Abstract
Objective
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) are systemic autoimmune diseases characterized by infiltration of T lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages in muscle tissues. Interleukin-17 (IL-17), a Th17 cytokine, has potent pro-inflammatory actions and plays a role in autoimmune diseases. We investigated the expression of IL-17 in muscle tissues of patients with IIMs.
Methods
We measured the IL-17 mRNA level of muscle tissues from 14 patients with IIMs (9 patients with dermatomyositis and 5 patients with polymyositis) by real-time RT-PCR and compared with controls. We also performed an immunohistochemical stain to detect IL-17 expression.
Go to : 
References
1. Briani C, Doria A, Sarzi-Puttini P, Dalakas MC. Update on idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Autoimmunity. 2006; 39:161–70.

2. Wiendl H, Hoflfeld R, Kieseier BC. Immunobiology of muscle: advances in understanding an immunological microenvironment. Trend Immunol. 2005; 26:373–80.

3. Salomonsson S, Lundberg I. Cytokines in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Autoimmunity. 2006; 39:177–90.

4. McFarland HF, Martin R. Multiple sclerosis: a complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2007; 8:913–9.

5. Toh ML, Miossec P. The role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis: new subsets and new targets. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007; 19:284–8.

6. Chevrel G, Page G, Granet C, Streichenberger N, Varennes A, Miossec P. Interleukin-17 increases the effects of IL-1 beta on muscle cells: arguments for the role of T cells in the pathogenesis of myositis. J Neuroimmunol. 2003; 137:125–33.
7. Page G, Chevrel G, Miossec P. Anatomic localization of immature and mature dendritic cell subsets in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:199–208.
8. Baird GS, Montine TJ. Multiplex immunoassay anlysis of cytokines in idiopathic inflammatory myo-pahty. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008; 132:232–8.
9. Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975; 292:403–7.
10. Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975; 292:403–7.
Go to : 
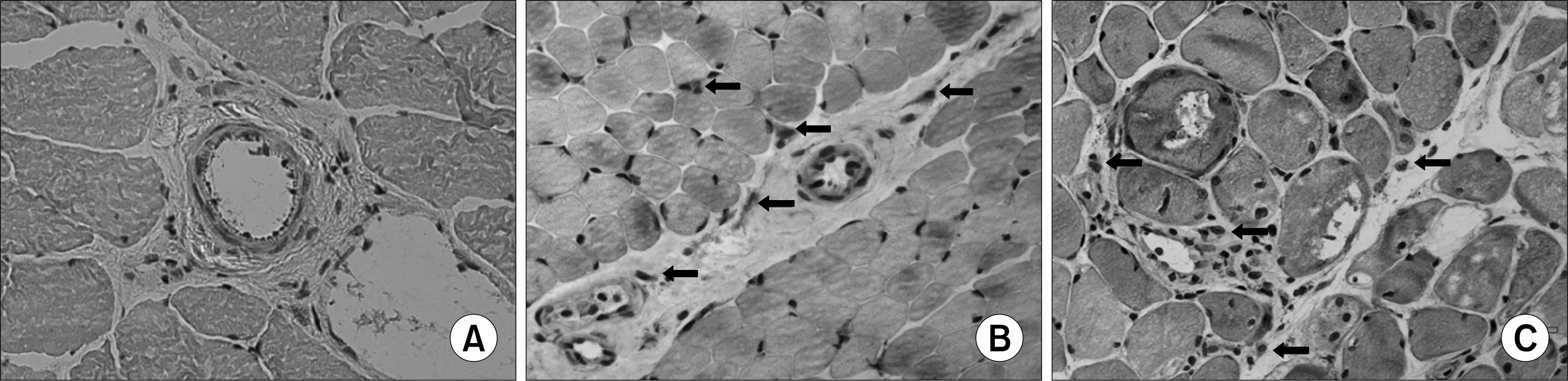 | Fig. 1.Immunohistochemistry of IL-17 in muscle tissues from patients with IIMs (B, C) and control (A). In DM (B) and PM (C), IL-17 was expressed in perimysial, endomysialand perivascular infiltrating inflammatory cells (arrow). Muscle tissue from control was negative (A). Magnification, ×200. IIMs: idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, DM: dermatomyositis, PM: polymyositis. |
Table 1.
Demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics in 14 patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download