Abstract
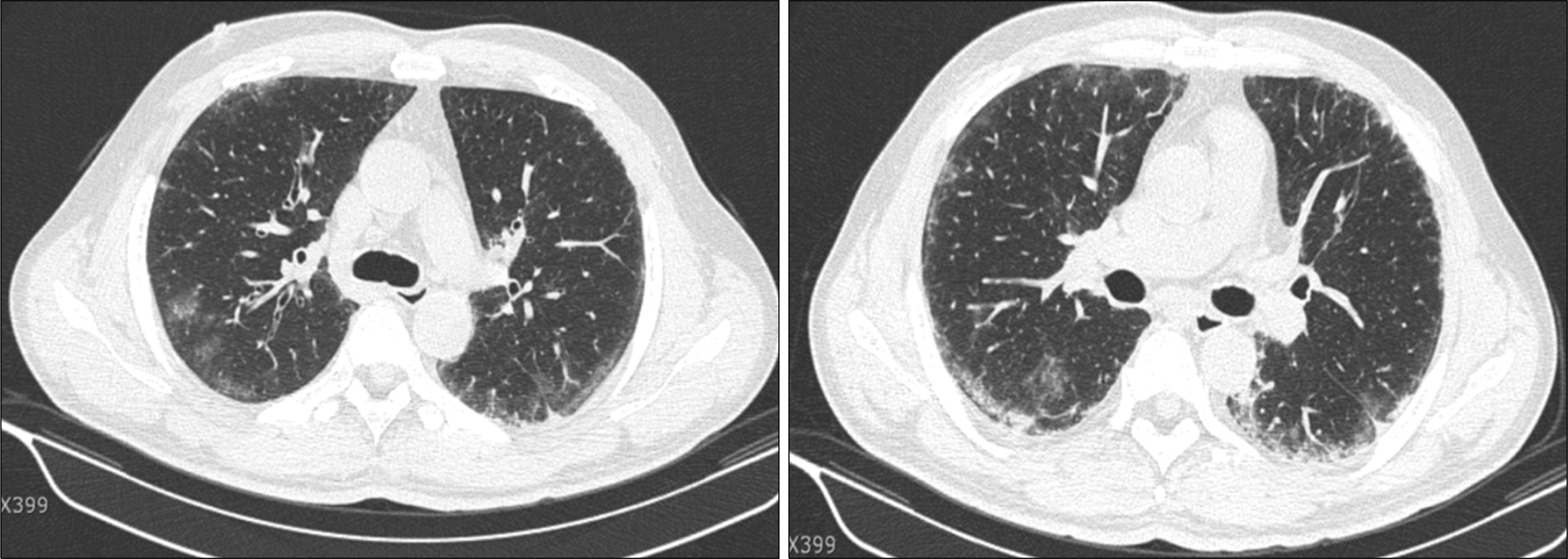
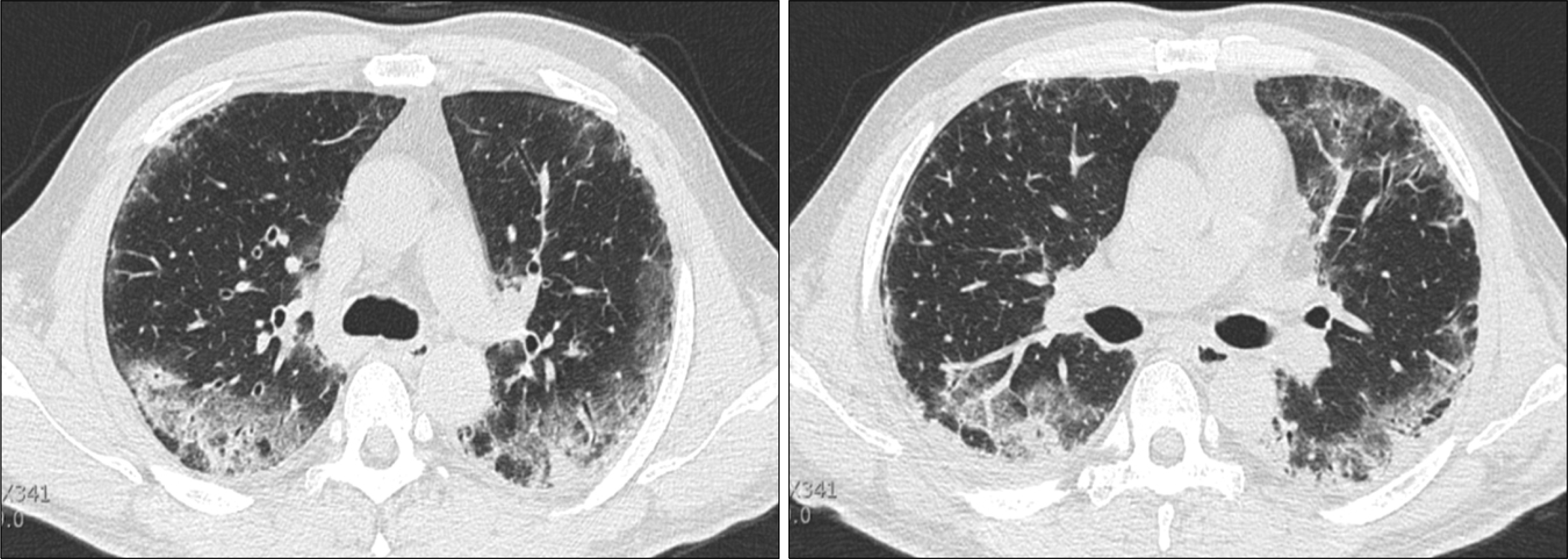
The clinical manifestations of antisynthetase syndrome are severe interstitial pneumonitis, mild polyarthritis, and myositis. This disease is accompanied by anti-Jo-1 antibodies and anti-Ro/SSA antibodies and occasionally by the concurrence of anti-Jo-1 and anti-Ro/SSA antibodies, which leads to a more severe form of interstitial lung disease. In this case, the patient was transferred to our hospital because of pulmonary fibrosis with myositis and diagnosed with antisynthetase syndrome and the concurrence of anti-Jo-1 with anti-Ro/SSA antibodies. He was refractory to glucocorticoids, and developed leucopenia and thrombocytopenia. He was treated with rituximab infusions, but the interstitial pneumonitis progressed very rapidly and he died.
REFERENCES
1). Sem M., Molberg M., Lund MB., Gran JT. Rituximab treatment of the antisynthetase syndrome: a retrospective case series. Rheumatology. 2009. 48:968–71.
2). Wilkes MR., Sereika SM., Fertig N., Lucas MR., Oddis CV. Treatment of antisynthetase-associated interstitial lung disease with tacrolimus. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:2439–46.

3). Arkfeld DG. The potential utility of B cell-directed biologic therapy in autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol Int. 2008. 28:205–15.

4). Vandenbroucke E., Grutters JC., Altenburg J., Boersma WG., ter Borg EJ., van den Bosch JM. Rituximab in life threatening antisynthetase syndrome. Rheumatol Int. 2009. 29:1499–502.

5). Imbert-Masseau A., Hamidou M., Agard C., Grolleau JY., CheArin P. Antisynthetase syndrome. Joint Bone Spine. 2003. 70:161–8.

6). Jankowska M., Butto B., Debska-Slizien A., Rutkowski B. Benefcial effect of treatment with cyclo-sporine A in a case of refractory antisynthetase syndrome. Rheumatol Int. 2007. 27:775–80.
7). VaAncsa A., CsiApo I., NeAmeth J., DeAveAnyi K., Gergely L., DankoA K. Characteristics of interstitial lung disease in SS-A positive/Jo-1 positive infammatory myopathy patients. Rheumatol Int. 2009. 29:989–94.
8). La Corte R., Lo Mo Naco A., Locaputo A., Dolzani F., Trotta F. In patients with antisynthetase syndrome the occurrence of anti-Ro/SSA antibodies causes a more severe interstitial lung disease. Autoimmunity. 2006. 39:249–53.

9). Silverman GJ., Weisman S. Rituximab therapy and autoimmune disorders: prospects for anti-B cell therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:1484–92.

10). Edwards JC., Szczepanski L., Szechinski J., Filipowicz-Sosnowska A., Emery P., Close DR, et al. efficacy of B-cell-Targeted Therapy with Rituximab in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthirtis. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:2572–81.
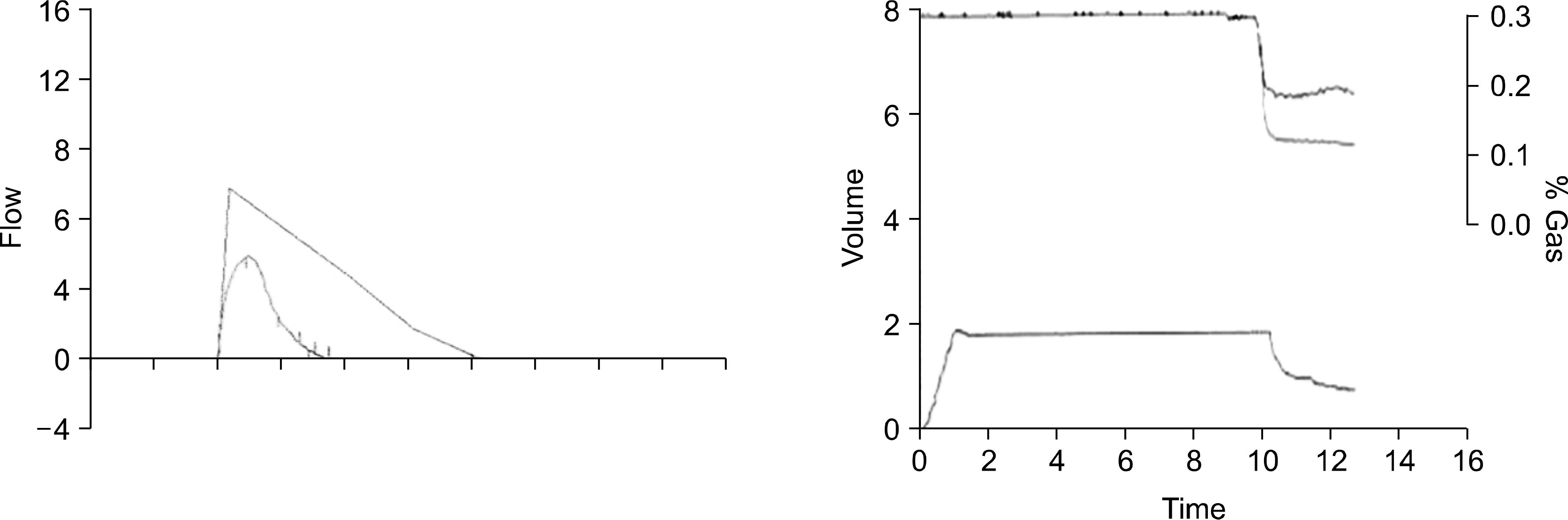
Fig. 1.
Pulmonary function test showed restrictive pattern and reduced diffusion capacity (forced vital capacity [FVC], 46%: forced expiratory volume in 1 sec [FEV1], 53%: CO diffusing capacity [DLCO], 44%).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download