Abstract
Renal involvement is frequently seen in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The occurrence of non-lupus nephritis, and especially IgA nephropathy, in SLE patients has rarely been reported. We describe here the case of a 30-year-old woman who had systemic lupus erythematosus and nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease, and her biopsy of a renal lesion was unexpectedly diagnostic of IgA nephropathy. Although both IgA nephropathy and lupus nephritis are immune complex mediated diseases, their laboratory and histopathologic findings and the extra-renal clinical manifestations are different and these all support a different pathogenesis for the 2 diseases. Renal biopsy plays a crucial role in identifying and diagnosing renal lesions, which may have prognostic and therapeutic implications that are distinct from those of lupus nephritis. In conclusion, performing a renal biopsy in SLE patients who have urinary abnormalities is important since a correct diagnosis would permit the most appropriate treatment to be started and so avoid unnecessary immunosuppressive treatments.
References
1. Kim HW, Kang SW, Choi KH, Lee HY, Han DS, Kie JH, et al. A case of IgA nephropathy with systemic lupus erythematosus. Korean J Med. 2004; 66:190–94.
2. Han KW, Lee YK, Lee HR, Hwang SI, Kim SG, Oh JE, et al. A case of IgA nephropathy with systemic lupus nephritis. Korean J Nephrol. 2005; 24:326–31.
3. Park MH. International society of nephropathy/renal pathology society 2003 classification of lupus nephritis. Korean J Pathol. 2006; 40:165–75.
5. Baranowska-Daca E, Choi YJ, Barrios R, Nassar G, Suki WN, Truong LD. Nonlupus nephritides in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a comprehensive clinicopathologic study and review of the literature. Hum Pathol. 2001; 32:1125–35.

6. Mac-Moune Lai F, Li EK, Tang NL, Li PK, Lui SF, Lai KN. IgA nephropathy: a rare lesion in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mod Pathol. 1995; 8:5–10.
7. Baranowska-Daca E, Choi YJ, Barrios R, Cartwigh J, Sheik-Hamad D, Truong LD. Nonlupus nephritis in patients with SLE. Lab Invest. 1999; 79:154A.
8. Corrado A, Quarta L, Di Palma AM, Gesualdo L, Cantatore FP. IgA nephropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007; 25:467–9.
9. De Siati L, Paroli M, Ferri C, Muda AO, Bruno G, Barnaba V. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy complicating pulmonary tuberculosis. Ann Diagn Pathol. 1999; 3:300–3.

10. Alifano M, Sofia M, Mormile M, Micco A, Mormile AF, Del Pezzo M, et al. IgA immune response against the mycobacterial antigen A60 in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Respiration. 1996; 63:292–7.

11. De Siati L, Paroli M, Ferri C, Muda AO, Bruno G, Barnaba V. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy complicating pulmonary tuberculosis. Ann Diagn Pathol. 1999; 3:300–3.

12. Chen SJ, Wen YK, Chen ML. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis associated with nontuberculous mycobacteria. J Chin Med Assoc. 2007; 70:396–9.

13. Wen YK, Chen ML. Crescentic glomerulonephritis associated with nontuberculous mycobacteria infection. Ren Fail. 2008; 30:339–41.

14. Gunnarsson J, Ronnelid J, Lundberg I, Jacobson SH. Occurence of anti-C1q antibodies in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997; 12:2263–8.
Fig. 1.
Multifocal infiltrations of non-tuberculosis mycobacterium in both lungs are noted on the chest X-ray.
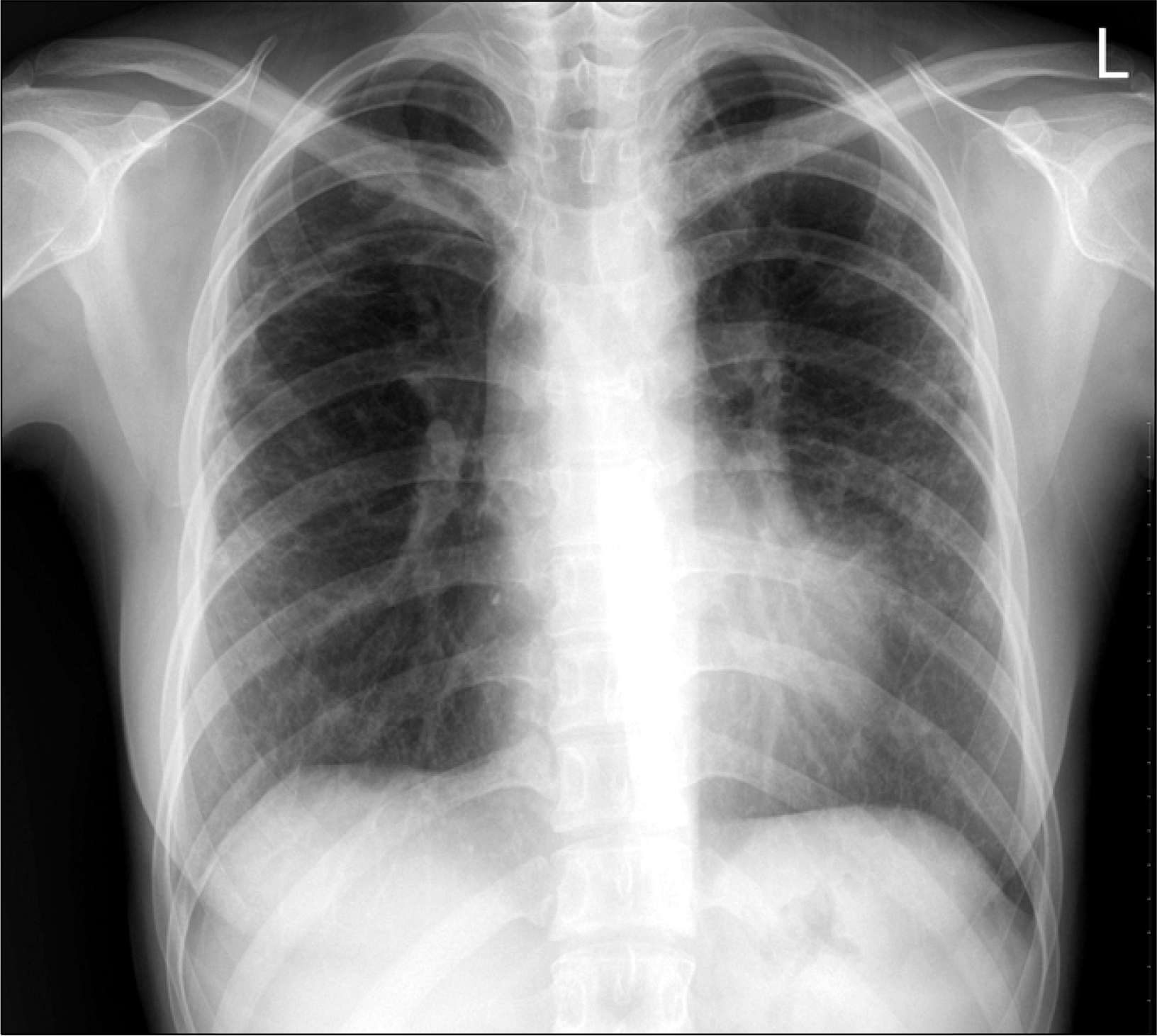
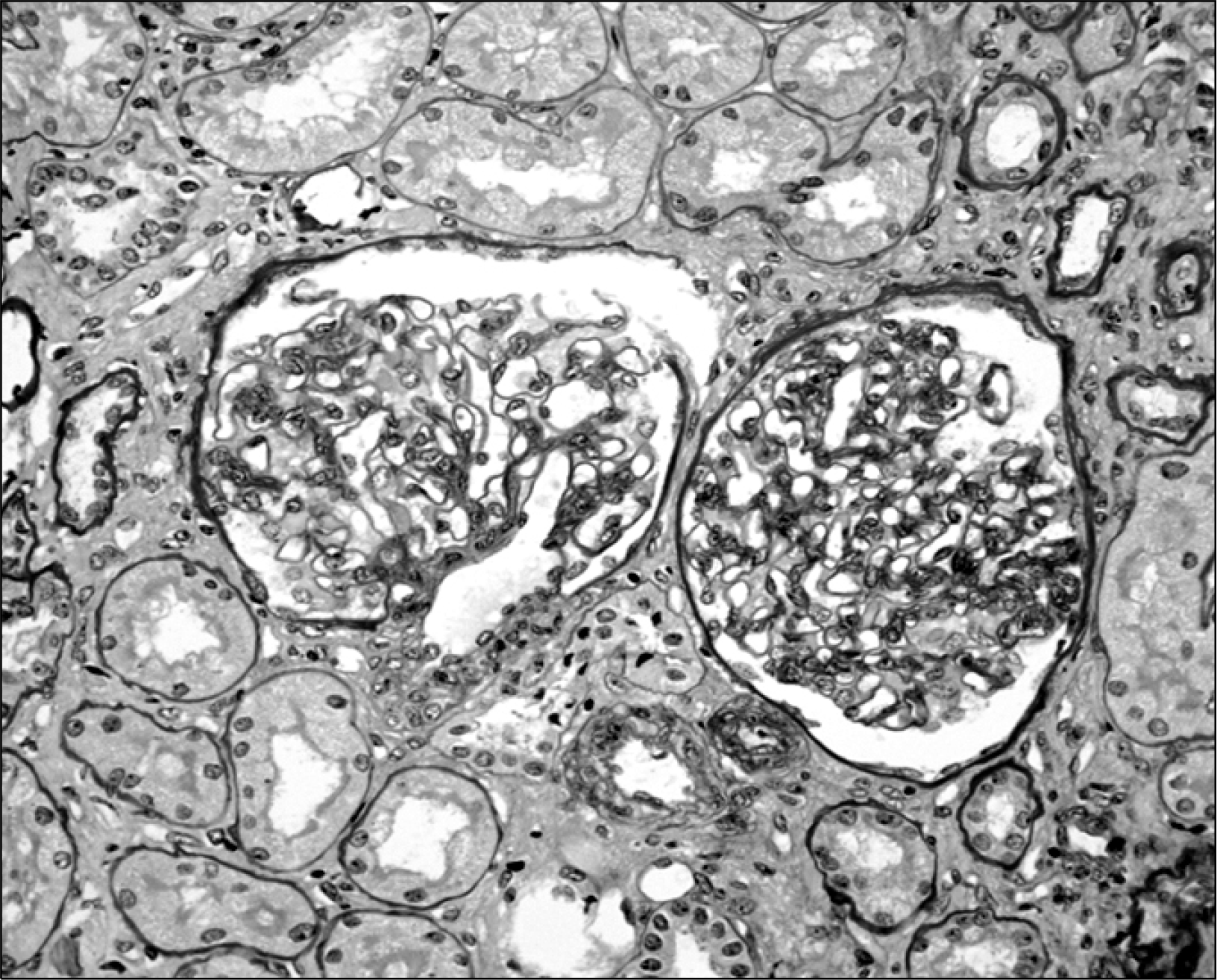
Fig. 2.
The mesangium is mildly expanded with proliferations of mesangial cells and expansion of the mesangial matrix. Mild tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis are seen (PAS, ×400).




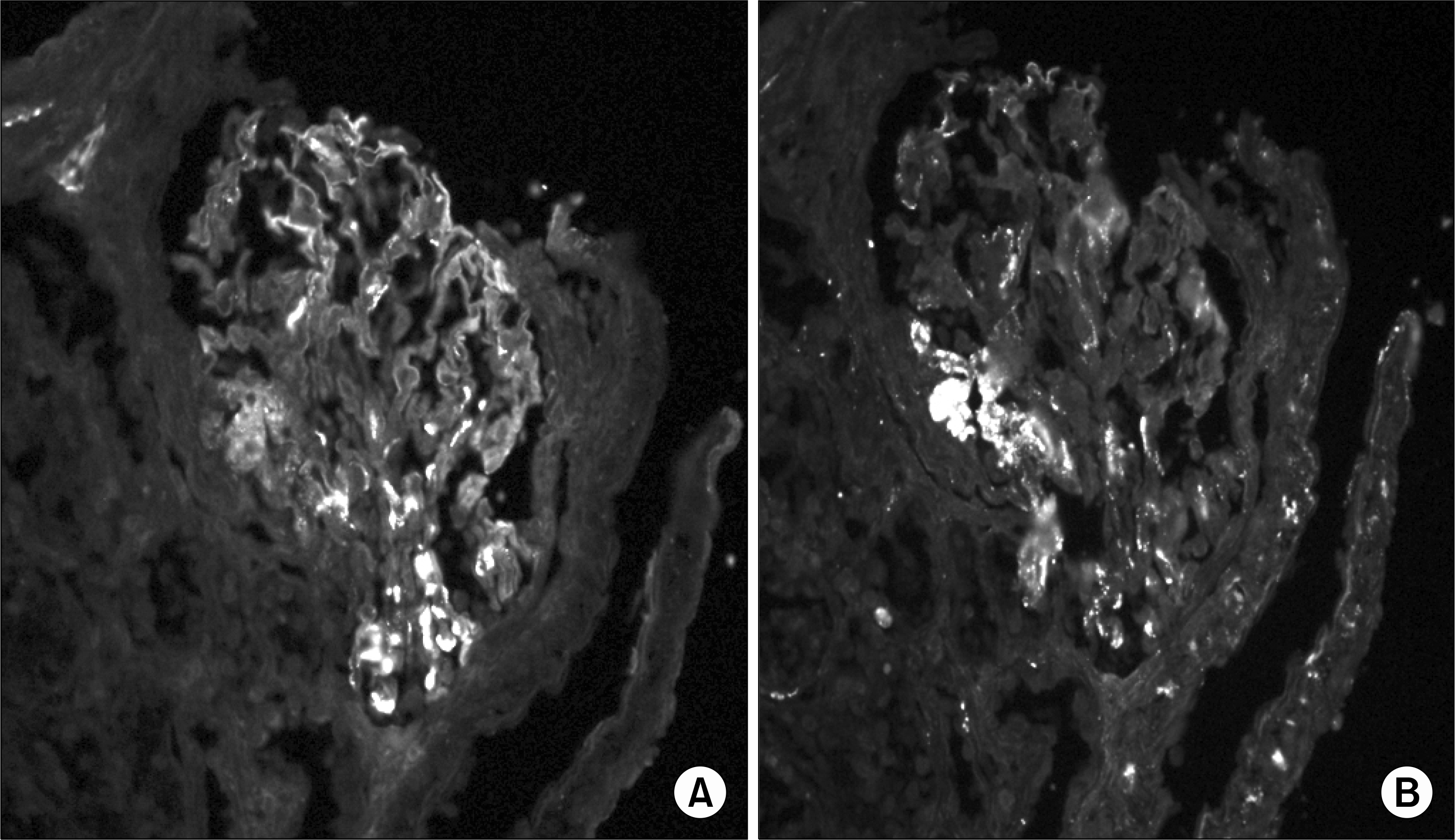
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


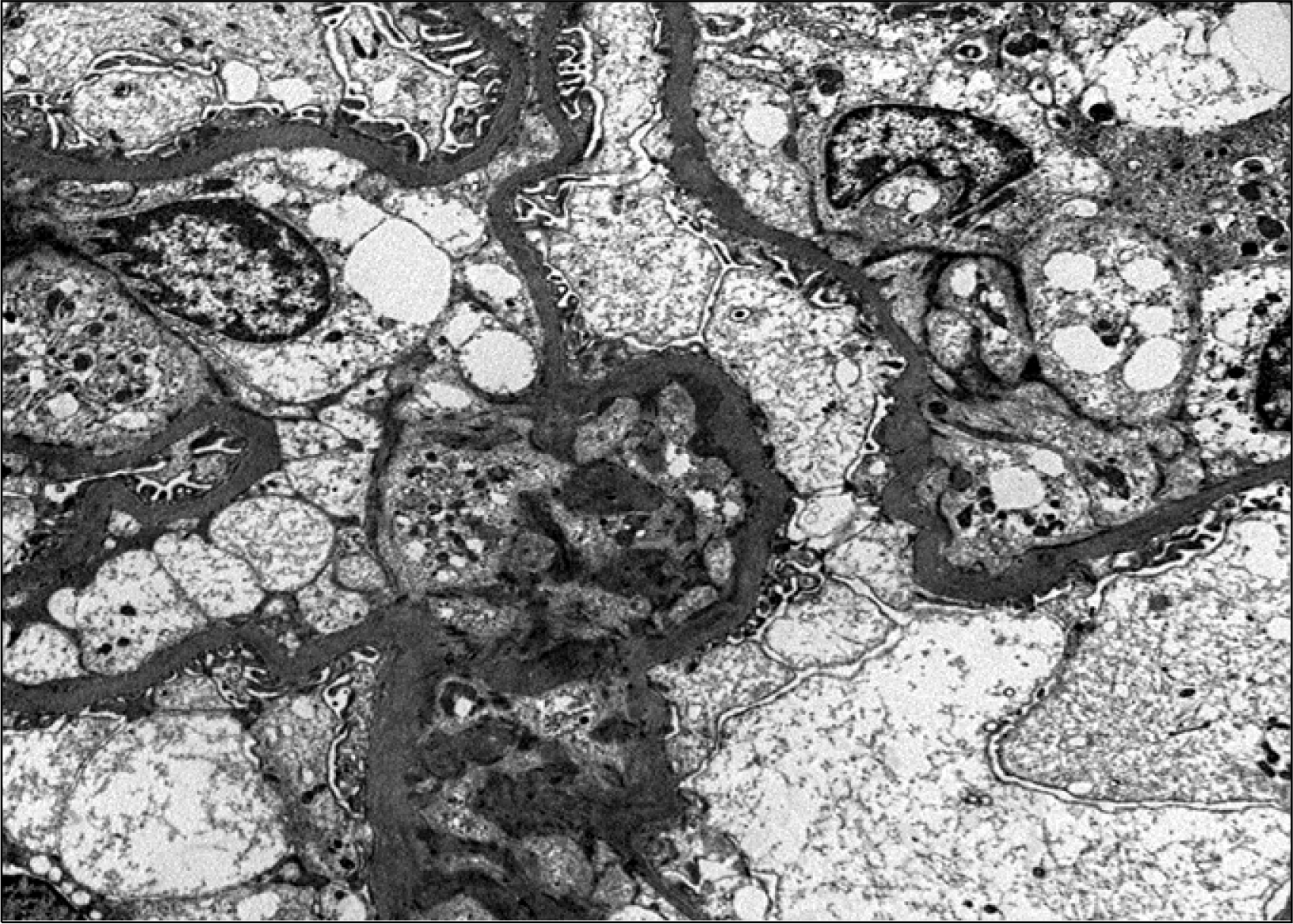
 XML Download
XML Download