Abstract
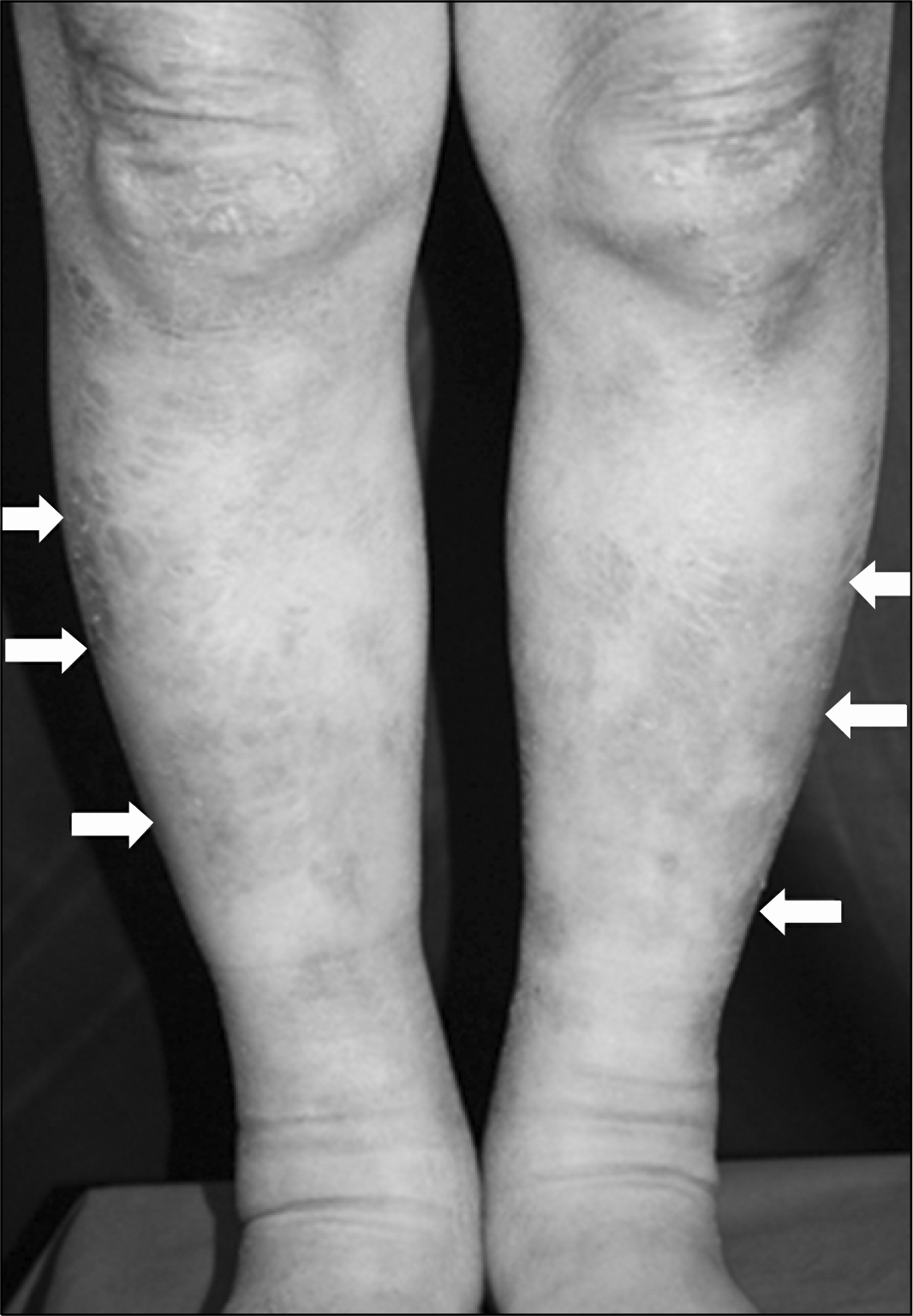
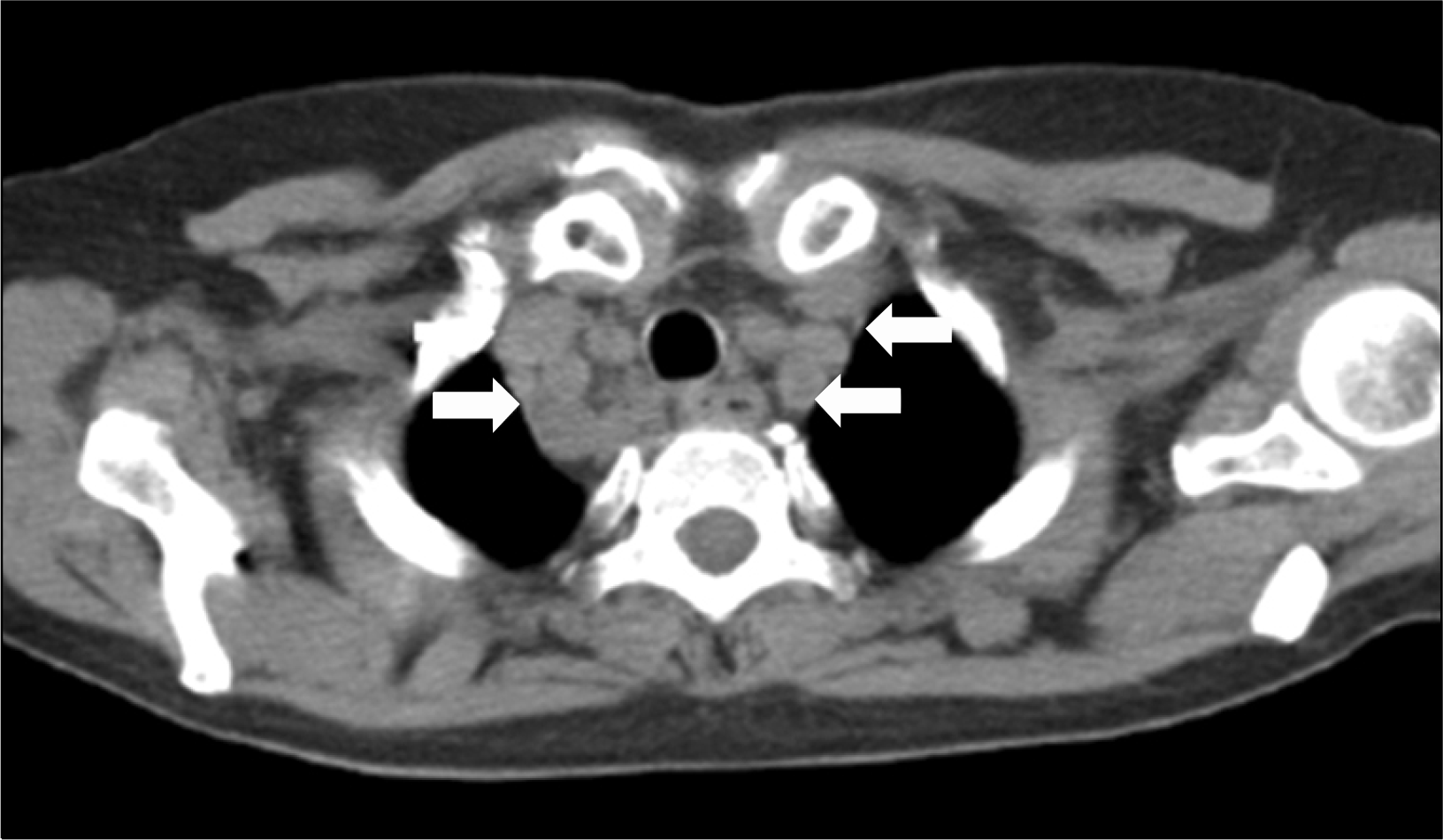
A 62-year-old Korean woman was admitted to our department to evaluate a chronic cough and sputum, which had begun several weeks ago. The patient had been diagnosed with systemic sclerosis in 2004. Autoantibody screening tests were negative for the anticentromere and antitopoisomerase antibodies. She received therapy with combined cyclophosphamide, a calcium channel blocker, D-penicillamine, and low dose steroid. In 2006, a pulmonary function test (PFT) showed a restrictive pattern, and a computed tomography (CT) scan of the lungs revealed interstitial lung disease, but no symptoms were present, so we maintained her on the medication. In October 2008, a chest x-ray and CT scan of the lungs demonstrated aggravation with bilateral basal interstitial infiltrates and hilar lymphadenopathy. Cyclophosphamide pulse therapy was conducted six times during 6 months, but there was no change on her chest CT and PFT, and she had no symptoms, so we decided to follow up. On admission, no significant interval change in the reticular opacity of both lower lungs was observed, but several lymph nodes were enlarged on a chest and neck CT. The skin showed multiple large polygonal-shaped scaled lesions on her upper and lower extremities. Biopsies were taken from the skin of the lower extremities and the left cervical lymph node. Typical noncaseating granulomas corresponding to sarcoidosis were found along with systemic sclerosis findings.
REFERENCES
1). Groen H., Postma DS., Kallenberg CG. Interstitial lung disease and myositis in a patient with simultaneously occurring sarcoidosis and scleroderma. Chest. 1993. 104:1298–300.

2). Maekawa Y., Nogami R. A case of progressive systemic sclerosis associated with sarcoidosis and esophageal adenocarcinoma. J Dermatol. 1993. 20:45–48.

3). Enzenauer RJ., West SG. Sarcoidosis in autoimmune disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992. 22:1–17.

4). Sharma OP., Ahamad I. The CREST syndrome and sarcoidosis. Another example of an overlap syndrome. Sarcoidosis. 1988. 5:71–3.
5). Wiesenhutter GW., Sharma OP. Is sarcoidosis an autoimmune disease?: report of four cases and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1979. 9:124–44.

6). Cox D., Conant E., Earle L., Newman J., Kahaleh B., Jimenez S, et al. Sarcoidosis in systemic sclerosis: report of 7 cases. J Rheumatol. 1995. 22:881–5.
7). Arapis J., Kaklamani V., Rapti A., Anagnostopoulou U. A case of scleroderma associated with sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1997. 15:337–8.
8). De Bandt M., Perrot S., Masson C., Meyer O. Systemic sclerosis and sarcoidosis, a report of five cases. Br J Rheumatol. 1997. 36:117–9.

9). Takahashi T., Munakata M., Homma Y., Kawakami Y. Association of progressive systemic sclerosis with pulmonary sarcoidosis. Just a chance occurrence? Intern Med. 1997. 36:435–8.
10). Biasi D., Caramaschi P., Carletto A., Bambara LM. Localized scleroderma associated with sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998. 16:761–2.
11). Lis-Swiety A., Brzezinska-Wcislo L., Pierzchala E., Wcislo-Dziadecka D. Systemic sclerosis-polymyositis overlap syndrome accompanied by autoimmune hepatitis and sarcoidosis of mediastinal lymphnodes. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006. 20:107–8.

Fig. 3.
Skin biopsy, showing dermal fibrosis and several noncaseating granulomas (black arrows). Granuloma consists of epitheloid cells and langerhans giant cells (Hematoxylin & Eosin stain, ×100).
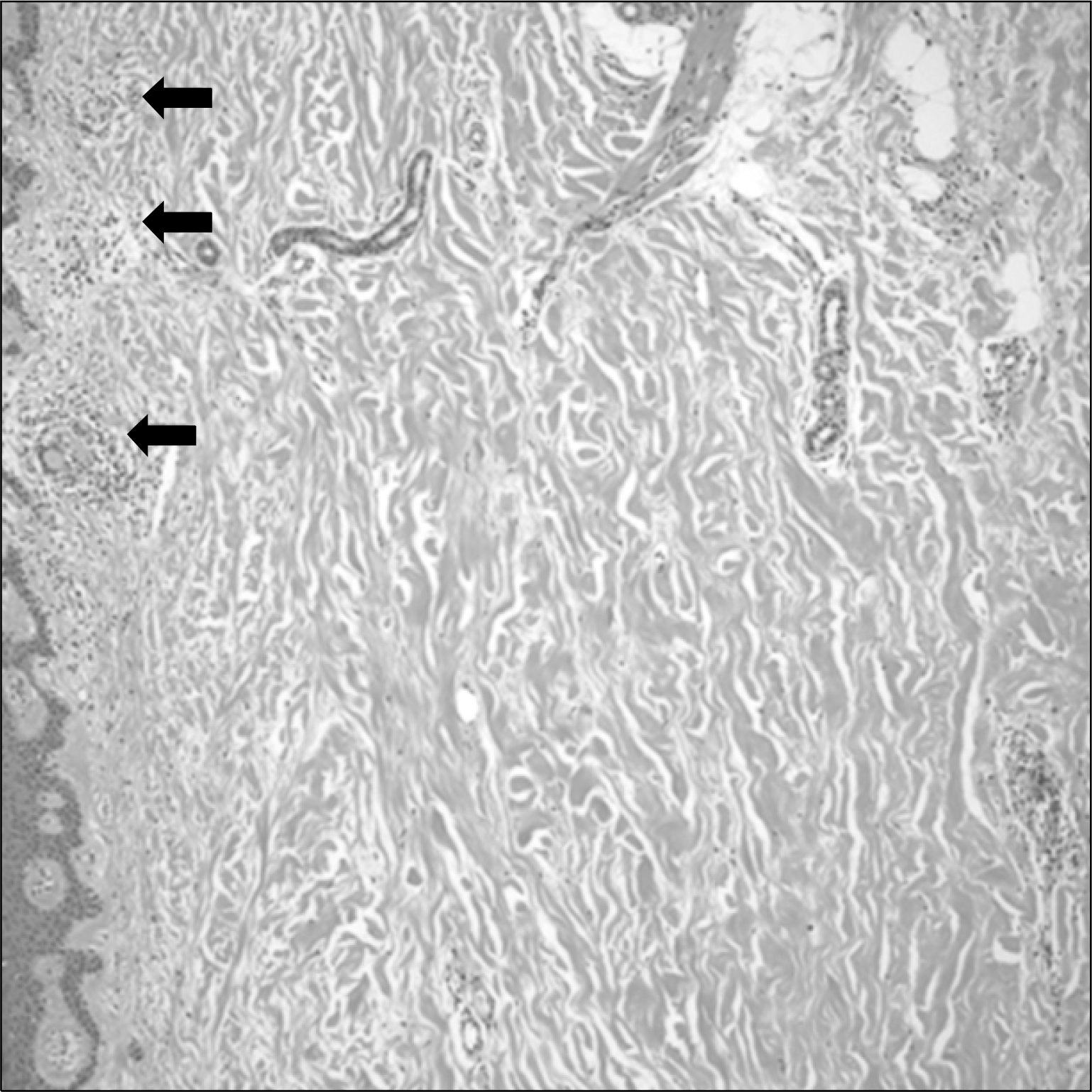
Fig. 4.
Lymph node biopsy, showing several noncaseating granulomas (black arrows). Granuloma consists of a localized collection of epithelioid histiocytes surrounded by a rim of variable numbers of lymphocytes (Hematoxylin & Eosin stain, ×100).
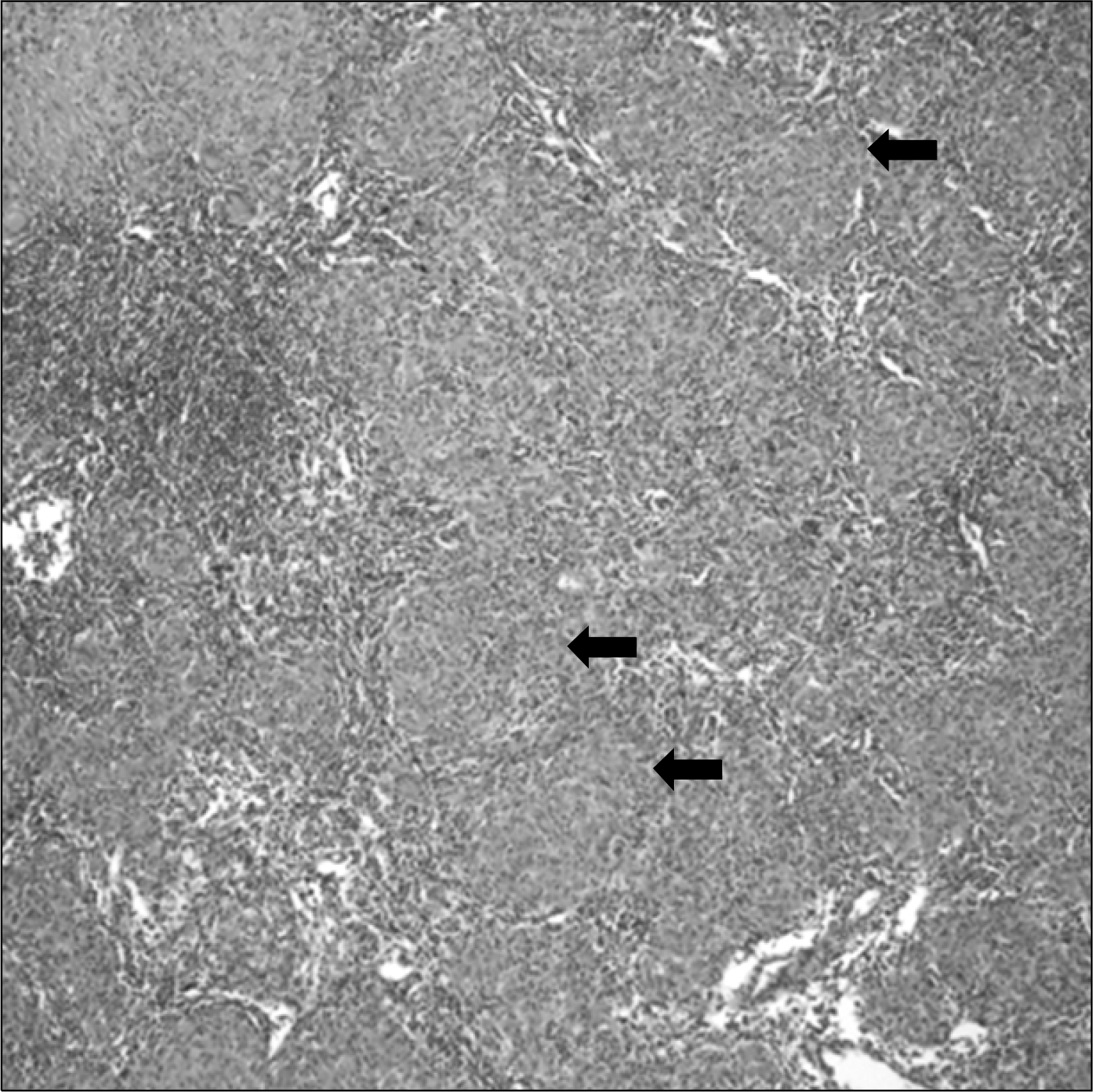
Table 1.
Characteristics, radiological features, and laboratory findings of 25 patients with coexistent systemic sclerosis and sarcoidosis
ACE: angiotensin converting enzyme, BAL: bronchoalveolar lavage, BHL: bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, C: anticentromere antibody, CT: chest CT, D: diffuse, Dec: decreased, F: female, ILD: interstitial lung disease, L: limited, LN: lymph node, M: male, Med: mediastinal, N: negative, ND: not done, SA: sarcoidosis, SSc: systemic sclerosis, T: antitopoisomerase antibody, Blank: unknown, +: positive




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download