Abstract
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) have been used for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with the aim of controlling synovitis and reducing radiologic progression. Although methotrexate (MTX) is one of the most effective DMARDs, it may cause severe adverse effects. Especially, hematologic toxicity including leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and fatal pancytopenia is reported in patients with impaired renal function, since renal excretion constitutes the major route of MTX elimination. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) inhibitors are well-established biologic agents for the treatment of RA and their clinical efficacy and safety are already demonstrated. But there were few reports on the efficacy and safety in dialysis patients. We described a case of hemodialysis patient with refractory RA that was successfully treated with etanercept, and discussed with literature review.
Go to : 
References
1. Songsiridej N, Furst DE. Methotrexate–the rapidly acting drug. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1990; 4:575–93.

2. Lim AY, Gaffney K, Scott DG. Methotrexate-induced pancytopenia: serious and under-reported? Our experience of 25 cases in 5 years. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005; 44:1051–5.

3. Moreland LW. Inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1999; 57:7–15.
4. Saxne T, Palladino MA Jr, Heinegard D, Talal N, Wollheim FA. Detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha but not tumor necrosis factor beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:1041–5.
5. Don BR, Spin G, Nestorov I, Hutmacher M, Rose A, Kaysen GA. The pharmacokinetics of etanercept in patients with end-stage renal disease on haemodialysis. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005; 57:1407–13.

6. Bologna C, Viu P, Picot MC, Jorgensen C, Sany J. Long-term follow-up of 453 rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with methotrexate: an open, retrospective, observational study. Br J Rheumatol. 1997; 36:535–40.

7. Kremer JM. Safety, efficacy, and mortality in a longterm cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking methotrexate: followup after a mean of 13.3 years. Arthritis Rheum. 1997; 40:984–5.
8. Gutierrez-Urena S, Molina JF, Garcia CO, Cuellar ML, Espinoza LR. Pancytopenia secondary to methotrexate therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 39:272–6.
9. Park GT, Jeon DW, Roh KH, Mun HS, Lee CH, Park CH, et al. A case of pancytopenia secondary to low-dose pulse methotrexate therapy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis and renal insufficiency. Korean J Intern Med. 1999; 14:85–7.
10. Kuitunen T, Malmstrom J, Palva E, Pettersson T. Pancytopenia induced by low-dose methotrexate. A study of the cases reported to the Finnish adverse drug reaction register from 1991 to 1999. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005; 34:238–41.

11. Sugioka Y, Inui K, Koike T. Use of etanercept in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis on hemodialysis. Mod Rheumatol. 2008; 18:293–5.

12. Hammoudeh M. Infliximab treatment in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis on haemodialysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006; 45:357–9.

13. Singh R, Cuchacovich R, Huang W, Espinoza LR. Infliximab treatment in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis on hemodialysis. J Rheumatol. 2002; 29:636–7.
14. Moreland LW, Cohen SB, Baumgartner SW, Tindall EA, Bulpitt K, Martin R, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28:1238–44.
Go to : 
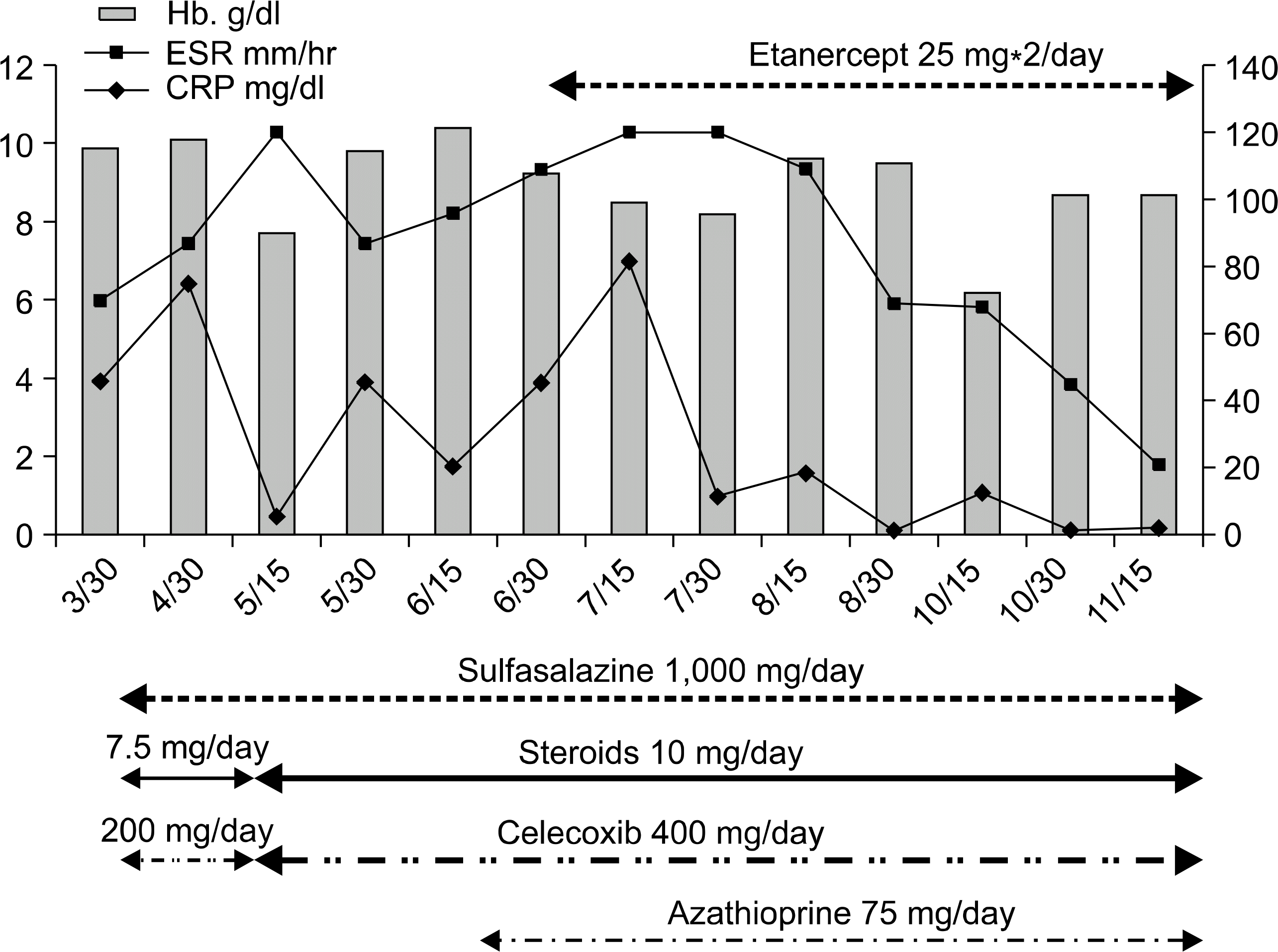 | Fig. 1.The alteration of erythrocyte segmentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) according to etanercept. |
Table 1.
Risk factors and outcomes in patients with methotrexate-related pancytopenia




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download