Abstract
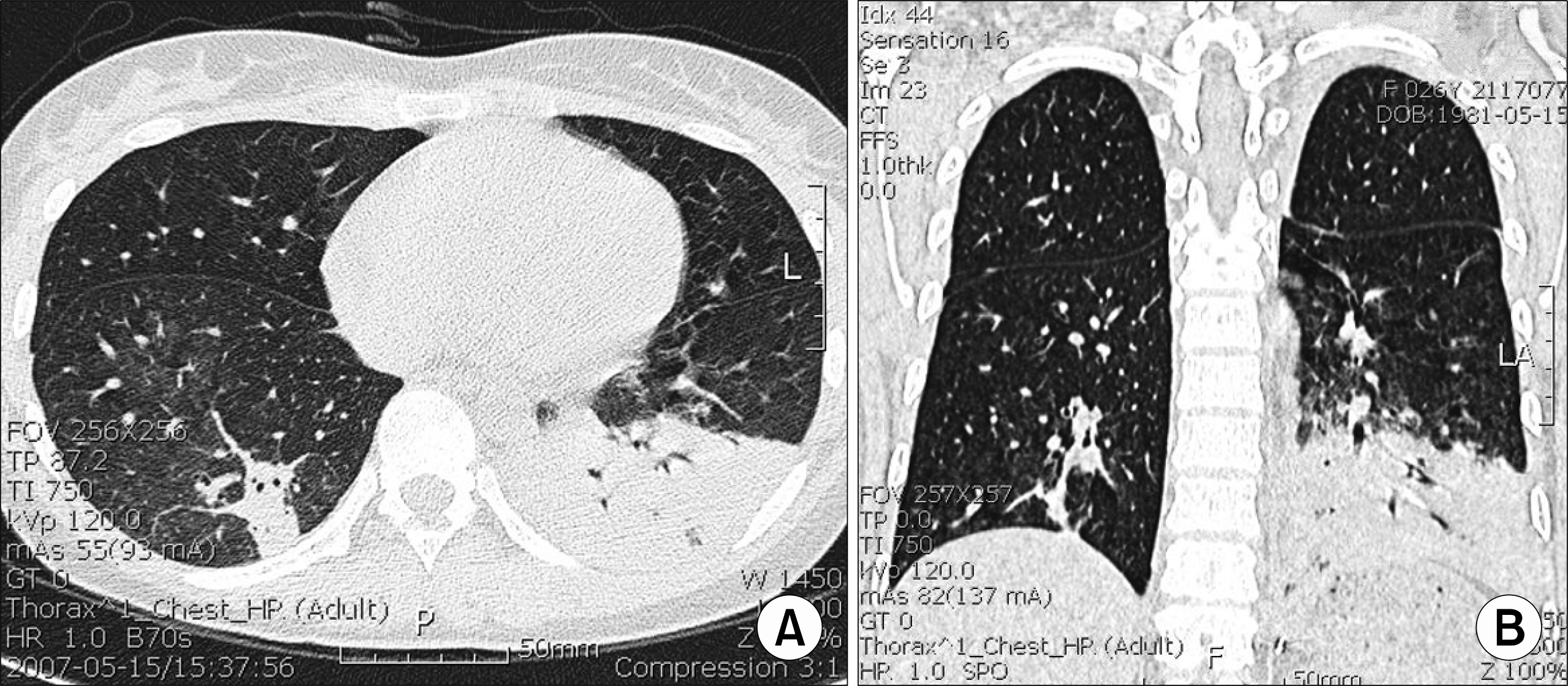
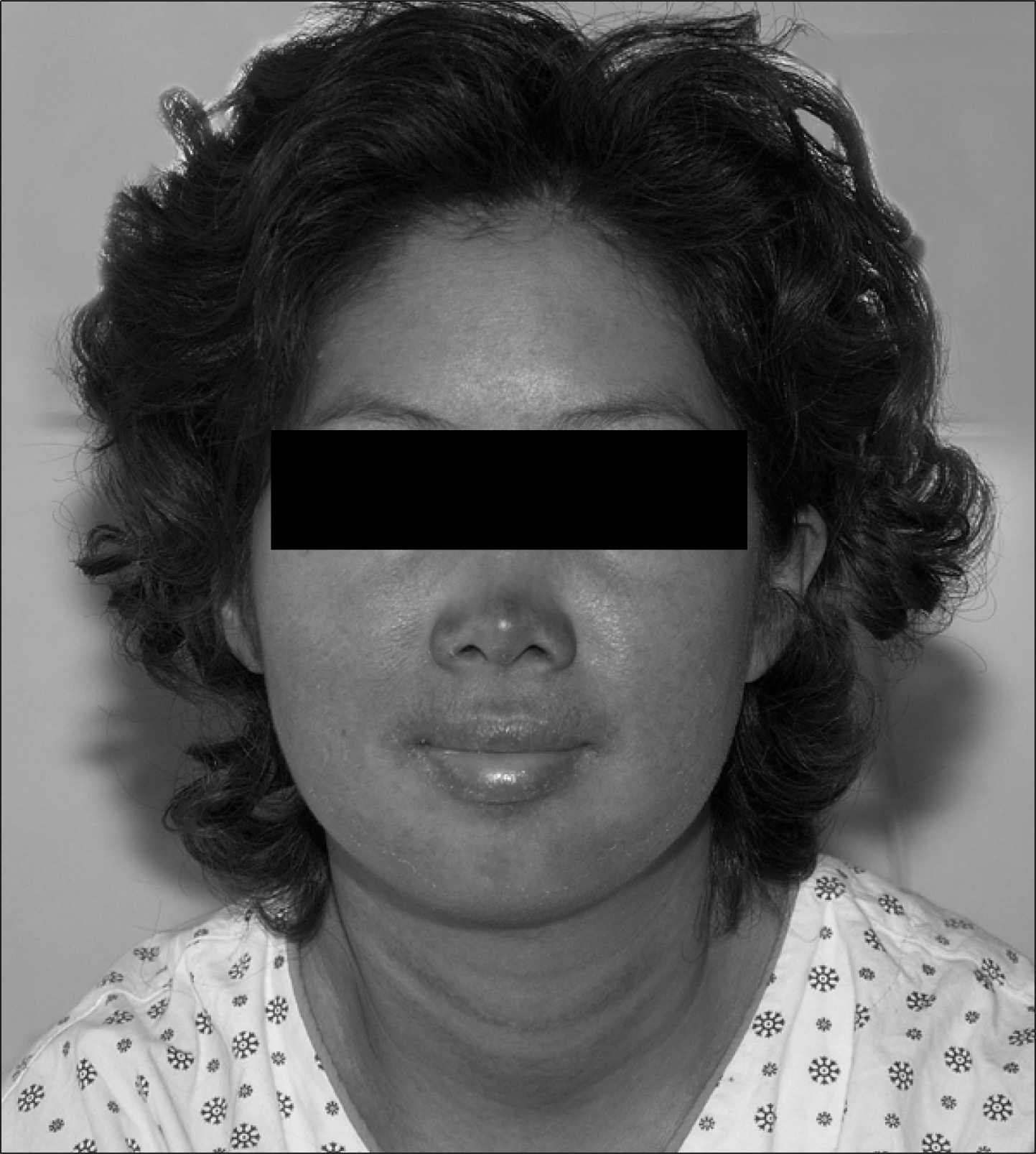
A severe adverse reaction to certain drug could be associated with hypersensitivity syndrome, showing the clinical features of infectious mononucleosis including maculopapular rash, fever, lymphadenopathy, leukocytosis, atypical lymphocytes, liver dysfunction, and renal disturbance. We report a systemic lupus erythematosus patient who developed infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome with administration of ceftriaxone/isepamicin for the treatment of pneumonia. This case warrants careful attention to infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome associated with antibiotics administration, especially in febrile patients with known autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Go to : 
References
1. Furukawa K, Ohtani T, Furukawa F, Suzuki Y. Infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome induced by salazosulfapyridine in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2007; 17:492–5.

2. Suzuki Y, Inagi R, Aono T, Yamanishi K, Shiohara T. Human herpesvirus 6 infection as a risk factor for the development of severe drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1998; 134:1108–12.

3. Mihas AA, Goldenberg DJ, Slaughter RL. Sulfasalazine toxic reactions. Hepatitis, fever, and skin rash with hypocomplementemia and immune complexes. JAMA. 1978; 239:2590–1.

4. Callot V, Roujeau JC, Bagot M, Wechsler J, Chosi-dow O, Souteyrand P, et al. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and hypersensitivity syndrome. Two different clinical entities. Arch Dermatol. 1996; 132:1315–21.

5. Vittorio CC, Muglia JJ. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1995; 155:2285–90.

6. Shiohara T, Kano Y. A complex interaction between drug allergy and viral infection. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007; 33:124–33.

7. Suzuki Y, Inagi R, Aono T, Yamanishi K, Shiohara T. Human herpesvirus 6 infection as a risk factor for the development of severe drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1998; 134:1108–12.

8. Naito T, Kudo N, Inui A, Matsumoto N, Takeda N, Isonuma S, et al. Causes of infectious mononucleosis-like syndrome in adult patients. Intern Med. 2006; 45:833–4.

9. Gopal MR, Thomson BJ, Fox J, Tedder RS, Honess RW. Detection by PCR of HHV-6 and EBV DNA in blood and oropharynx of healthy adults and HIV-ser-opositives. Lancet. 1990; 335:1598–9.

10. Jarrett RF, Clark DA, Josephs SF, Onions DE. Detection of human herpesvirus-6 DNA in peripheral blood and saliva. J Med Virol. 1990; 32:73–6.

11. Shear NH, Spielberg SP, Grant DM, Tang BK, Kalow W. Differences in metabolism of sulfonamides predisposing to idiosyncratic toxicity. Ann Intern Med. 1986; 105:179–84.

12. Shear NH, Spielberg SP. Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome. In vitro assessment of risk. J Clin Invest. 1988; 82:1826–32.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download