Abstract
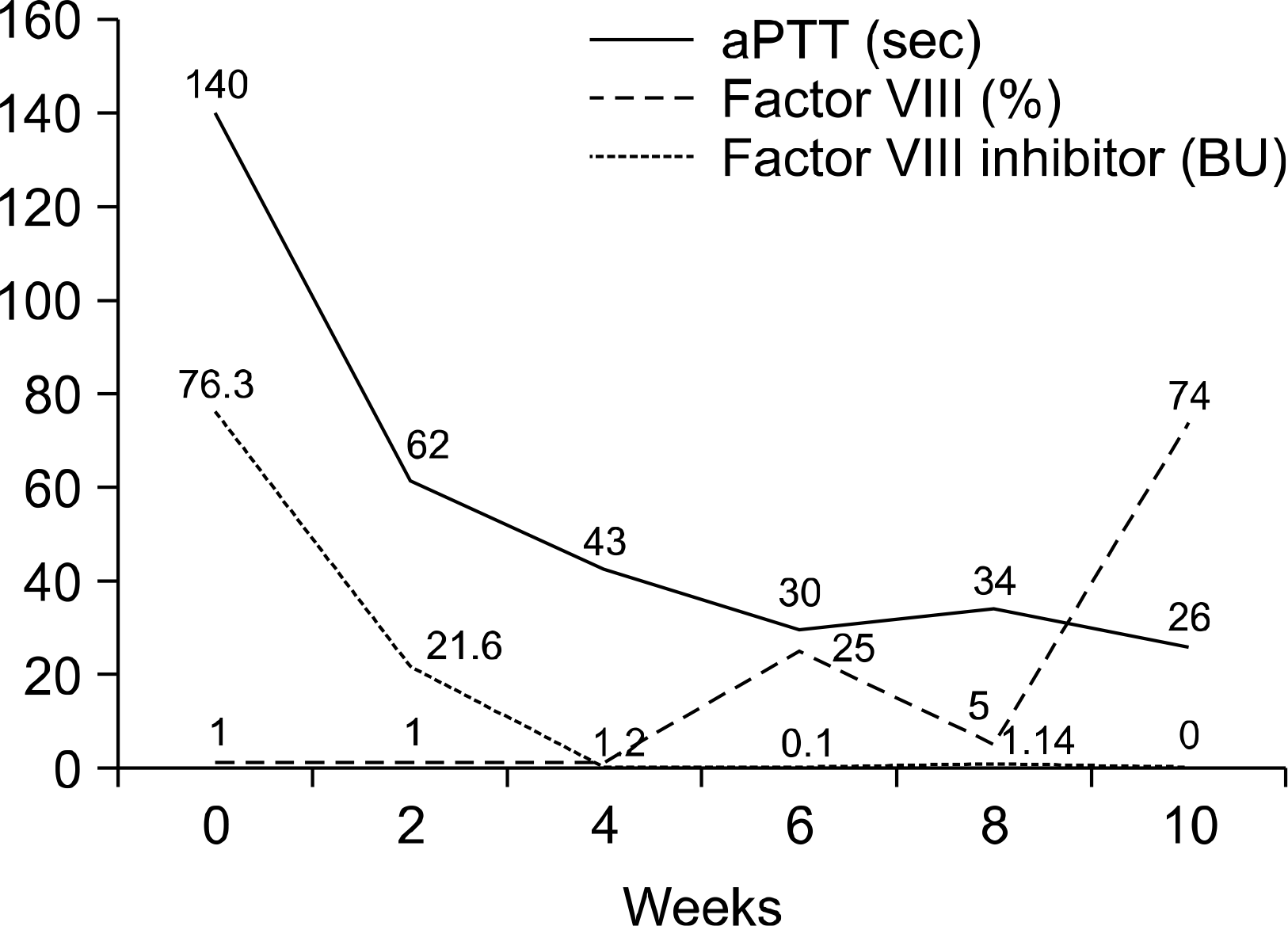
Acquired hemophilia is a rare disease caused by an autoimmune reaction to coagulation factor VIII, The mortality rate of this disease is very high (8~22%). Clinical manifestations are different from congenital hemophilia. Various diseases are associated with acquired hemophilia, including autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis (RA), tumors, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, asthma, diabetes, acute hepatitis B or C, and drug reactions. However, the underlying cause is unknown in approximately 50% of cases. A few cases of acquired hemophilia with RA have been published. However, no cases have been reported in Korea. We had a patient with longstanding RA and acquired hemophilia who was suffering from upper and lower extremity purpura with a deep intramuscular hematoma. The patient was successfully treated using cyclophosphamide combined with steroid.
REFERENCES
1). Green D., Lechner K. A survey of 215 non-hemophilic patients with inhibitors to factor VIII. Thromb Haemost. 1981. 45:200–3.

2). Franchini M., Gandini G., Di Paolantonio T., Mariani G. Acquired hemophilia A: a concise review. Am J Hematol. 2005. 80:55–63.

3). Delgado J., Yimenez-Yuste V., Hernandez-Navarro F., Villar A. Acquired haemophilia: review and meta-analysis focused on therapy and prognostic factors. Br J Haematol. 2003. 121:21–35.

4). Collins PW., Hirsch S., Baglin TP., Dolan G., Hanley J., Makris M, et al. Acquired hemophilia A in the United Kingdom; a 2-year national surveillance study by the United Kingdom Haemophilia Centre Doctors' Organisation. Blood. 2007. 109:1870–7.

5). Soriano RM., Matthews JM., Guerado-Parra E. Acquired haemophilia and rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1987. 26:381–3.

6). Ballard HS., Nyamuswa G. Life-threatening haemorrhage in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and a lupus anticoagulant coexisting with acquired autoantibodies against factor VIII. Br J Rheumatol. 1993. 32:515–7.

7). Oliveira B., Arkfeld DG., Weitz IC., Shinada S., Ehresmann G. Successful rituximab therapy of acquired factor VIII inhibitor in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2007. 13:89–91.

8). Green D., Schueette PT., Wallace WH. Factor VIII antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Effect of cyclophosphamide. Arch Intern Med. 1980. 140:1232–6.

9). Nishino Y., Ueki K., Suto M., Uchiumi H., Ota F., Tamura S, et al. Successful treatment of patients with rheumatic disorders and acquired factor VIII inhibitors with cyclophosphamide and prednisolone combination therapy: two case reports. J Int Med Res. 2001. 29:432–6.

12). Ng HJ., Tan DC., Lee LH. Treatment and outcome of acquired haemophilia A with a standard conventional regimen in a cohort without associated conditions. Haemophilia. 2006. 12:423–8.

13). Franchini M. Rituximab in the treatment of adult acquired hemophilia A: a systemic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007. 63:47–52.
14). Aggarwal A., Grewal R., Green RJ., Boggio L., Green D., Weksler BB, et al. Rituximab for autoimmune haemophilia: a proposed treatment algorithm. Haemophilia. 2005. 11:13–9.

15). Franchini M., Tagliaferri A., Mannucci PM. The management of hemophilia in elderly patients. Clin Interv Aging. 2007. 2:361–8.
Fig. 1.
(A) Multiple petechiae and ecchymosis on both lower extremities and marked swelling of the left leg compared to the right leg. (B) Endoscopy showing deep gastric ulcer at the lesser curvature.
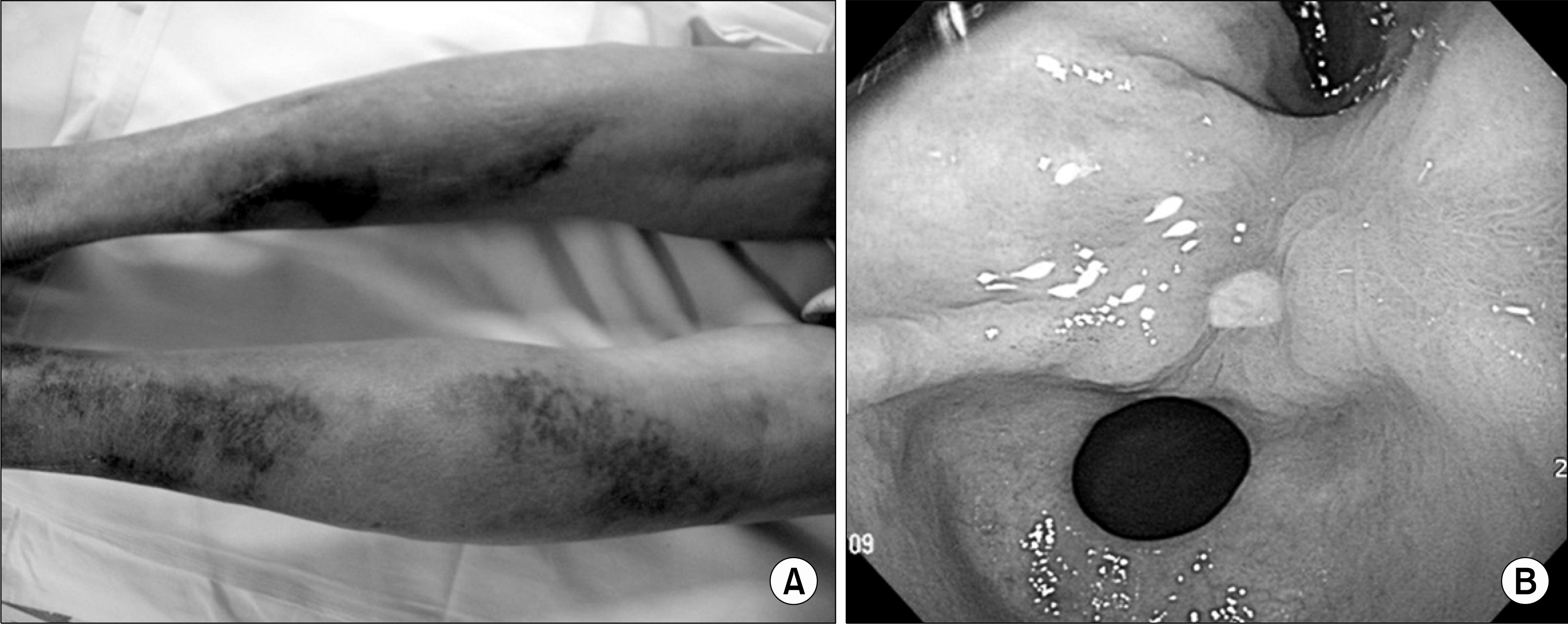
Fig. 2.
(A) X-ray of the hand showing joint space narrowing and multifocal erosive changes at the bilateral radiocarpal, intercarpal, and carpometacarpal joints. Bony erosion at the left trapezium and right radial head (arrows). (B) X-ray of the foot showing multifocal bony erosions at the right fifth metatarsal head (arrow).
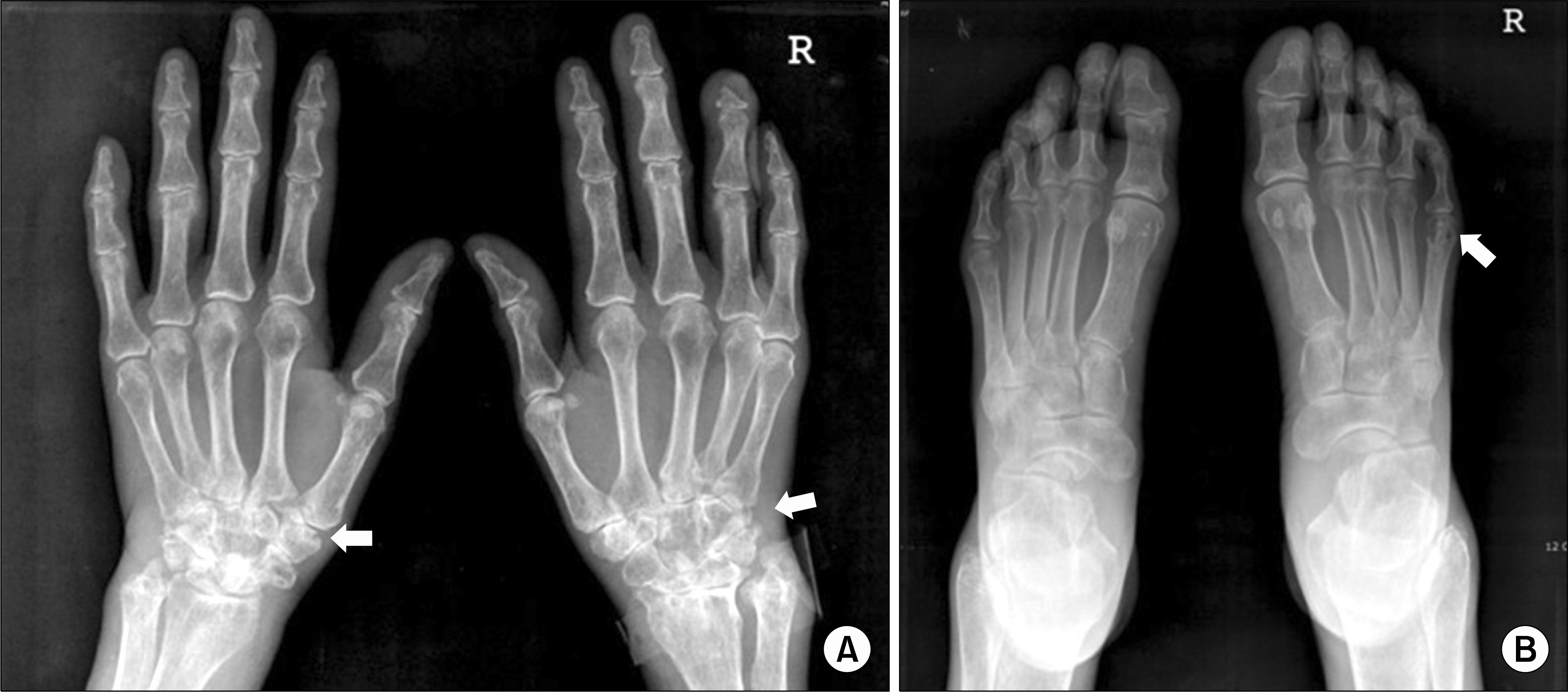
Fig. 3.
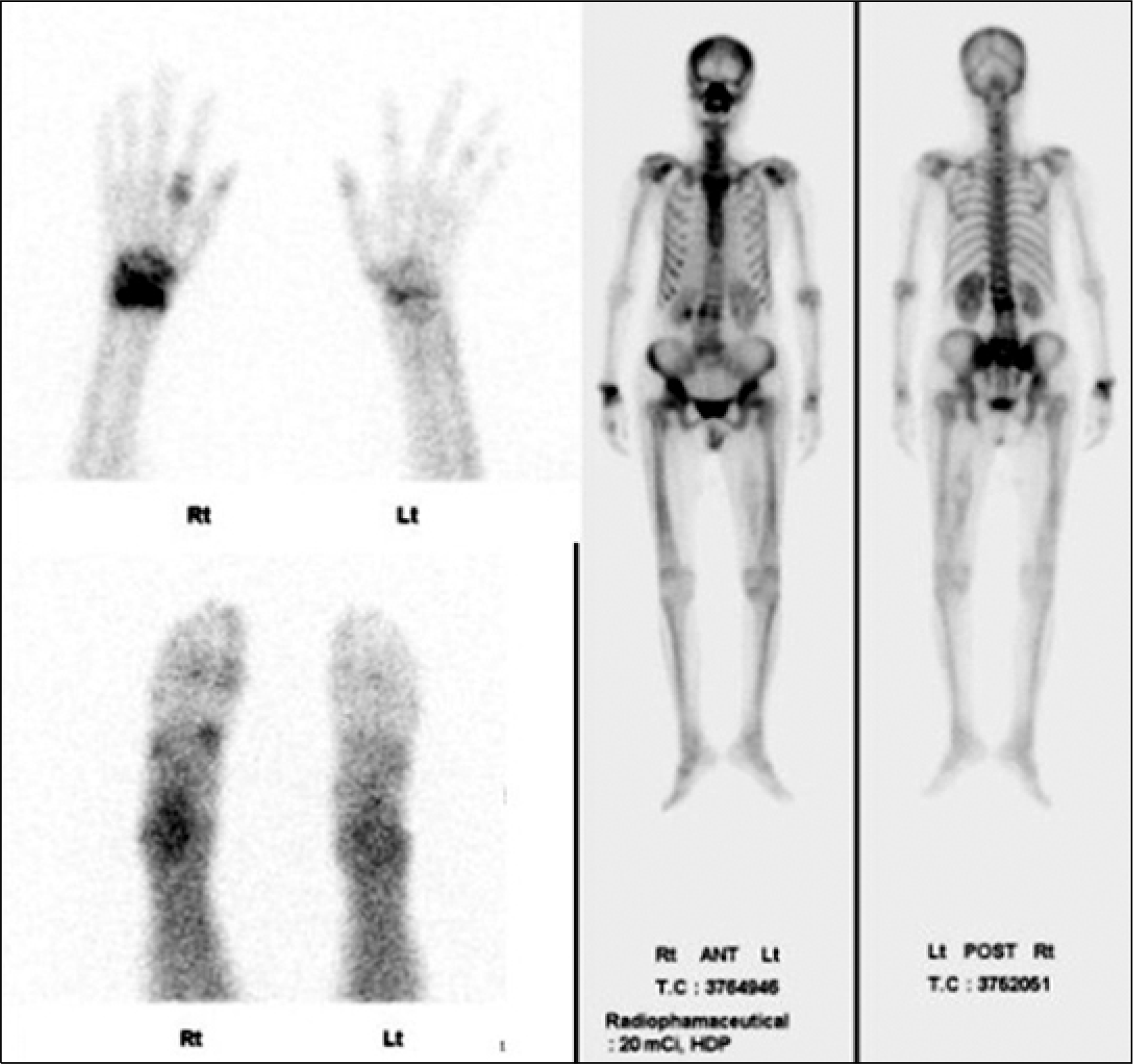
Whole-body bone scan demonstrating increased uptake into multiple joints of both hands, both wrists, left elbow, right ankle, the medial aspect of the left knee joint, and both hip joints.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download