Abstract
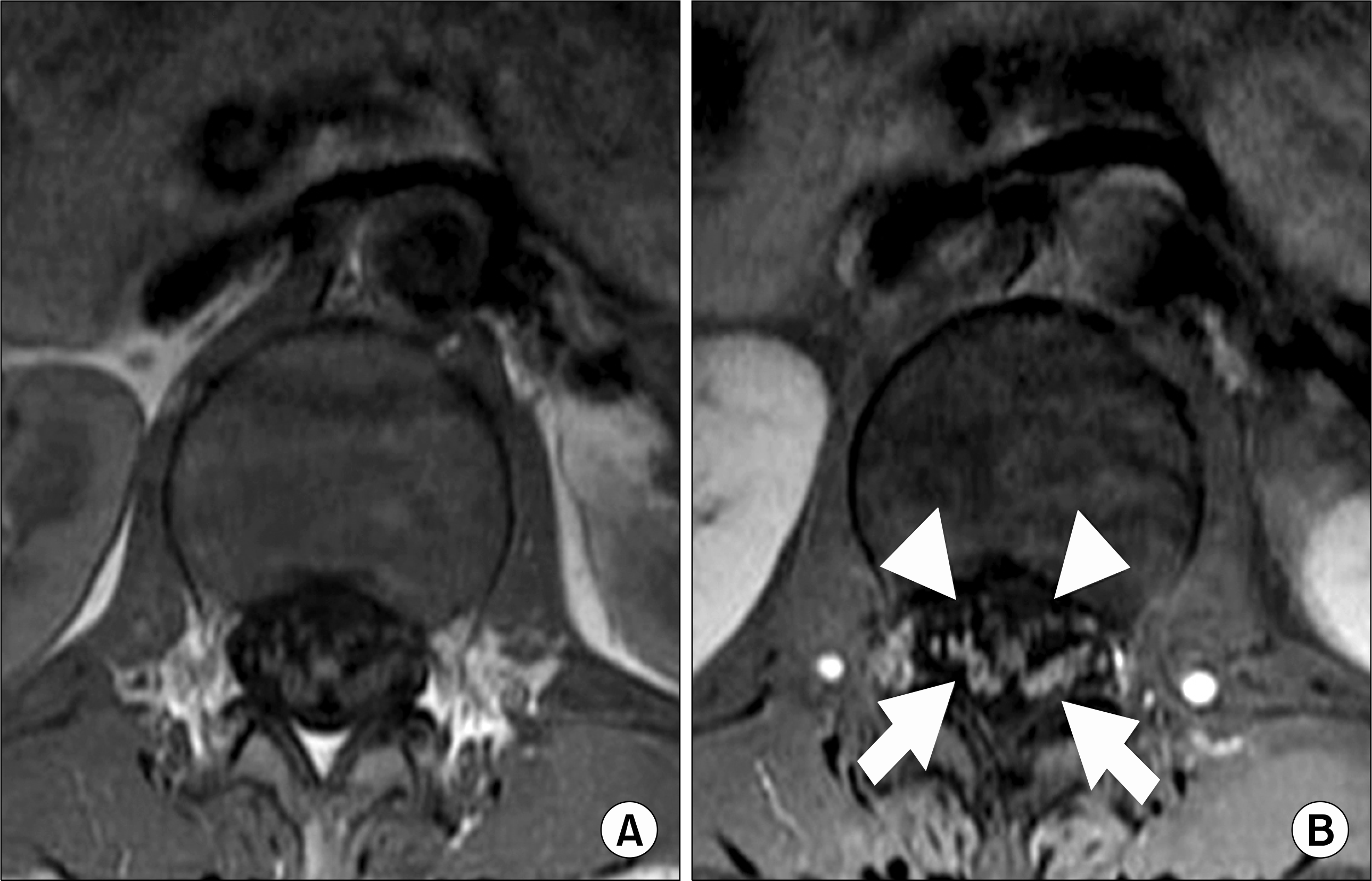
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is characterized by symmetrical weakness, impaired sensation, absent or diminished tendon reflexes, an elevated cerebrospinal fluid protein level and nerve-conduction studies that show demyelination. The occurrence of CIDP in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has been rarely reported. We experienced a case of a 33 year-old woman with SLE and she presented with fever, abdominal pain, a tingling sensation of both of her hands and feet, and symmetrical weakness in both the proximal and distal extremities. Her symptoms had persisted for over 1 months before she visited our department. The CSF examination showed an elevated protein level and the nerve conduction studies revealed demyelination. Her symptoms showed minimal improvement with high dose steroid and immunoglobulin therapy, but she responded to cyclophosphamide therapy.
Go to : 
References
1. Rezania K, Gundogdu B, Soliven B. Pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Front Biosci. 2004; 9:939–45.

2. Koller H, Kieseier BC, Jander S, Hartung HP. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1343–56.

3. Takigawa T, Yasuda H, Terada M, Haneda M, Kashiwagi A, Saito T, et al. The sera from GM1 ganglioside antibody positive patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome or chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy blocks Na+ currents in rat single mye-linated nerve fibers. Intern Med. 2000; 39:123–7.

4. Sindern E, Stark E, Haas J, Steck AJ. Serum antibodies to GM1 and GM3-gangliosides in systemic lupus erythematosus with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991; 83:399–402.

5. Research criteria for diagnosis of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Report from an Ad Hoc Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology AIDS Task Force. Neurology. 1991; 41:617–8.
6. Saperstein DS, Katz JS, Amato AA, Barohn RJ. Clinical spectrum of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Muscle Nerve. 2001; 24:311–24.

7. Hughes R, Bensa S, Willison H, Van den Bergh P, Comi G, Illa I, et al. Randomized controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin versus oral prednisolone in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann Neurol. 2001; 50:195–201.

9. Bosboom WM, van den Berg LH, Franssen H, Giesbergen PC, Flach HZ, van Putten AM, et al. Diagnostic value of sural nerve demyelination in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain. 2001; 124:2427–38.

10. Sedgwick RP, Von Hagen KO. The neurological manifestations of lupus erythematosus and periarteritis nodosa; report of ten cases. Bull Los Angel Neuro Soc. 1948; 13:129–42.
11. Rhee WI, Lee JA, Shin CH, Lee JY. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy in patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2008; 32:112–5.
12. Hughes RA, Cornblath DR. Guillain-Barre syndrome. Lancet. 2005; 366:1653–66.
13. Vina ER, Fang AJ, Wallace DJ, Weisman MH. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: prognosis and outcome. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 35:175–84.

14. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Pe-ripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2005; 10:220–8.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download