Abstract
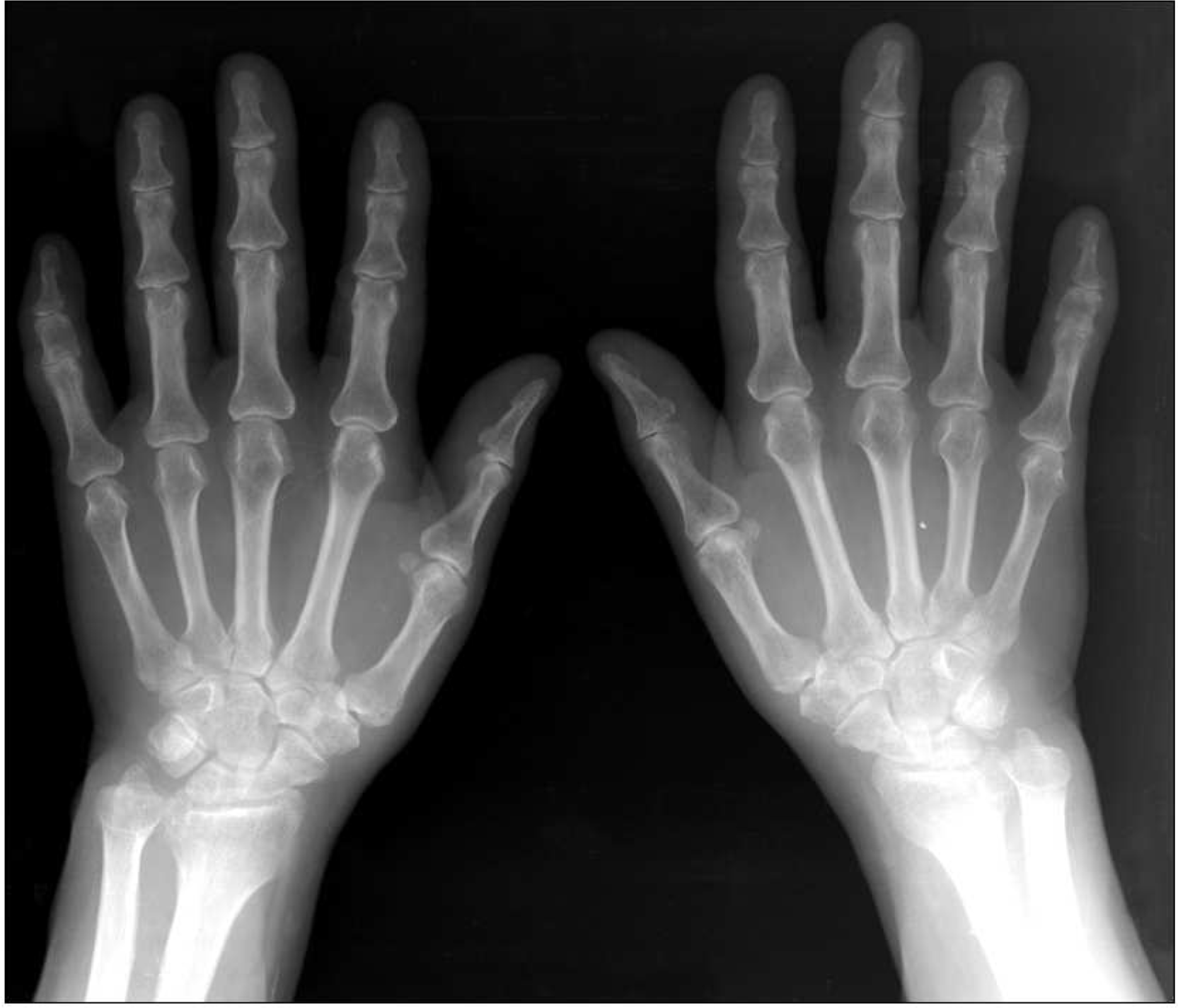
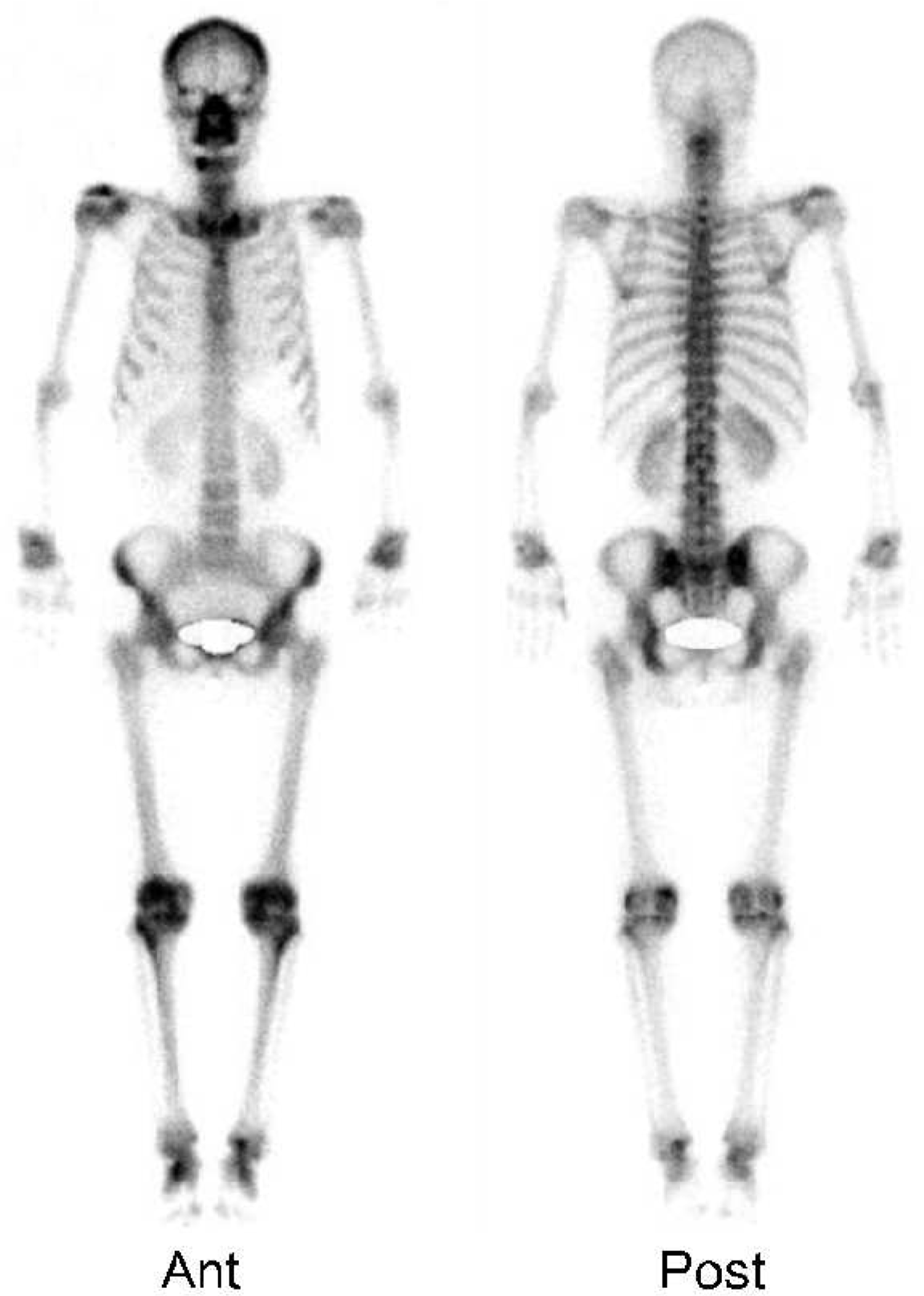
We report here on a case of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) that progressed from the spine to the peripheral joints. In RA, the involvement of the cervical spine usually correlates with the progressive erosion of peripheral joints, such as the hand or foot, and the elevation of disease activity. Generally, it takes over 2 years of rheumatoid involvement of the cervical spine to cause laxity of the transverse ligament. The common types of rheumatoid cervical spine are anterior atlantoaxial subluxation, vertical subluxation and subaxial subluxation. We describe a 61-year-old woman with only neck pain initially. An MRI of the cervical spine showed atlantoaxial subluxation with features of the rheumatoid involvement. Arthritis later developed in both hands and symmetrically in other peripheral joints. She was diagnosed as having RA. This is the first case report of RA presenting initially as atlantoaxial subluxation.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Oda T., Fujiwara K., Yonenobu K., Azuma B., Ochi T. Natural course of cervical spine lesions in rheumatoid arthritis. Spine. 1995. 20:1128–35.

2). Fujiwara K., ᄋwaki H., Fujimoto M., Yonenobu K., Ochi T. A long-term follow up study of cervical lesions in rheumatoid arthritis. J Spinal Disord. 2000. 13:519–26.
3). Shen FH., Samartizis D., Jenis LG., An HS. Rheumatoid arthritis; evaluation and surgical management of the cervical spine. Spine J. 2004. 4:689–700.

4). van Eijk IC., Nielen MM., van Soesbergen RM., Hamburger HL., Kerstens PJ., Dijkmans BA, et al. Cervical spine involvement is rare in early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:973–4.

5). Neva MH., Hakkinen A., Makinen H., Hannonen P., Kauppi M., Sokka T. High prevalence of asymptomatic cervical spine subluxation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis waiting for orthopaedic surgery. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:884–8.

6). Winfield J., Cooke D., Brook AS., Corbett M. A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981. 40:109–14.

7). Winfield J., Young A., William P., Corbett M. Prospective study of the radiological changes in hands, feet, and cervical spine in adult rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983. 42:613–8.

8). Neva MH., Kauppi MJ., Kautiainen H., Luukkainen R., Hannonen P., Leirisalo-repo M, et al. Combination drug therapy retards the development of rheumatoid atlantoaxial subluxations. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. 43:2397–401.

9). Paimela L., Laasonen L., Kankaanpaa E., Leirisalo-Repo M. Progression of cervical spine changes in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:1280–4.
10). Neva MH., Kaarela K., Kauppi M. Prevalence of radiological changes in the cervical spine– a cross sectional study after 20 years from presentation of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000. 27:90–3.
11). Zikou AK., Alamanos Y., Argyropoulou MI., Tsifetaki N., Tsampoulas C., Voulgari PV, et al. Radiological cervical spine involvement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross sectional study. J Rheumatol. 2005. 32:801–6.
12). Neva MH., Isomaki P., Hannonen P., Kauppi M., Krishnan E., Sokka T. Early and extensive erosiveness in peripheral joints predicts atlantoaxial subluxations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:1808–13.

13). Kauppi M., Barcelos A., da Silva JA. Cervical complications of rheumatoid arthrtis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:355–8.
14). Battiata AP., Pazos G. Grisel's syndrome: the two-hit hypothesis– a case report and literature review. Ear Nose Throat J. 2004. 83:553–5.
15). Daumen-Legre V., Lafforgue P., Champsaur P., Chagnaud C., Pham T., Kasbarian M, et al. Anteroposterior atlantoaxial subluxation in cervical spine osteoarthritis: case reports and review of the literature. J Rheumatol. 1999. 26:687–91.
Go to : 
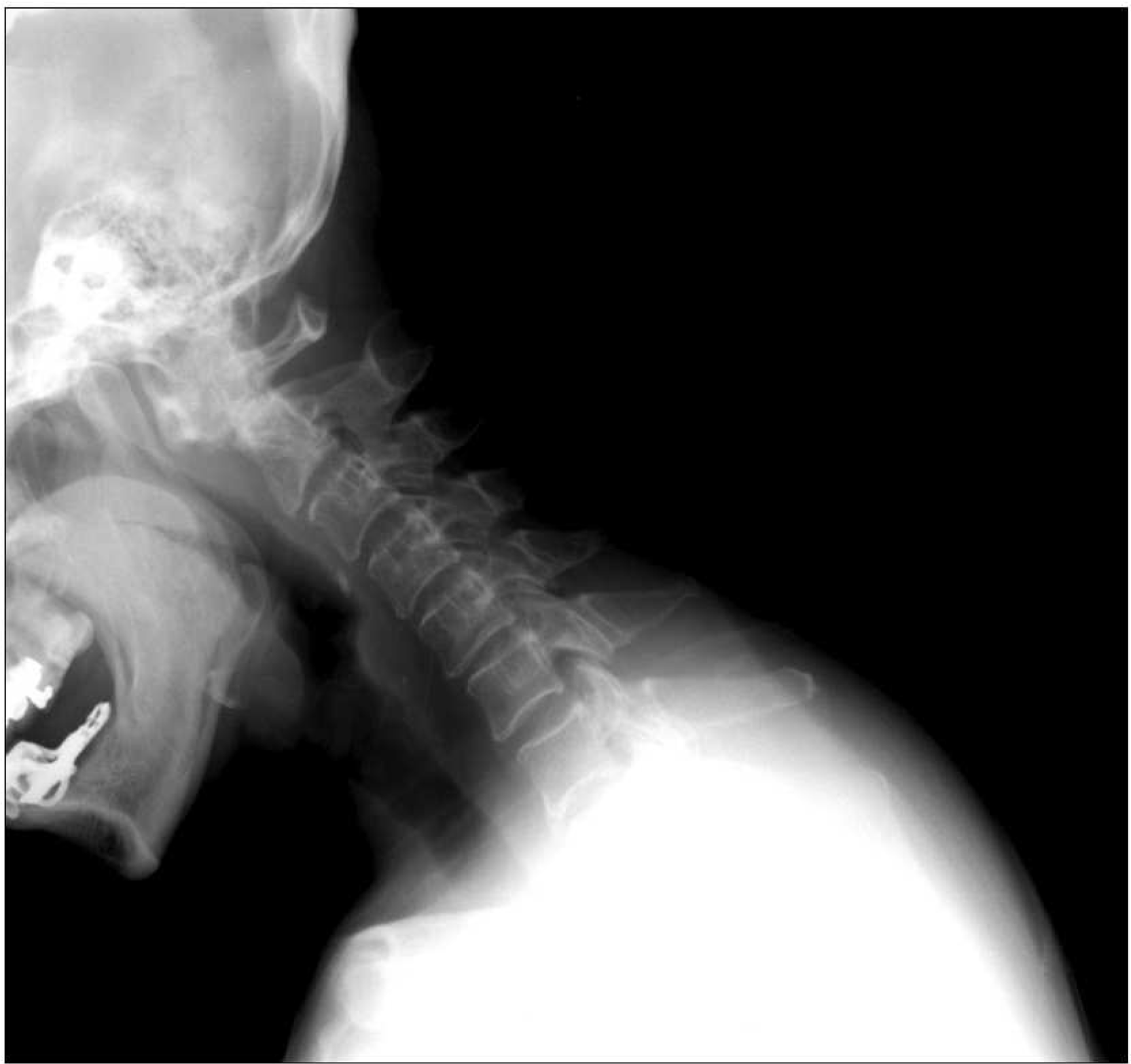 | Fig. 1.Cervical spine lateral flexion view. Subluxation of the first cervical vertebra on the odontoid. C-spine flexion image shows anterior slippling of the atlas on the axis. Narrowing of the C2-3 and C5-6 interspace without hypertrophic change suggests rheumatoid arthritis. |
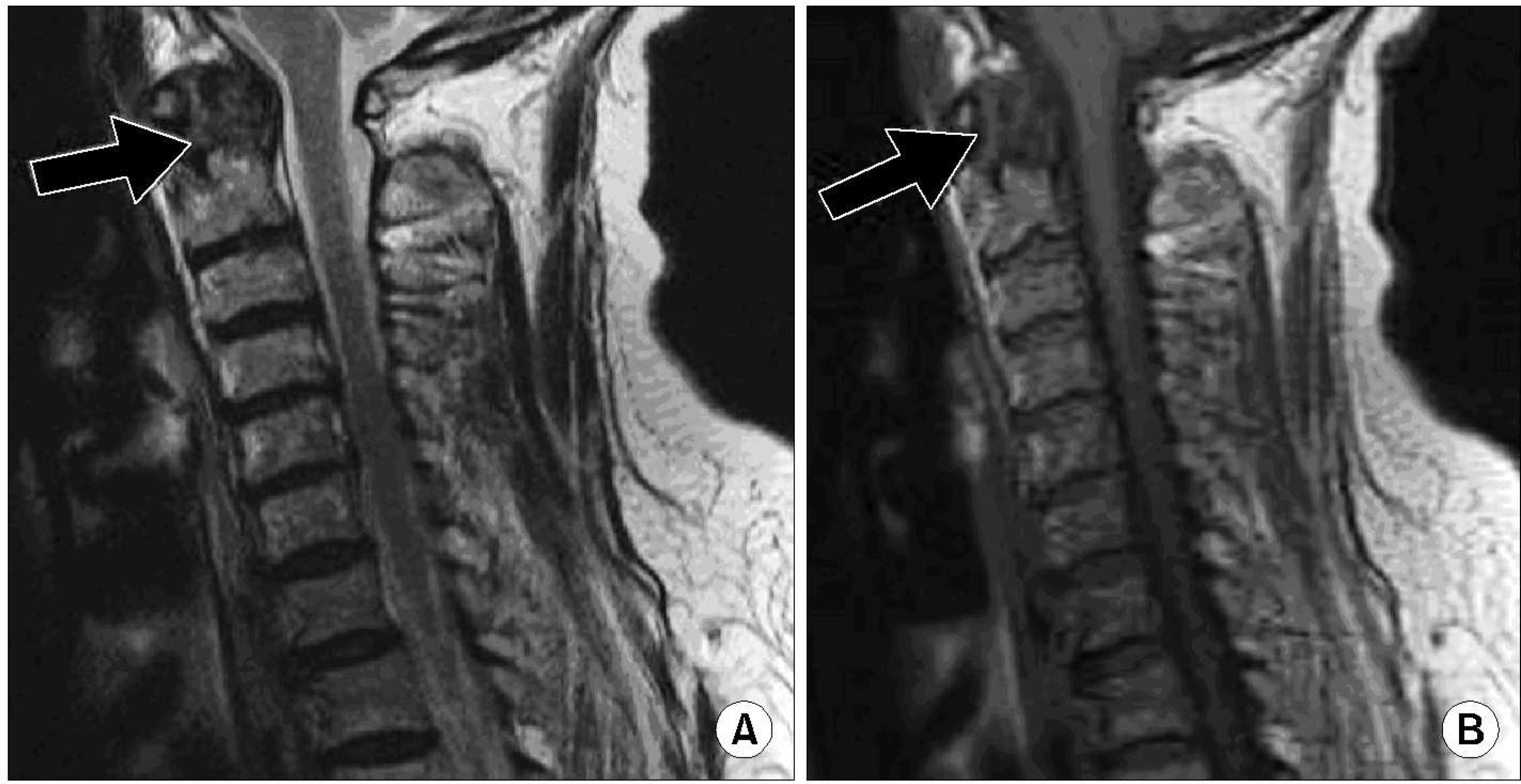 | Fig. 2.Cervical MRI. (A) A sagittal T1-weighted spin echo image of the upper cervical spine reveals a mass of intermediate signal intensity (arrow) that is eroding the odonotoid process and mild indentation of the anterior thecal sac. (B) A sagittal T2-weighted spin echo image of the upper cervical spine reveals a mass of heterogeneous intermediate signal intensity (arrow) that is same findings in T1-weighted spin echo image and eroding the lateral masses of the atlas. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download