Abstract
Objective
To estimate the prevalence of musculoskeletal diseases, especially osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis and lumbar disc herniation, in Korean adults. For arthritis and total musculoskeletal diseases, trend of the age-standardized prevalence rates were evaluated.
Methods
This study was based on the data obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) I, II and III, conducted in 1998, 2001 and 2005, respectively. KNHANES is a nationwide cross-sectional study using a stratified, multistage probability sampling design for the selection of household units. Annual self-reported prevalence and its confidence interval were estimated in adults aged over 19, using Health Interview Survey in KNHANES. All analyses were done using SAS 9.1 with "survey procedure" except for age-standardized prevalence rates for comparison prevalence rates of each survey. Age-standardized prevalence rates were calculated using a direct-method.
Results
The prevalence of musculoskeletal diseases was 144.6, 140.0 and 197.2 and the annual self-reported prevalence of arthritis was 117.9, 109.2 and 146.4 per 1,000 population in 1998, 2001 and 2005, respectively. In KNHANES III, osteoarthritis was the most prevalent disease of the musculoskeletal diseases for both sex. Fifty-eight percent of the over 65 year-old population had at least one musculoskeletal disease and it was higher in women with 73%.
Go to : 
References
1. Brooks PM. The burden of musculoskeletal disease-a global perspective. Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 25:778–81.

2. Mili F, Helmick CG, Zack MM. Prevalence of arthritis: analysis of data from the US behavioral risk factor surveillance system, 1996–99. J Rheumatol. 2002; 29:1981–8.
3. 엄완식, 윤정이, 박용욱, 김혜련, 남정자, 이혜순 등. 한국인 관절염의 본인인지 유병률과 역학적 특성: 1998 국민건강ㆍ영양조사. 대한류마티스학회지. 2004; 11:116–26.
4. 보건복지부ㆍ질병관리본부. 국민건강영양조사 제3기 (2005) 총괄보고서. 2006.
5. 보건복지부ㆍ질병관리본부. 2005 국민건강영양조사 진행보고서 – 건강면접 및 보건의식행태조사. 2005.
6. 남정자, 김혜련. 1998년도 국민건강ㆍ영양조사 진행 보고서. 보건복지부. 1999.
7. 남정자. 2001년도 국민건강ㆍ영양조사 진행보고서. 보건복지부. 2002.
8. 보건복지부ㆍ한국보건사회연구원. 한국인의 주요 상 병 및 건강행태 분석 – 2001년 국민건강ㆍ영양조사 건강부문 심층분석 결과. 2003.
9. Kopec A, Rahman M, Berthelot JM, Petit C, Agha-jania J, Sayre EC, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of osteroarthritis in British Columbia, Canada. J Rheumatol. 2007; 34:1–8.
10. Centers for Disease Control and Prevaention (CDC). Prevalence of self-reported arthritis or chronic joint symptioms among adults – United States, 2001. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002; 51:948–50.
11. Wilkins K. Incident arthritis in relation to excess weight. Health Rep. 2004; 15:39–49.
12. 박남규, 김우규, 신동혁, 최영미, 이윤종, 이은봉 등. 두 지역사회에서 골관절염 및 류마티스 관절염의 유 병률. 대한류마티스학회지. 2003; 10:147–51.
13. Anderson JJ, Felson DT. Factors associated with osteoarthritis of the knee in the first National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES I). Evidence for an association with overweight, race, and physical demands of work. Am J Epidemiol. 1988; 128:179–89.
14. Dillon CF, Rasch EK, Gu Q, Hirsch R. Prevalence of knee oesteoarthritis in the United States: arthritis data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Exami-natin Survey 1991–94. J Rheumatol. 2006; 33:2271–9.
15. Pedersen MS, Jacobsen E, Klarlund M, Frisch M. Sociosconomic status and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a Danish case-control study. J Rheumatol. 2006; 33:1069–74.
16. 보건복지부ㆍ한국보건사회연구원. 1998 국민건강ㆍ 영양조사 총괄보고서. 1999.
17. 보건복지부ㆍ한국보건사회연구원. 1998 국민건강ㆍ 영양조사 건강부문 심층․연계 분석. 2000.
18. Symmons D, Turner G, Webb R, Asten P, Barrett E, Lunt M, et al. The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United Kingdom: new estimates for a new century. Rheumatology. 2002; 41:793–800.

19. Rousculp MD, Long SR, Wang S, Scheonfeld MJ, Meadows ES. Economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in medicaid. Value Health. 2007; 10:144–52.

20. Ray NF, Chan JK, Thamer M, Melton LJ III. Medical expenditures for the treatment of osteoporotic fractures in the United States in 1995: report from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. J Bone Miner Res. 1997; 12:24–35.

Go to : 
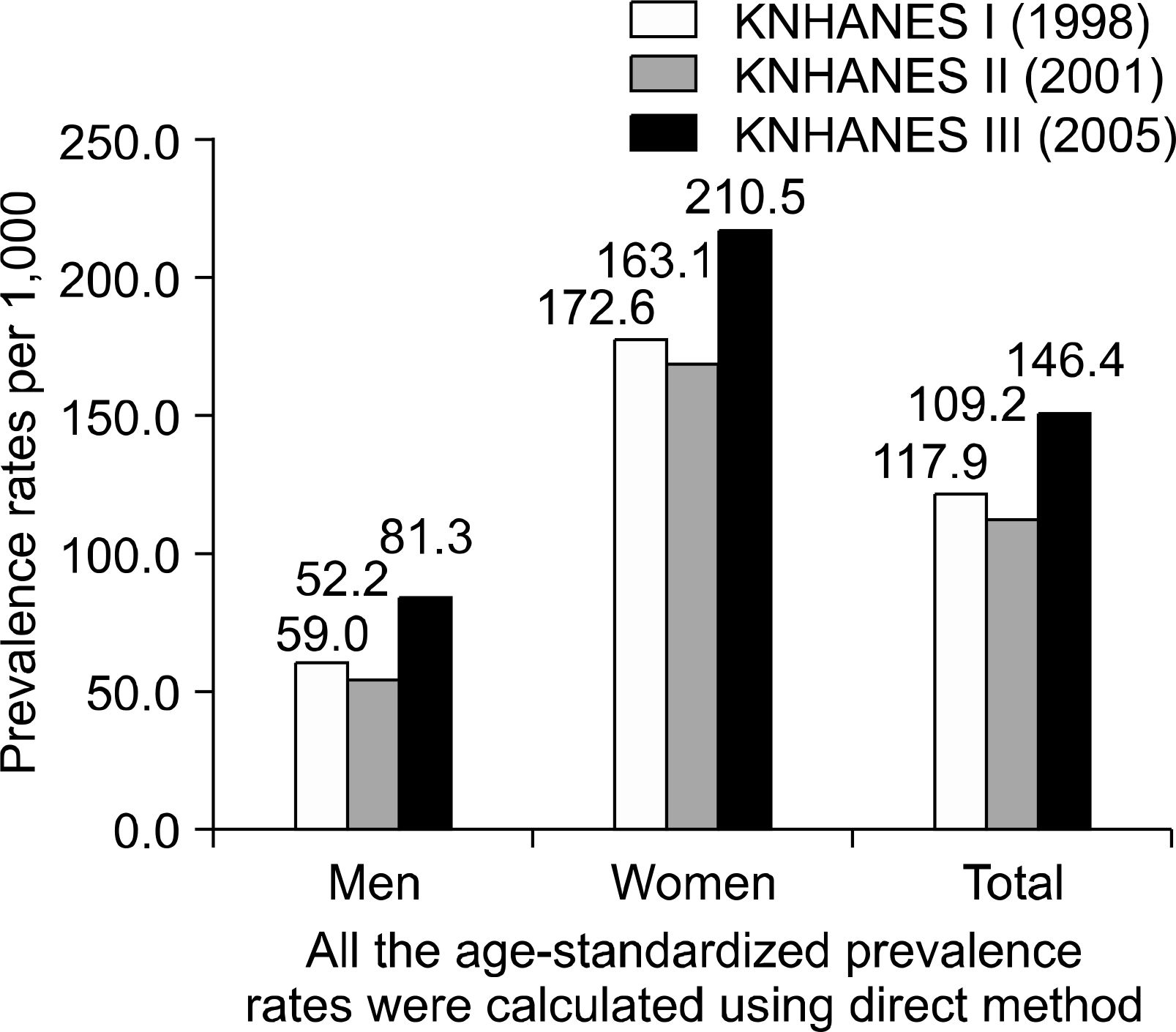 | Fig. 1.Age-standardized prevalence rates of arthritis in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) I, II and III. |
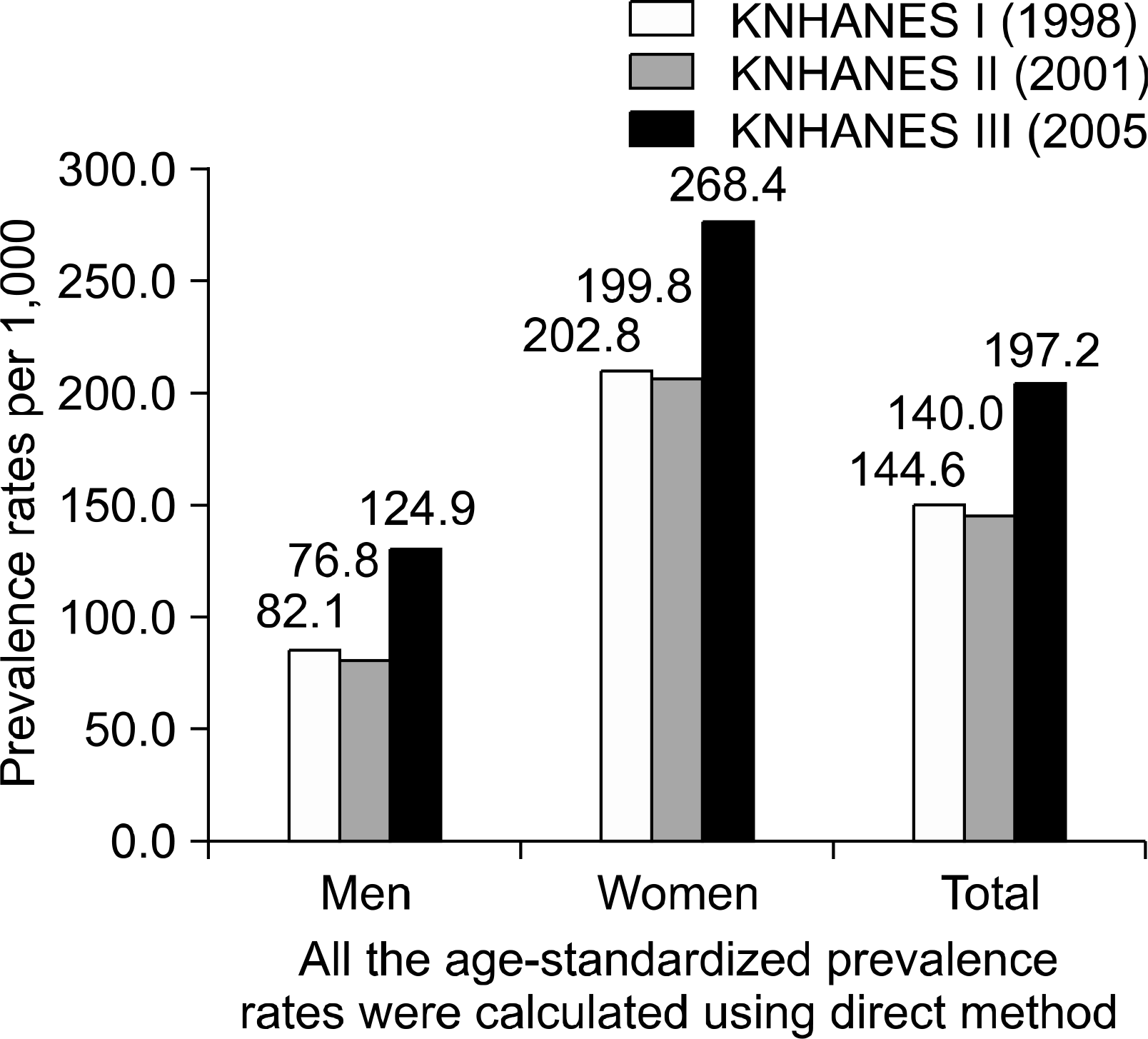 | Fig. 2.Age-standardized prevalence rates of musculoskeletal diseases in KNHANES I, II and III. |
Table 1.
Comparison of the survey methods used for musculoskeletal diseases in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) during 1998∼2005
Table 2.
Crude annual self-reported prevalence rates of musculoskeletal diseases in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) during 1998∼2005. Values are person per 1,000 (95% CI)
Table 3.
Prevalence rates according to its definitions and age groups in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III. Values are person per T31,000 (95% CI)
| Four musculoskeletal diseases | Arthritis | Osteoarthritis | Rheumatoid arthritis | Osteoporosis | Herniated disc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | |||||||
| Annual self-reported prevalence rates∗ | 197.2 (190.0∼204.3) | 146.4 (140.1∼152.7) | 129.7 (123.9∼135.6) | 21.1 (18.9∼23.3) | 40.9 (38.0∼ 43.8) | 62.1 (58.2∼ 66.1) | |
| Lifetime self-reported prevalence rates∗∗ | 211.3 (204.1∼218.5) | 151.5 (145.2∼157.8) | 133.5 (127.6∼139.4) | 22.7 (20.5∼24.9) | 42.0 (39.1∼ 44.9) | 73.1 (68.9∼ 77.3) | |
| Annual physician-diagnosed prevalence rates∗∗∗ | 163.4 (157.2∼169.5) | 112.6 (107.3∼117.8) | 99.0 (94.1∼103.9) | 16.9 (15.1∼18.8) | 38.6 (35.8∼ 41.4) | 54.9 (51.5∼ 58.4) | |
| Lifetime physician-diagnosed prevalence rates† | 177.3 (171.0∼183.6) | 117.3 (112.0∼122.6) | 102.4 (97.4∼107.3) | 18.5 (16.6∼20.4) | 39.7 (36.9∼ 42.5) | 65.7 (62.0∼ 69.5) | |
| Men | |||||||
| Annual self-reported prevalence rates∗ | 124.9 (117.9∼131.8) | 81.3 (75.6∼ 87.0) | 70.8 (65.6∼ 76.0) | 11.6 (9.3∼13.9) | 5.2 (3.8∼ 6.5) | 52.8 (48.2∼ 57.4) | |
| Lifetime self-reported prevalence rates∗∗ | 140.7 (133.5∼147.9) | 85.4 (79.6∼ 91.1) | 74.0 (68.8∼ 79.2) | 12.6 (10.3∼14.9) | 5.3 (3.9∼ 6.6) | 65.8 (60.7∼ 70.8) | |
| Annual physician-diagnosed prevalence rates∗∗∗ | 96.4 (90.7∼102.2) | 56.2 (51.7∼ 60.6) | 47.9 (44.0∼ 51.9) | 09.1 (7.2∼10.9) | 4.8 (3.6∼ 6.1) | 45.0 (40.8∼ 49.1) | |
| Lifetime physician-diagnosed prevalence rates† | 111.5 (105.3∼117.6) | 59.6 (55.0∼ 64.1) | 50.4 (46.4∼ 54.5) | 10.1 (8.1∼12.0) | 4.9 (3.6∼ 6.2) | 57.5 (52.8∼ 62.2) | |
| Women | |||||||
| Annual self-reported prevalence rates∗ | 268.4 (258.4∼278.5) | 210.5 (201.3∼219.8) | 187.9 (179.2∼196.6) | 30.4 (27.1∼33.8) | 76.1 (70.6∼ 81.6) | 71.3 (65.8∼ 76.8) | |
| Lifetime self-reported prevalence rates∗∗ | 280.8 (270.9∼290.8) | 216.7 (207.5∼226.0) | 192.2 (183.5∼201.0) | 32.6 (29.1∼36.0) | 78.2 (72.7∼ 83.7) | 80.3 (74.5∼ 86.2) | |
| Annual physician-diagnose pre valence rates∗∗∗ | 229.3 (220.3∼238.4) | 168.2 (160.1∼176.3) | 149.4 (141.7∼157.0) | 24.7 (21.8∼27.6) | 71.9 (66.6∼ 77.2) | 64.8 (60.0∼ 69.6) | |
| Lifetime physician-diagnosed prevalence rates† | 242.1 (233.2∼251.2) | 174.2 (166.1∼182.3) | 153.6 (145.9∼161.2) | 26.8 (23.8∼29.8) | 74.0 (68.6∼ 79.3) | 73.8 (68.6∼ 79.0) | |
| Life cycle (age) | |||||||
| Total | 19∼44 | 66.9 (61.8∼ 72.1) | 31.0 (27.6∼ 34.4) | 21.2 (18.5∼ 23.9) | 10.0 (8.1∼11.9) | 3.4 (2.4∼ 4.4) | 36.6 (32.9∼ 40.4) |
| 45∼64 | 294.6 (282.0∼307.2) | 224.6 (213.2∼236.0) | 201.2 (190.3∼212.1) | 30.0 (25.5∼34.5) | 58.7 (53.1∼ 64.4) | 86.2 (78.8∼ 93.5) | |
| 65+ | 578.9 (559.9∼598.0) | 505.0 (485.2∼524.9) | 472.6 (452.3∼492.9) | 52.0 (43.3∼60.7) | 176.8 (162.0∼191.6) | 124.2 (111.9∼136.5) | |
| Men | 19∼44 | 61.8 (55.1∼ 68.5) | 24.5 (20.5∼ 28.4) | 16.0 (12.9∼ 19.0) | 8.6 (6.2∼11.0) | 0.3‡ (0.0∼ 1.2) | 39.8 (34.4∼ 45.2) |
| 45∼64+ | 177.0 (163.9∼190.0) | 125.2 (113.7∼136.7) | 110.6 (99.8∼121.4) | 16.1 (11.5∼20.7) | 5.5 (3.1∼ 7.8) | 64.0 (55.9∼ 72.2) | |
| 65+ | 351.7 (325.0∼378.4) | 295.2 (268.9∼321.6) | 284.5 (258.2∼310.9) | 16.2 (9.1∼23.3) | 32.5 (22.2∼ 42.7) | 98.2 (82.3∼114.0) | |
| Women | 19∼44 | 72.4 (65.6∼ 79.3) | 37.9 (33.1∼ 42.8) | 26.7 (22.7∼ 30.8) | 11.5 (8.7∼14.3) | 6.3 (4.3∼ 8.3) | 33.3 (28.6∼ 38.0) |
| 45∼64 | 411.6 (393.6∼429.6) | 323.4 (306.4∼340.5) | 291.3 (274.9∼307.8) | 43.8 (36.8∼50.9) | 111.7 (101.0∼122.4) | 108.1 (97.3∼119.0) | |
| 65+ | 731.3 (710.2∼752.5) | 645.8 (622.2∼669.4) | 598.8 (574.4∼623.2) | 76.0 (62.9∼89.1) | 273.7 (250.8∼296.5) | 141.7 (125.3∼158.0) | |
∗∗∗ Having disease more than 3 months during one year or having it now and physician diagnosed the disease,
Table 4.
Annual self-reported prevalence rates according to the place of residence in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III. Values are person per 1,000 (95% CI)
Table 5.
Annual self-reported prevalence rates according to the sociodemographic characteristics in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III. Values are person per 1,000 (95% CI)
| Musculoskeletal diseases | Arthritis | Osteoarthritis | Rheumatoid arthritis | Osteoporosis | Herniated disc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marrital status | ||||||
| Single | 46.2 (39.5∼ 53.0) | 18.1 (14.1∼ 22.0) | 11.5 (8.6∼ 14.5) | 6.7 (4.0∼ 9.3) | 2.4 (1.1∼ 3.7) | 28.8 (23.6∼ 33.9) |
| Married | 200.8 (192.5∼209.1) | 146.5 (139.1∼153.8) | 129.1 (122.2∼136.0) | 21.2 (18.6∼23.8) | 36.8 (33.6∼ 40.1) | 65.1 (60.4∼ 69.9) |
| Other | 488.7 (469.4∼508.0) | 411.0 (391.9∼430.1) | 616.2 (597.3∼635.1) | 50.3 (42.0∼58.5) | 143.4 (131.0∼155.7) | 114.2 (101.2∼127.3) |
| Education | ||||||
| No formal education | 636.8 (614.5∼659.0) | 558.7 (534.8∼582.6) | 519.9 (496.3∼543.6) | 63.2 (51.6∼74.8) | 199.6 (179.6∼219.7) | 134.8 (119.4∼150.2) |
| Elementary school | 460.2 (441.6∼478.7) | 374.2 (355.8∼392.7) | 343.6 (325.2∼362.1) | 43.6 (36.5∼50.7) | 112.6 (101.8∼123.5) | 119.2 (106.0∼132.3) |
| Middle school | 284.4 (265.2∼303.6) | 208.4 (191.2∼225.7) | 187.3 (171.1∼203.6) | 25.6 (19.0∼32.1) | 50.6 (41.4∼ 59.7) | 96.2 (84.0∼108.3) |
| High school | 110.5 (103.5∼117.4) | 66.0 (60.6∼ 71.3) | 52.8 (48.0∼ 57.6) | 14.2 (11.4∼17.0) | 11.9 (9.9∼ 14.0) | 45.5 (41.1∼ 49.9) |
| College or higher | 63.4 (56.6∼ 70.2) | 32.7 (28.1∼ 37.3) | 26.0 (21.9∼ 30.1) | 7.0 (4.7∼ 9.3) | 7.0 (5.0∼ 9.0) | 31.4 (26.5∼ 36.3) |
| Occupation | ||||||
| High & middle high class | 59.2 (45.5∼ 72.9) | 29.7 (19.9∼ 39.5) | 21.8 (13.7∼ 29.9) | 7.9 (2.5∼13.4)∗ | 6.1 (1.9∼ 10.3)∗ | 28.7 (18.8∼ 38.5) |
| New middle class | 65.3 (50.1∼ 80.5) | 35.1 (24.6∼ 45.6) | 20.5 (12.3∼ 28.8) | 14.5 (7.4∼21.7) | 5.1 (0.8∼ 9.5)∗ | 30.4 (18.7∼ 42.0) |
| Old middle class | 162.7 (145.3∼180.1) | 107.3 (92.5∼122.0) | 94.2 (80.7∼108.0) | 16.3 (10.6∼21.9) | 21.0 (15.2∼ 26.8) | 62.5 (51.2∼ 73.9) |
| Labors | 115.2 (102.2∼128.2) | 73.5 (62.8∼ 84.2) | 62.7 (53.0∼ 72.4) | 11.3 (7.1∼15.6) | 7.6 (4.3∼ 10.9) | 47.7 (38.9∼ 56.6) |
| Low class | 334.9 (313.9∼355.9) | 266.4 (247.4∼285.4) | 242.7 (224.1∼261.2) | 35.6 (28.6∼42.6) | 62.9 (53.4∼ 72.4) | 95.4 (83.2∼107.5) |
| Others | 207.9 (199.1∼216.7) | 156.8 (148.9∼164.6) | 139.2 (131.9∼146.6) | 21.9 (19.1∼24.7) | 50.8 (46.8∼ 54.9) | 62.4 (57.8∼ 67.0) |
| Health insurance | ||||||
| Self-employed insured | 199.8 (190.1∼209.5) | 144.7 (136.5∼152.9) | 129.3 (121.5∼137.1) | 20.1 (17.1∼23.2) | 36.3 (32.4∼ 40.2) | 65.8 (60.0∼ 71.6) |
| Employee insured | 177.6 (169.8∼185.3) | 132.5 (125.7∼139.3) | 116.3 (109.9∼122.8) | 19.8 (17.0∼22.5) | 38.8 (35.3∼ 42.3) | 55.1 (50.6∼ 59.6) |
| Medical aid | 463.0 (425.3∼500.6) | 374.4 (336.7∼412.1) | 337.1 (301.6∼372.5) | 51.4 (36.6∼66.2) | 123.9 (104.6∼143.3) | 127.8 (103.3∼152.2) |
| Monthly income (Won) | ||||||
| <1 million | 374.3 (357.7∼391.0) | 306.2 (290.2∼322.1) | 277.7 (262.4∼293.0) | 40.7 (34.8∼46.5) | 91.2 (82.7∼ 99.7) | 104.1 (94.7∼113.4) |
| ≤1∼2 million | 174.5 (164.6∼184.3) | 122.9 (114.6∼131.1) | 107.4 (99.6∼115.2) | 18.9 (15.2∼22.6) | 31.3 (27.3∼ 35.3) | 59.1 (52.7∼ 65.5) |
| ≤2∼3 million | 133.3 (123.3∼143.3) | 91.8 (83.5∼100.0) | 81.3 (73.4∼ 89.2) | 11.5 (8.6∼14.4) | 21.8 (17.9∼ 25.7) | 43.7 (37.4∼ 50.0) |
| ≤3∼4 million | 118.1 (105.9∼130.2) | 82.4 (72.6∼ 92.3) | 68.9 (59.8∼ 78.0) | 14.7 (9.4∼19.9) | 19.3 (14.4∼ 24.2) | 42.8 (34.9∼ 50.7) |
| ≤4 million | 120.0 (105.8∼134.2) | 74.0 (63.2∼ 84.7) | 62.0 (52.0∼ 71.9) | 13.4 (8.7∼18.1) | 27.6 (21.3∼ 33.9) | 42.9 (34.3∼ 51.4) |
Table 6.
Annual self-reported prevalence rates according to the sociodemographic characteristics in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III (Men). Values are person per 1,000 (95% CI)
| Four musculoskeletal diseases | Arthritis | Osteoarthritis | Rheumatoid arthritis | Osteoporosis | Herniated disc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marrital status | ||||||
| Single | 52.8 (43.5∼ 62.1) | 17.4 (12.4∼ 22.5) | 11.1 (7.1∼ 15.1) | 6.3 (3.1∼ 9.6) | 1.1 (0.0∼ 2.3)∗ | 36.8 (29.4∼ 44.2) |
| Married | 148.1 (139.4∼156.8) | 101.7 (94.3∼109.1) | 89.8 (83.0∼ 96.7) | 13.1 (10.3∼15.8) | 6.3 (4.6∼ 8.0) | 57.8 (52.2∼ 63.3) |
| Other | 230.0 (196.6∼263.4) | 176.7 (146.6∼206.9) | 159.6 (130.0∼189.1) | 22.5 (10.4∼34.6) | 13.6 (4.8∼22.3)∗ | 79.0 (57.0∼100.9) |
| Education | ||||||
| No formal education | 378.5 (334.9∼422.1) | 306.1 (263.8∼348.3) | 293.4 (250.0∼336.8) | 16.7 (4.5∼29.0) | 37.3 (19.5∼55.1) | 114.5 (85.8∼143.3) |
| Elementary school | 314.8 (286.6∼343.1) | 242.1 (215.7∼268.6) | 221.9 (195.7∼248.2) | 23.4 (14.2∼32.7) | 17.5 (9.9∼25.1) | 102.0 (82.8∼121.2) |
| Middle school | 223.7 (197.5∼250.0) | 155.4 (132.8∼178.0) | 140.5 (119.3∼161.8) | 17.1 (9.6∼24.6) | 7.7 (2.4∼13.0) | 89.2 (73.2∼105.2) |
| High school | 94.8 (86.1∼103.6) | 52.0 (45.8∼ 58.2) | 40.8 (35.3∼ 46.3) | 11.9 (8.5∼15.4) | 2.5 (1.2∼ 3.8) | 47.4 (41.1∼ 53.7) |
| College or higher | 54.6 (46.6∼ 62.5) | 27.9 (22.4∼ 33.3) | 22.8 (18.0∼ 27.7) | 5.0 (2.5∼7.5) | 1.3 (0.1∼ 2.4)∗ | 29.6 (23.3∼ 35.9) |
| Occupation | ||||||
| High & middle high class | 53.5 (37.5∼ 69.6) | 34.8 (21.5∼ 48.1) | 24.4 (13.2∼ 35.5) | 10.4 (2.3∼18.5) | 1.6 (0.0∼ 3.9)∗ | 23.2 (12.2∼ 34.2) |
| New middle class | 73.1 (53.7∼ 92.5) | 38.1 (24.4∼ 51.8) | 26.7 (15.3∼ 38.2) | 11.4 (3.3∼19.4) | 2.1 (0.0∼ 5.4)∗ | 37.8 (21.9∼ 53.6) |
| Old middle class | 111.7 (94.8∼128.7) | 59.9 (47.0∼ 72.8) | 53.7 (41.7∼ 65.6) | 7.2 (2.7∼11.7)∗ | 5.6 (0.0∼ 2.1)∗ | 56.5 (43.7∼ 69.4) |
| Labors | 98.8 (83.6∼113.9) | 52.7 (40.7∼ 64.7) | 44.7 (34.0∼ 55.5) | 8.0 (3.0∼13.0)∗ | 1.9 (0.0∼ 4.1)∗ | 54.3 (42.4∼ 66.1) |
| Low class | 234.6 (213.8∼255.4) | 173.3 (155.1∼191.6) | 153.3 (135.9∼170.7) | 23.2 (15.2∼31.2) | 6.0 (2.3∼ 9.8)∗ | 81.6 (67.8∼ 95.4) |
| Others | 119.0 (109.3∼128.6) | 78.9 (71.0∼ 86.7) | 69.5 (62.0∼ 76.9) | 10.5 (7.5∼13.4) | 6.6 (4.5∼ 8.7) | 48.9 (42.6∼ 55.1) |
| Health insurance | ||||||
| Self-employed insured | 130.0 (119.5∼140.5) | 79.1 (71.3∼ 86.8) | 70.1 (62.8∼ 77.4) | 10.0 (7.2∼12.8) | 5.3 (3.3∼ 7.4) | 59.8 (52.3∼ 67.3) |
| Employee insured | 110.5 (102.3∼118.7) | 74.6 (67.7∼ 81.5) | 63.3 (57.0∼ 69.6) | 11.9 (8.7∼15.1) | 4.3 (2.7∼ 5.8) | 43.8 (38.6∼ 49.1) |
| Medical aid | 320.0 (267.0∼373.1) | 234.7 (187.1∼282.4) | 217.3 (171.0∼263.5) | 29.1 (11.6∼46.6)∗ | 20.2 (5.3∼ 3.5)∗ | 123.1 (81.0∼165.1) |
| Monthly income (Won) | ||||||
| <1 million | 221.3 (201.8∼240.8) | 162.1 (145.3∼178.9) | 148.8 (132.7∼164.9) | 17.7 (12.3∼23.1) | 12.2 (7.7∼16.7) | 84.3 (71.6∼ 97.0) |
| ≤1∼2 million | 120.6 (109.8∼131.4) | 74.1 (65.5∼ 82.7) | 62.8 (55.1∼ 70.5) | 11.6 (7.4∼15.8) | 4.8 (2.7∼ 7.0) | 54.5 (46.6∼ 62.3) |
| ≤2∼3 million | 99.0 (86.8∼111.3) | 60.5 (51.1∼ 69.8) | 53.0 (44.5∼ 61.5) | 7.5 (3.7∼11.3) | 0.3 (0.0∼ 1.0)∗ | 42.8 (34.5∼ 51.2) |
| ≤3∼4 million ≤ | 78.6 (64.2∼ 93.1) ∼ | 46.4 (35.2∼ 57.5) ∼ | 38.2 (28.3∼ 48.2) ∼ | 8.5 (3.1∼13.8)∗∼ | 1.0 (0.0∼ 2.1)∗∼ | 38.5 (28.1∼ 48.9)∼ |
| ≤4 million | 70.0 (56.1∼ 84.0) | 40.9 (30.2∼ 51.5) | 28.7 (19.8∼ 37.5) | 12.9 (6.6∼19.1) | 1.7 (0.0∼ 3.7)∗ | 30.6 (20.9∼ 40.4) |
Table 7.
Annual self-reported prevalence rates according to the sociodemographic characteristics in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III (Women). Values are person per 1,000 (95% CI)
| Musculoskeleal diseases | Arthritis | Osteoarthritis | Rheumatoid arthritis | Osteoporosis | Herniated disc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marrital status | ||||||
| Single | 36.5 (28.4∼ 44.6) | 19.0 (13.5∼ 24.6) | 12.2 (7.8∼ 16.6) | 7.2 (3.7∼10.6) | 4.4 (1.8∼ 7.0)∗ | 16.8 (10.9∼ 22.8) |
| Married | 255.4 (244.3∼266.6) | 192.8 (182.7∼203.0) | 169.8 (160.2∼179.3) | 29.6 (25.7∼33.6) | 68.4 (62.3∼ 74.6) | 72.8 (66.2∼ 79.3) |
| Other | 560.8 (539.1∼582.5) | 476.4 (454.1∼498.6) | 438.5 (417.1∼460.0) | 58.0 (48.3∼67.8) | 179.6 (164.2∼195.0)∗ | 124.0 (108.9∼139.2) |
| Education | ||||||
| No formal education | 707.4 (683.8∼731.0) | 627.7 (601.3∼654.2) | 581.9 (555.5∼608.2) | 75.9 (61.5∼90.3) | 244.0 (219.8∼268.3) | 140.3 (122.8∼157.8) |
| Elementary school | 557.4 (533.4∼581.3) | 462.6 (438.6∼486.6) | 425.0 (401.0∼449.0) | 57.1 (47.2∼67.1) | 176.2 (159.1∼193.4) | 130.7 (112.3∼149.1) |
| Middle school | 338.5 (312.8∼364.2) | 255.8 (232.1∼279.4) | 229.1 (206.6∼251.5) | 33.1 (23.2∼43.0) | 88.7 (72.3∼105.2) | 102.4 (84.6∼120.1) |
| High school | 128.1 (118.3∼138.0) | 81.7 (73.7∼ 89.8) | 66.4 (59.1∼ 73.6) | 16.8 (12.7∼20.9) | 22.6 (18.4∼ 26.8) | 43.4 (37.4∼ 49.4) |
| College or higher | 75.2 (64.2∼ 86.2) | 39.1 (31.3∼ 47.0) | 30.1 (23.5∼ 36.7) | 9.7 (5.6∼13.8) | 14.5 (10.1∼ 18.9) | 33.8 (26.9∼ 40.7) |
| Occupation | ||||||
| High & middle high class | 69.1 (43.9∼ 94.3) | 20.9 (7.7∼ 34.0)∗ | 17.3 (5.7∼ 28.8)∗ | 3.6 (0.0∼ 8.4)∗ | 14.0 (3.3∼ 24.8)∗ | 38.2 (21.2∼ 55.2) |
| New middle class | 50.1 (26.7∼ 73.5) | 29.2 (12.0∼ 46.4) | 8.3 (0.0∼ 18.3)∗ | 20.8 (6.4∼35.3)∗ | 11.1 (0.1∼ 22.2)∗ | 15.7 (30.0∼ 28.5)∗ |
| Old middle class | 263.7 (228.6∼298.9) | 201.0 (168.8∼233.3) | 174.5 (143.2∼205.8) | 34.3 (20.8∼47.7) | 51.5 (35.9∼ 67.2) | 74.4 (53.5∼ 95.3) |
| Labors | 141.0 (119.3∼162.6) | 106.1 (88.5∼123.7) | 90.9 (75.1∼106.6) | 16.6 (8.6∼24.6) | 16.6 (8.8∼ 24.4) | 37.5 (25.1∼ 50.0) |
| Low class | 444.4 (414.9∼473.9) | 367.9 (339.1∼396.6) | 340.2 (311.1∼369.3) | 49.1 (38.3∼60.0) | 124.9 (106.0∼143.8) | 110.4 (92.5∼128.3) |
| Others | 272.0 (260.5∼283.5) | 212.9 (202.3∼223.5) | 189.5 (179.6∼199.5) | 30.2 (26.2∼34.1) | 82.7 (76.1∼ 89.3) | 72.2 (66.0∼ 78.4) |
| Health insurance | ||||||
| Self-employed insured | 270.7 (256.6∼284.8)∼ | 211.3 (198.5∼224.1)∼ | 189.3 (177.1∼201.5) ∼ | 30.4 (25.3∼35.5)∼ | 67.8 (60.4∼ 75.1)∼ | 71.8 (63.8∼ 79.8)∼ |
| Employee insured | 243.9 (232.8∼255.1) | 189.7 (180.0∼199.9) | 168.9 (159.2∼178.5) | 27.6 (23.6∼31.6) | 73.0 (66.3∼ 79.6) | 66.2 (59.8∼ 72.7) |
| Medical aid | 558.1 (513.0∼603.1) | 467.3 (419.0∼515.6) | 416.7 (371.6∼461.9) | 66.2 (45.5∼86.8) | 192.9 (164.2∼221.6) | 130.9 (102.1∼159.6) |
| Monthly income (Won)< | ∼ | ∼ | ∼ | ∼ | ∼ | ∼ |
| <1 million ≤ ∼ | 497.9 (477.3∼518.5)∼ | 422.5 (401.4∼443.7)∼ | 381.8 (361.4∼402.3) ∼ | 59.2 (50.2∼68.2)∼ | 155.0 (141.0∼169.1)∼ | 120.0 (107.2∼132.9)∼ |
| ≤1∼2 million | 231.1 (216.0∼246.3) | 174.2 (161.1∼187.2) | 154.3 (141.9∼166.8) | 26.7 (21.3∼32.0) | 59.1 (51.4∼ 66.8) | 64.0 (55.2∼ 72.8) |
| ≤2∼3 million ≤ ∼ | 169.2 (154.3∼184.1)∼ | 124.6 (111.9∼137.3)∼ | 111.0 (99.1∼122.9) ∼ | 15.7 (11.1∼20.3)∼ | 41.4 (33.8∼ 49.0)∼ | 44.7 (35.9∼ 53.4)∼ |
| ≤3∼4 million ≤4 million | 159.7 (141.6∼177.8) 168.7 (146.9∼190.4) | 120.5 (105.5∼135.6) 106.2 (89.7∼122.7) | 101.2 (86.8∼115.6) 94.4 (78.8∼110.0) | 21.2 (13.3∼29.1) 13.9 (8.0∼19.8) | 38.7 (28.5∼ 48.9) 52.8 (40.6∼ 64.9) | 47.3 (35.8∼ 58.8) 54.7 (42.4∼ 67.1) |
| ≤4 million | 168.7 (146.9∼190.4) | 106.2 (89.7∼122.7) | 94.4 (78.8∼110.0) | 13.9 (8.0∼19.8) | 52.8 (40.6∼ 64.9) | 54.7 (42.4∼ 67.1) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download