Abstract
Behcet's disease is a chronic, relapsing vasculitis of unknown origin that affects nearly all organs. The most frequent extra-oral sites of gastrointestinal involvement are the ileocecal lesion and the colon. The lesions are typically resistant to medical treatment and frequently recur with surgical treatment. We describe a patient who had intestinal Behcet's disease complicated perforation and enterocutanous fistula with a good response to infliximab.
REFERENCES
1). Chang HK., Kim JW. The clinical features of Behcet's disease in Yongdong districts: analysis of a cohort followed from 1997 to 2001. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:784–9.

2). Scane T., Takeno M., Suzuki N., Inaba G. Behcet's diasease. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1284–91.
3). 차성덕: 임영석: 김지원: 김찬규: 김주성: 장동경등. 베체트장염환자에있어서내과적치료에대한반응도: 경과및재발률에대한연구. 대한소화기학회지. 1997. 30:472–80.
4). 김남렬: 정석인: 조용걸: 엄준원: 배정원: 서성옥등. 장관베체트병의외괴적치료. 대한외과학회지. 2001. 60:331–6.
5). 장현규. 베체트병병인의최신지견. 대한류마티스학회지. 2004. 11:193–204.
6). Imamura Y., Kurokawa MS., Yoshikawa H., Nara K., Takada ., Masuda C, et al. Involvement of Th1 cells and heat shock protein 60 in the pathogenesis of interstinal Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. 139:371–8.
7). International Study Group for Behcet's disease. Evaluation of diagnostic (Classification) Criteria in Behcet's disease: toward internationally agreed criteria. Lancet. 1990. 335:1078–80.
8). Behcet's disease Research Committee of Japan. Behcet's disease: guide to diagnosis of Behcet's disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1974. 18:291–4.
9). Bayraktar Y., Ozaslan E., Van Thiel DH. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behcet's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000. 30:144–54.

10). Chang HK., Kim JS., Chung HR. Ileocecal ulcer with a cecocecal fistula in Behcet's disease. Korean J Intern Med. 2000. 15:99–101.

11). Lee KS., Kim SJ., Lee BC., Yoon DS., Lee WJ., Chi HS. Surgical treatment of intestinal Behcet's disease. Yonsei Med J. 1997. 38:455–60.
12). 김주성: 문해: 최일주: 박민정: 김유선: 이진혁등. 베체트장염의대장내시경분류에따른내과적치료효과및누적수술률분석. 대한소화기내시경학회지. 2000. 20:254–61.
13). Misumi M., Hagiwara E., Takeno M., Takeno Y., Inoue Y., Tsuii T, et al. Cytokine production profile in patients with Behcet's disease treated with infliximab. Cytokine. 2003. 24:210–8.

14). Hassard PV., Blinder SW., Nelson V., Vasiliaukas EA. Anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody for gastrointestinal Behcet's disease: a case report. Gastroenterology. 2001. 120:995–9.
15). Travis SP., Cazjkowski M., McGovern DP., Watson RG., Bell AC. Treatment of intestinal Behcet's syndrome with chimeric tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody. Gut. 2001. 49:725–8.
Fig. 1.
Resected right colon showed marked serosal adhesion with peritonitis. The mucosal surface of the one segment shows multifocal ulcers with many deep fissure formation.
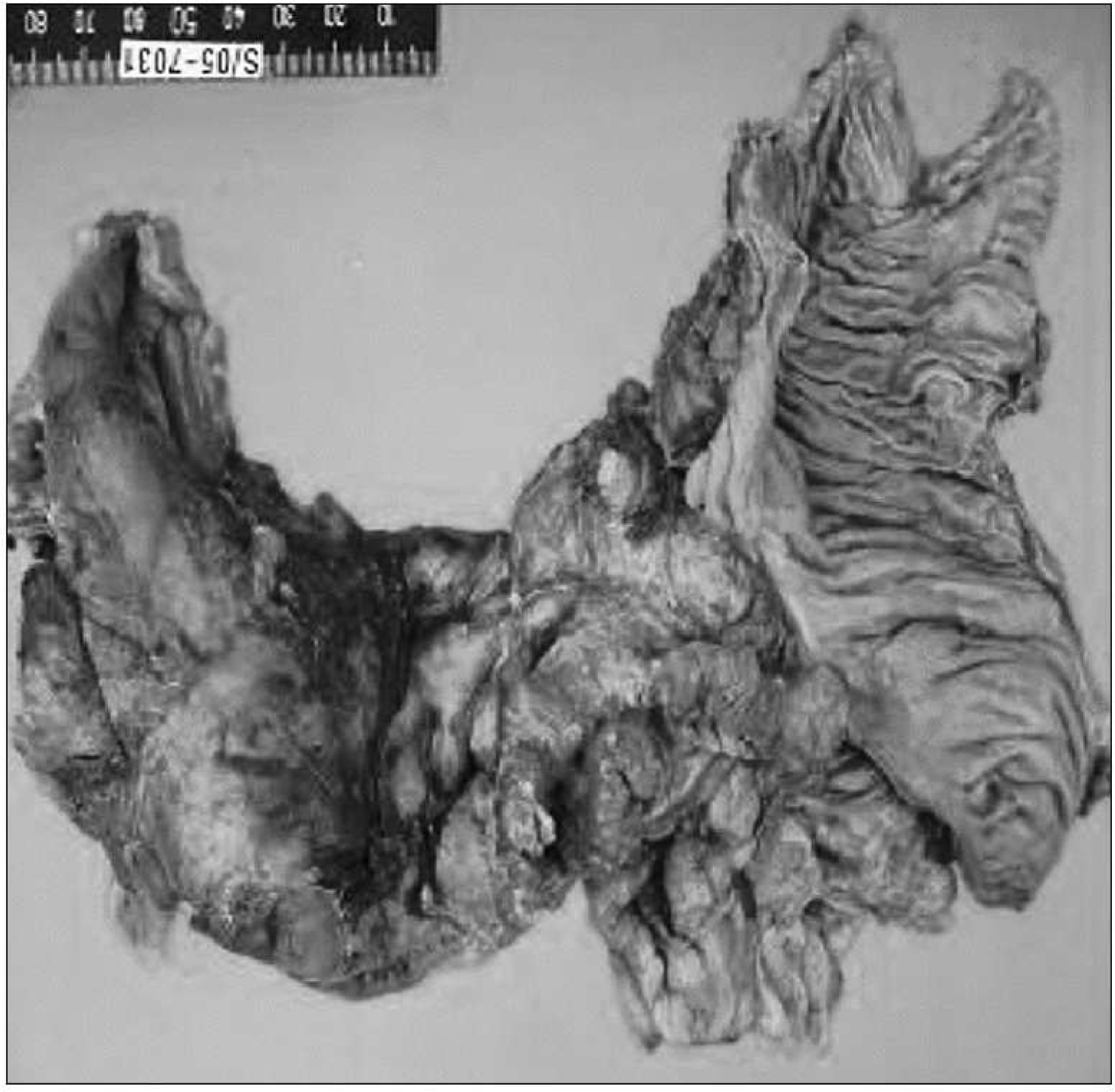
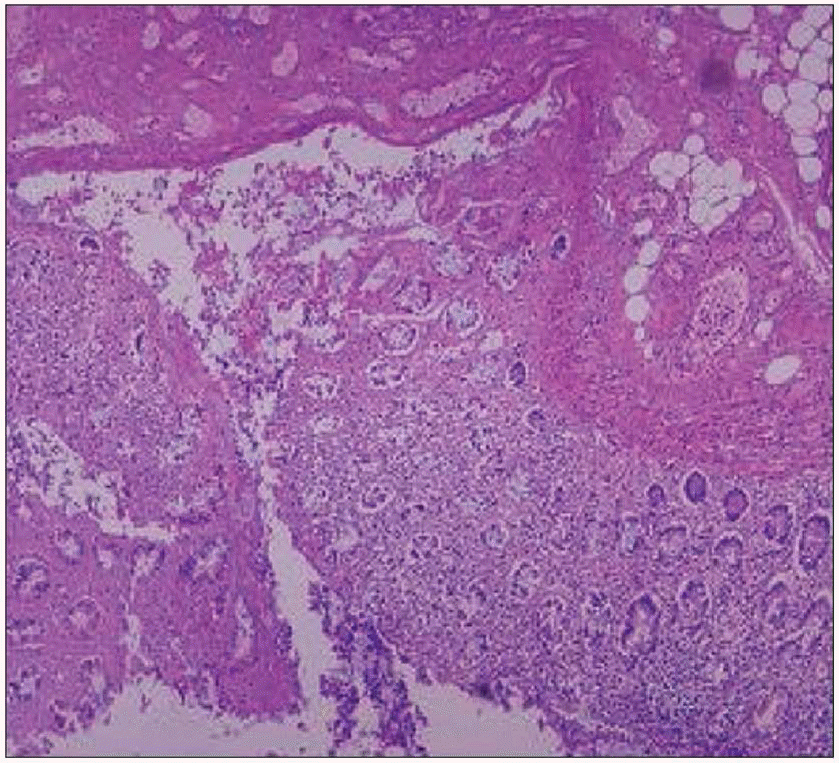
Fig. 2.
Ulcerative lesions are typically sharply demarcated from the adjacent mucosa and have mucosal collarettes (H&E stain, X100).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download