1987-1989. Forensic Sci Int. 1991; 52:85–92.

7. Halmagyi DF. Lung changes and incidence of respiratory arrest in rats after aspiration of sea and fresh water. J Appl Physiol. 1961; 16:41–4.

8. Reidbord HE, Spitz WU. Ultrastructural alterations in rat lungs. Changes after intratracheal perfusion with fresh water and seawater. Arch Pathol. 1966; 81:103–11.
9. Fuller RH. The 1962 Wellcome prize essay. Drowning and the postimmersion syndrome. A clinicopathologic study. Mil Med. 1963; 128:22–36.
11. Toklu AS, Alkan N, Gurel A, et al. Comparison of pulmonary autopsy findings of the rats drowned at surface and 50 ft depth. Forensic Sci Int. 2006; 164:122–5.
12. Nishitani Y, Fujii K, Okazaki S, et al. Weight ratio of the lungs and pleural effusion to the spleen in the diagnosis of drowning. Leg Med. 2006; 8:22–7.

13. Sugimura T, Kashiwagi M, Matsusue A, et al. Application of the drowning index to actual drowning cases. Legal Med. 2010; 12:68–72.

14. Yarulmaz C, Arican N, Afacan I, et al. Pleural effusion in bodies recovered from water. Forensic Sci Int. 2003; 136:16–21.
15. Terazawa K, Haga K. The role of pleural effusion in drowning. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1996; 17:173–4.

16. Modell JH, Bellefleur M, Davis JH. Drowning without aspiration: is this an appropriate diagnosis? J Forensic Sci. 1999; 44:1119–23.

17. Modell JH, Moya F. Effects of volume of aspirated fluid during chlorinated fresh water drowning. Anesthesiology. 1966; 27:662–72.

18. Modell JH, Moya F, Newby EJ, et al. The effects of fluid volume in sea water drowning. Ann Intern Med. 1967; 67:66–80.
19. Lunetta P, Modell JH, Sajantila A. What is the Incidence and Significance of “dry-lungs” in Bodies Found in Water? Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2004; 25:291–301.

20. Orlowski JP, Szpilman D. Drowning. Rescue, resuscitation and reanimation. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2001; 48:627–46.
Fig. 1.
Thoracic cage was opened to examine the volume of pleural effusion (a: seawater, 2 hr; b: seawater, 20 hr; c: postmortem, seawater, 20 hr; d: freshwater, 2 hr; e: freshwater, 20 hr; f: postmortem, freshwater, 20 hr).
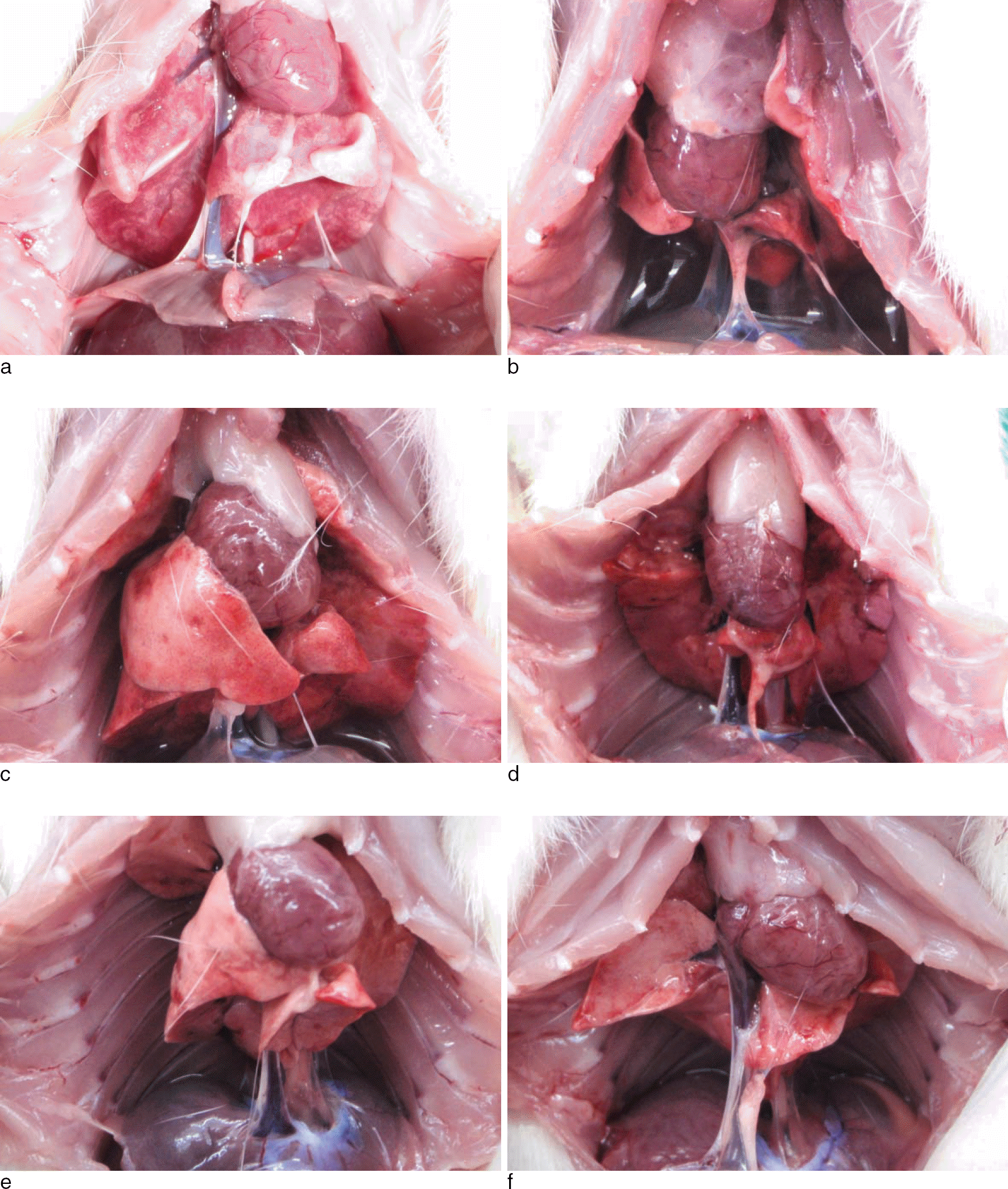
Fig. 3.
Photograph shows ventral surface of the lung (a: seawater, 2 hr; b: seawater, 20 hr; c: postmortem, seawater, 20 hr; d: freshwater, 2 hr; e: freshwater, 20 hr; f: postmortem, freshwater, 20 hr).
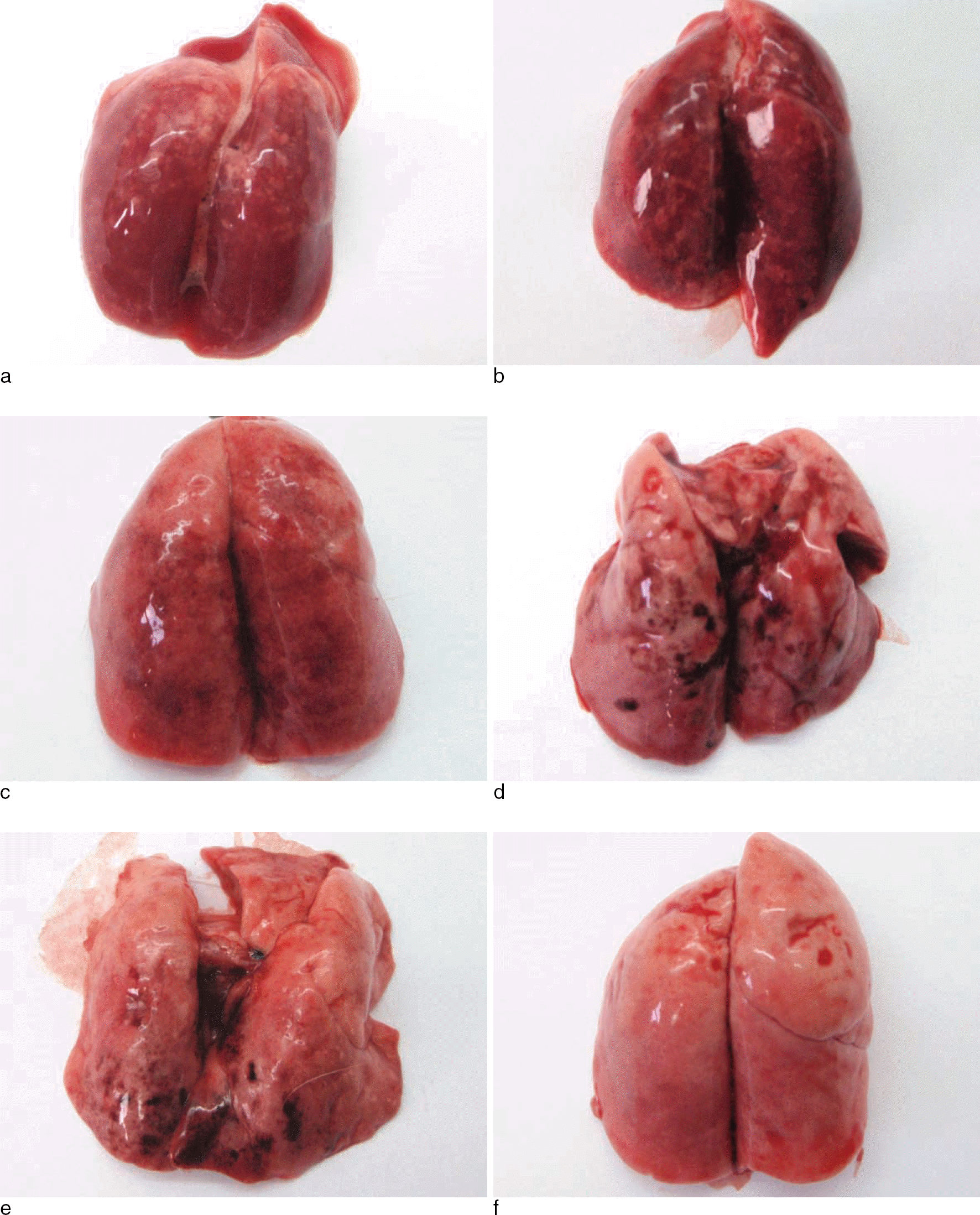
Fig. 4.
Histologic section of rat’ s lung tissues shows alveolar edema, perivascular edema, alveolar hemorrhage and bronchiolar hemorrhage (a: 3+ of alveolar edema in #18, H&E, × 200; b: 3+ of perivascular edema in #4, H & E, × 200; c: 3+of alveolar hemorrhage in #20, H & E, × 200; d: 3+ of bronchiolar hemorrhage in #14, H & E, × 200).
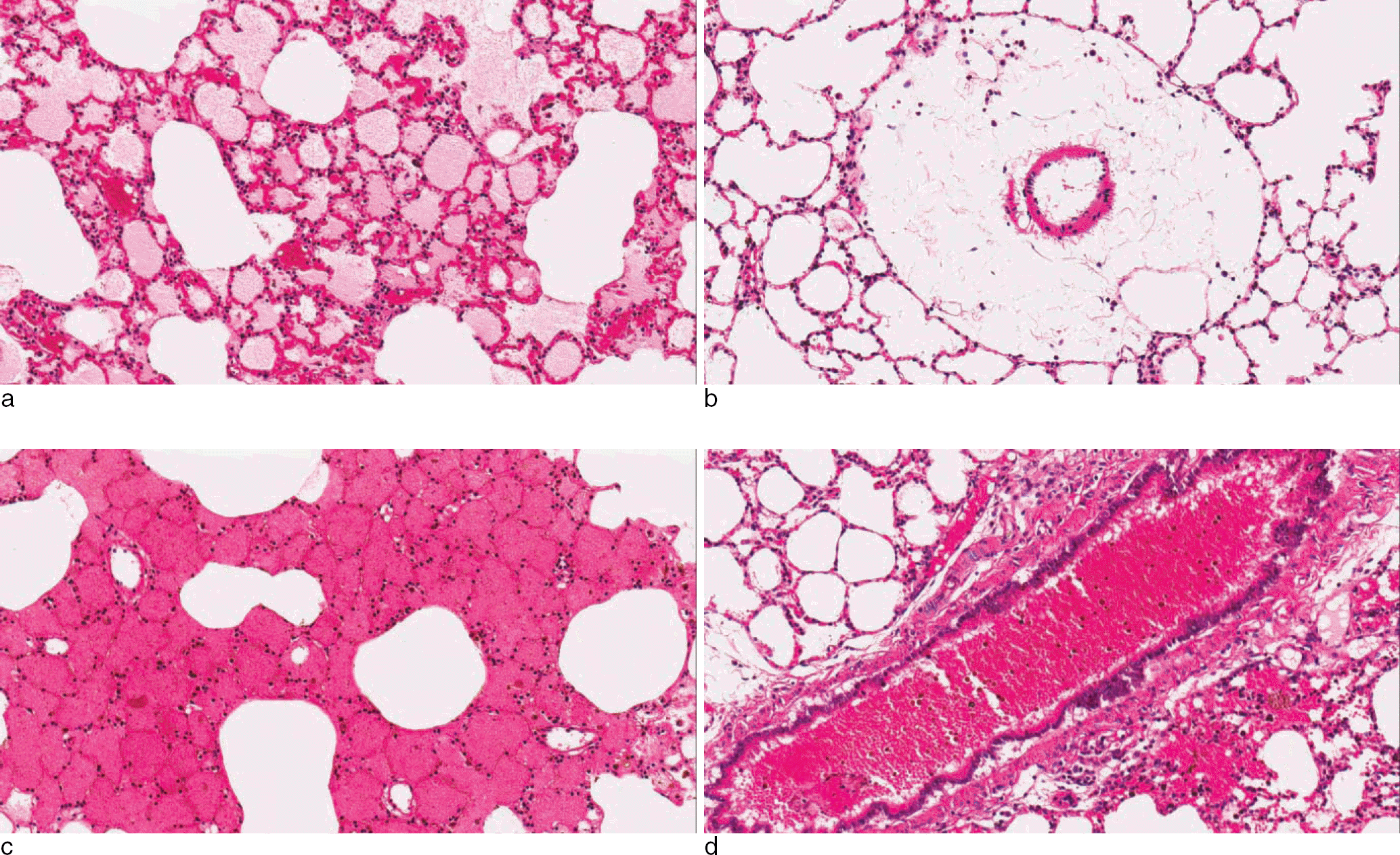
Table 1.
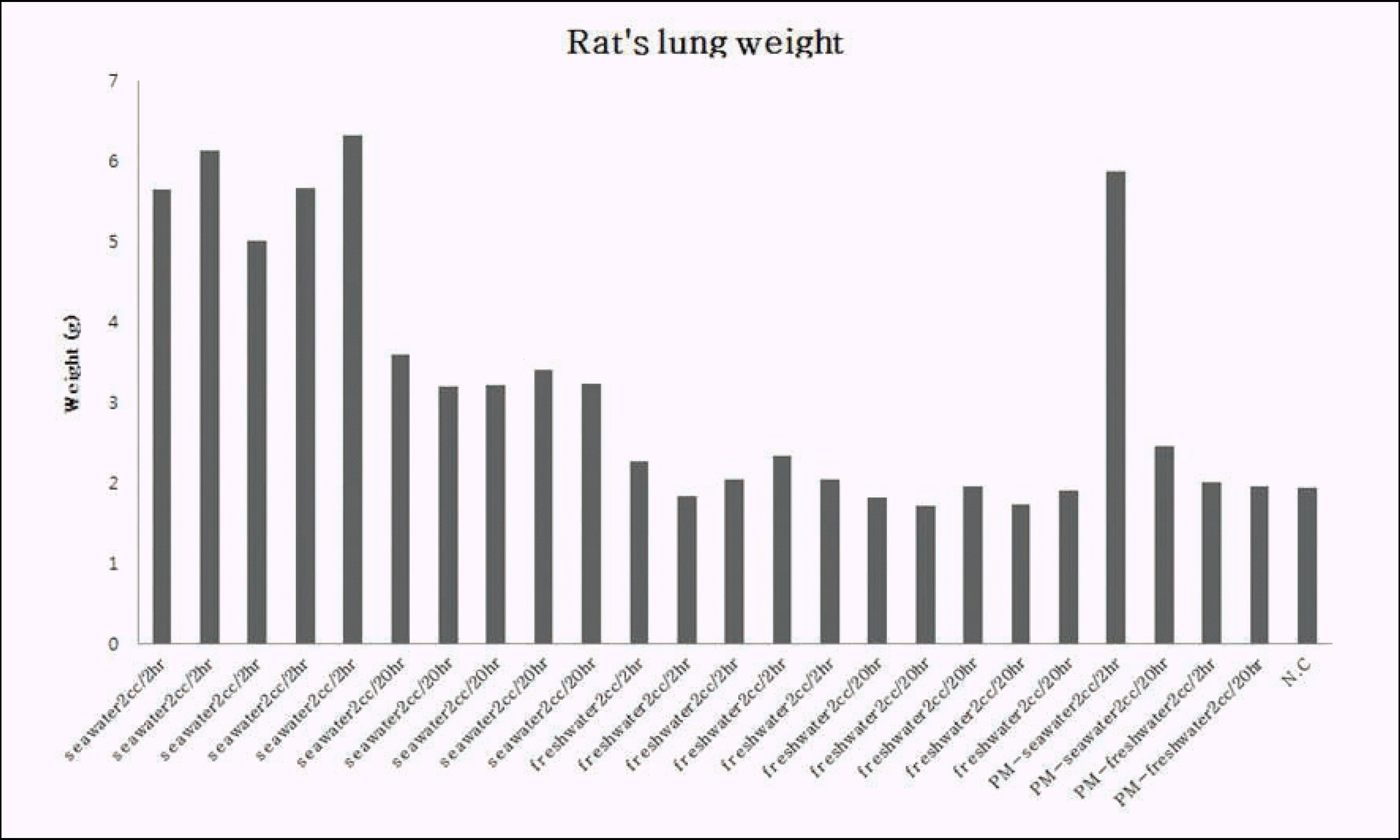
Summary of Experimental Condition and the Results Including Correlation with Pleural Effusion and Lung Weight
| No. | Condition | Weight (g) | Total pleural effusion (㎖) (A) | Total lung weight (g) (B) | Total lung weight / NC∗ lung weight (C) | A+B | A+C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 279 | 0.10 | 5.65 | 2.93 | 5.75 | 3.03 |
| 2 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 270 | trace | 6.13 | 3.18 | 6.13 | 3.18 |
| 3 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 275 | trace | 5.00 | 2.59 | 5.00 | 2.59 |
| 4 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 270 | 0.10 | 5.66 | 2.93 | 5.76 | 3.03 |
|
5 |
seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr |
272 |
trace |
6.32 |
3.27 |
6.32 |
3.27 |
| Average | 273 | UC† | 5.75 | 2.98 | 5.79 | 3.02 | |
| 6 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 290 | 1.40 | 3.60 | 1.87 | 5.00 | 3.27 |
| 7 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 272 | 2.00 | 3.19 | 1.65 | 5.19 | 3.65 |
| 8 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 270 | 1.97 | 3.21 | 1.66 | 5.18 | 3.63 |
| 9 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 280 | 1.80 | 3.40 | 1.76 | 5.20 | 3.56 |
|
10 |
seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr |
283 |
1.50 |
3.23 |
1.67 |
4.73 |
3.17 |
| Average | 279 | 1.73 | 3.33 | 1.72 | 5.06 | 3.46 | |
| 11 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 290 | 0.01 | 2.27 | 1.18 | 2.28 | 1.19 |
| 12 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 290 | trace | 1.84 | 0.95 | 1.84 | 0.95 |
| 13 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 292 | trace | 2.05 | 1.06 | 2.05 | 1.06 |
| 14 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 285 | trace | 2.33 | 1.21 | 2.33 | 1.21 |
|
15 |
freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr |
279 |
0.02 |
2.04 |
1.06 |
2.06 |
1.08 |
| Average | 287 | UC | 2.11 | 1.09 | 2.11 | 1.10 | |
| 16 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 281 | trace | 1.82 | 0.94 | 1.82 | 0.94 |
| 17 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 270 | trace | 1.71 | 0.89 | 1.71 | 0.89 |
| 18 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 297 | trace | 1.96 | 1.02 | 1.96 | 1.02 |
| 19 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 274 | 0.03 | 1.73 | 0.90 | 1.76 | 0.93 |
|
20 |
freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr |
278 |
trace |
1.90 |
0.98 |
1.90 |
0.98 |
| Average | 280 | UC | 1.82 | 0.95 | 1.83 | 0.95 | |
| 21 | PM† seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 273 | trace | 5.86 | 3.04 | 5.86 | 3.04 |
| 22 | PM seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 270 | 0.86 | 2.46 | 1.27 | 3.32 | 2.13 |
| 23 | PM freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 287 | trace | 2.00 | 1.04 | 2.00 | 1.04 |
| 24 | PM freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 287 | trace | 1.96 | 1.02 | 1.96 | 1.02 |
|
25 |
Negative control |
282 |
trace |
1.93 |
1.00 |
1.93 |
1.00 |
Table 2.
Summary of Histologic Changes of Lung according to Experimental Condition
| No. | Condition | Histologic findings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alveolar edema | Perivascular edema | Alveolar hemorrhage | Bronchiolar hemorrhage | Subpleural congestion or hemorrhage | Atelectasis | Emphysema | ||
| 1 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 0 | 2+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 2 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 0 | 2+ | 1+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 2+ |
| 3 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 1+ | 2+ | 2+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 2+ |
| 4 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 1+ | 3+ | 3+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 2+ |
| 5 | seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 1+ | 3+ | 3+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 2+ |
| 6 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 0 | 3+ | 0 | 2+ | 0 | 1+ | 1+ |
| 7 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 2+ | 2+ | 2+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 8 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 2+ | 1+ | 2+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 9 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 10 | seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 11 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 2+ | 1+ | 2+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 12 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 1+ | 1+ | 3+ | 2+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 13 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 14 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | 3+ | 0 | 1+ | 2+ |
| 15 | freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 2+ | 1+ | 2+ | 1+ | 0 | 1+ | 2+ |
| 16 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 2+ | 1+ | 2+ | 2+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 17 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 18 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 3+ | 2+ | 3+ | 3+ | 2+ | 2+ | 1+ |
| 19 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 1+ | 0 | 2+ | 2+ | 0 | 2+ | 2+ |
| 20 | freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 1+ | 2+ | 3+ | 1+ | 0 | 1+ | 1+ |
| 21 | PM∗ seawater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 0 | 2+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2+ |
| 22 | PM seawater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 0 | 1+ | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2+ |
| 23 | PM freshwater 2 ㎖/2 hr | 0 | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 24 | PM freshwater 2 ㎖/20 hr | 0 | 2+ | 2+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ |
| 25 | Negative control | 0 | 1+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download