Abstract
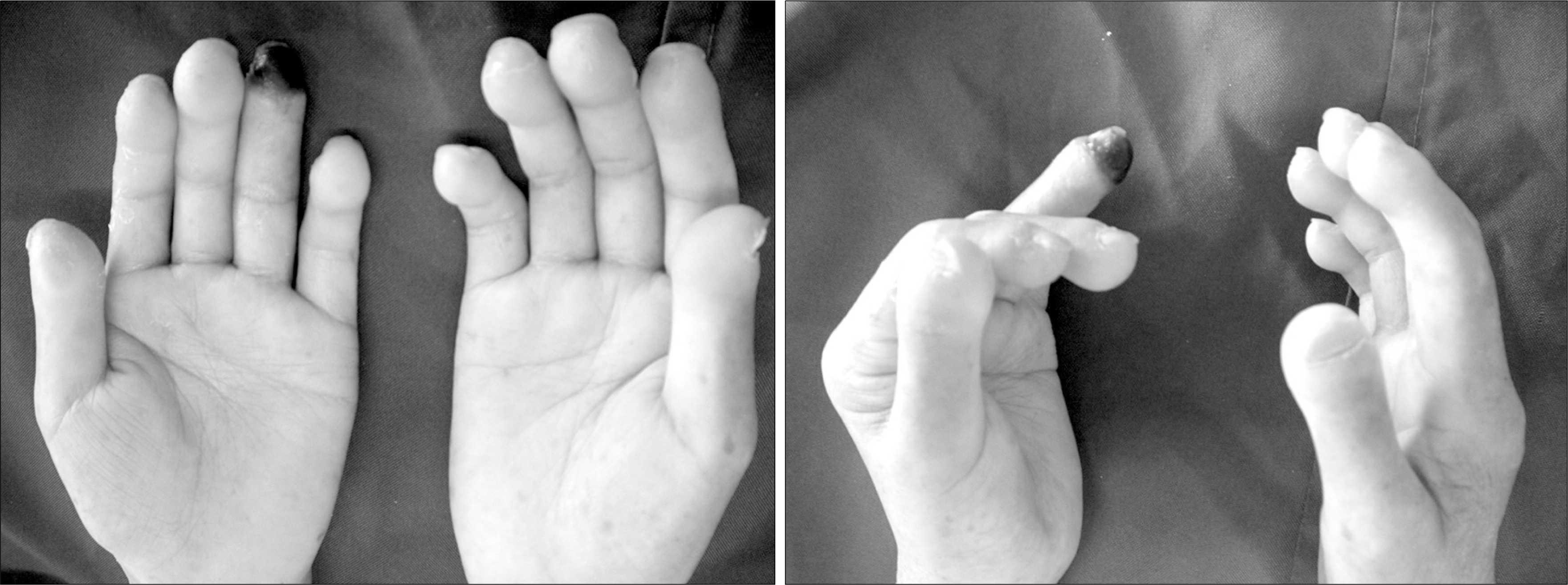
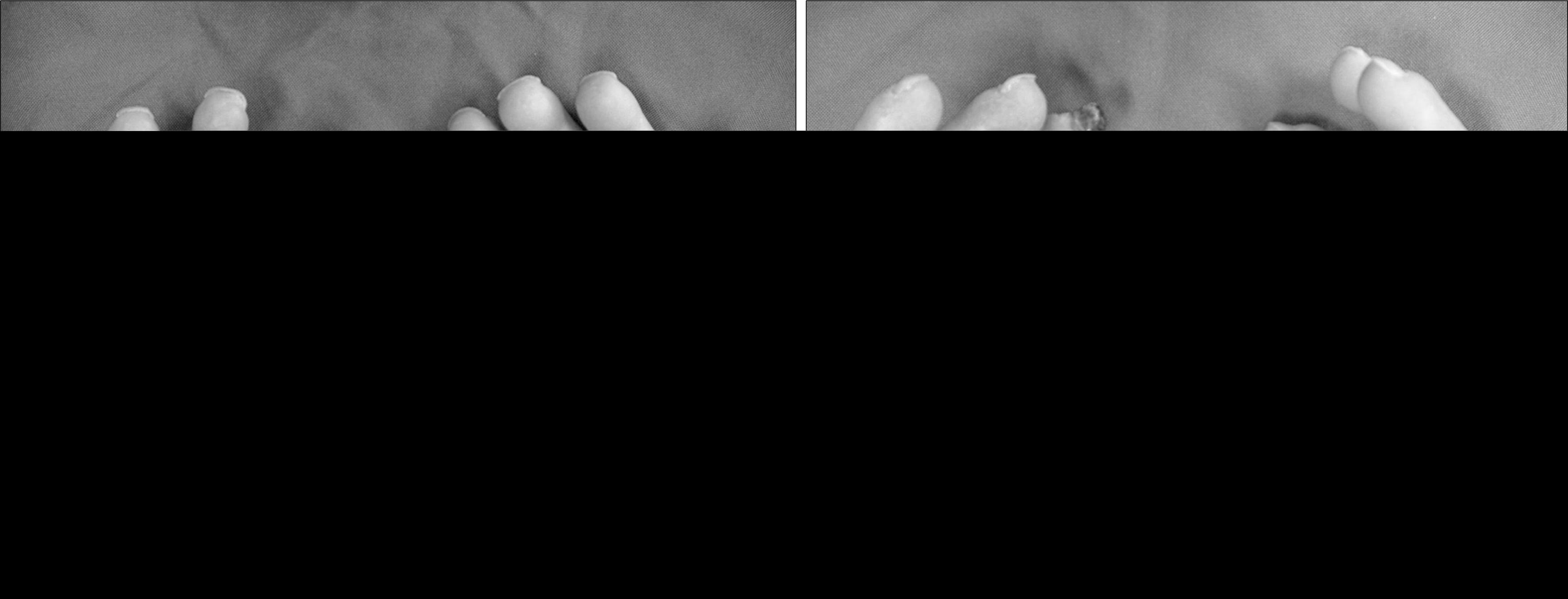
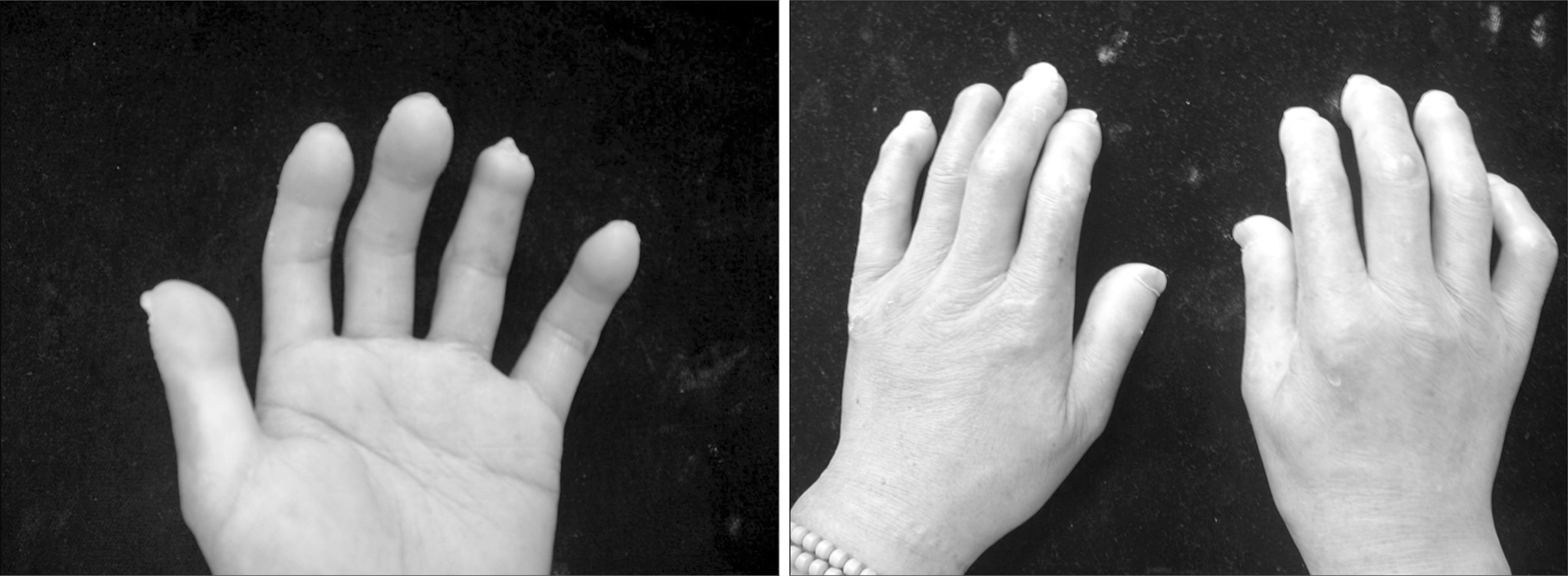
Systemic sclerosis is a connective tissue disease characterized by cutaneous and visceral fibrosis, as well as vascular disease involving arterioles, small and medium arteries of the peripheral circulation. Digital ulcers, defined as necrotic lesions that occur either at distal aspects of digits or over bony prominence, occur in up to 50% of patients with limited or diffuse systemic sclerosis. These lesions are exquisitely painful, heal slowly, and lead to substantial functional disability. We describe a 59-year-old woman with systemic sclerosis, suffering from a painful, non-healing digital ulcer despite conventional therapies, who demonstrated dramatic improvement with oral sildenafil treatment.
REFERENCES
1). Chung L., Fiorentino D. Digital ulcers in patients with systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2006. 5:125–8.

2). Clements P., Lachenbruch P., Siebold J., White B., Weiner S., Martin R, et al. Inter and intraobserver variability of total skin thickness score (modified Rodnan TSS) in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1995. 22:1281–5.
4). Hummers LK., Wigley FM. Management of Raynaud's phenomenon and digital ischemic lesions in scleroderma. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2003. 29:293–313.

5). Ferri C., Valentini G., Cozzi F., Sebastiani M., Michelassi C., La Montagna G, et al. Systemic sclerosis: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 1, 012 Italian patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2002. 81:139–53.
6). Palesch YY., Valter I., Carpentier PH., Maricq HR. Association between cigarette and alcohol consumption and Raynaud's phenomenon. J Clin Epidemiol. 1999. 52:321–8.

7). Janini SD., Scott DG., Coppock JS., Bacon PA., Kendall MJ. Enalapril in Raynaud's phenomenon. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1988. 13:145–50.

8). Dziadzio M., Denton CP., Smith R., Howell K., Blann A., Bowers E, et al. Losartan therapy for Raynaud's phenomenon and scleroderma: clinical and biochemical findings in a fifteen-week, randomized, parallel-group, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:2646–55.

9). Thompson AE., Shea B., Welch V., Fenlon D., Pope JE. Calcium-channel blockers for Raynaud's phenomenon in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:1841–7.

10). Gore J., Silver R. Oral sildenafil for the treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon and digital ulcers secondary to systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:1387.

11). Lichtenstein JR. Use of sildenafil citrate in Raynaud's phenomenon: comment on the article by Thompson et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:282–3.

12). Rosenkranz S., Diet F., Karasch T., Weihrauch J., Wassermann K., Erdmann E. Sildenafil improved pulmonary hypertension and peripheral blood flow in a patient with scleroderma-associated lung fibrosis and the raynaud phenomenon. Ann Intern Med. 2003. 139:871–3.

13). McCullough AR. Four-year review of sildenafil citrate. Rev Urol. 2002. 4(Suppl 3):S26–38.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download