Abstract
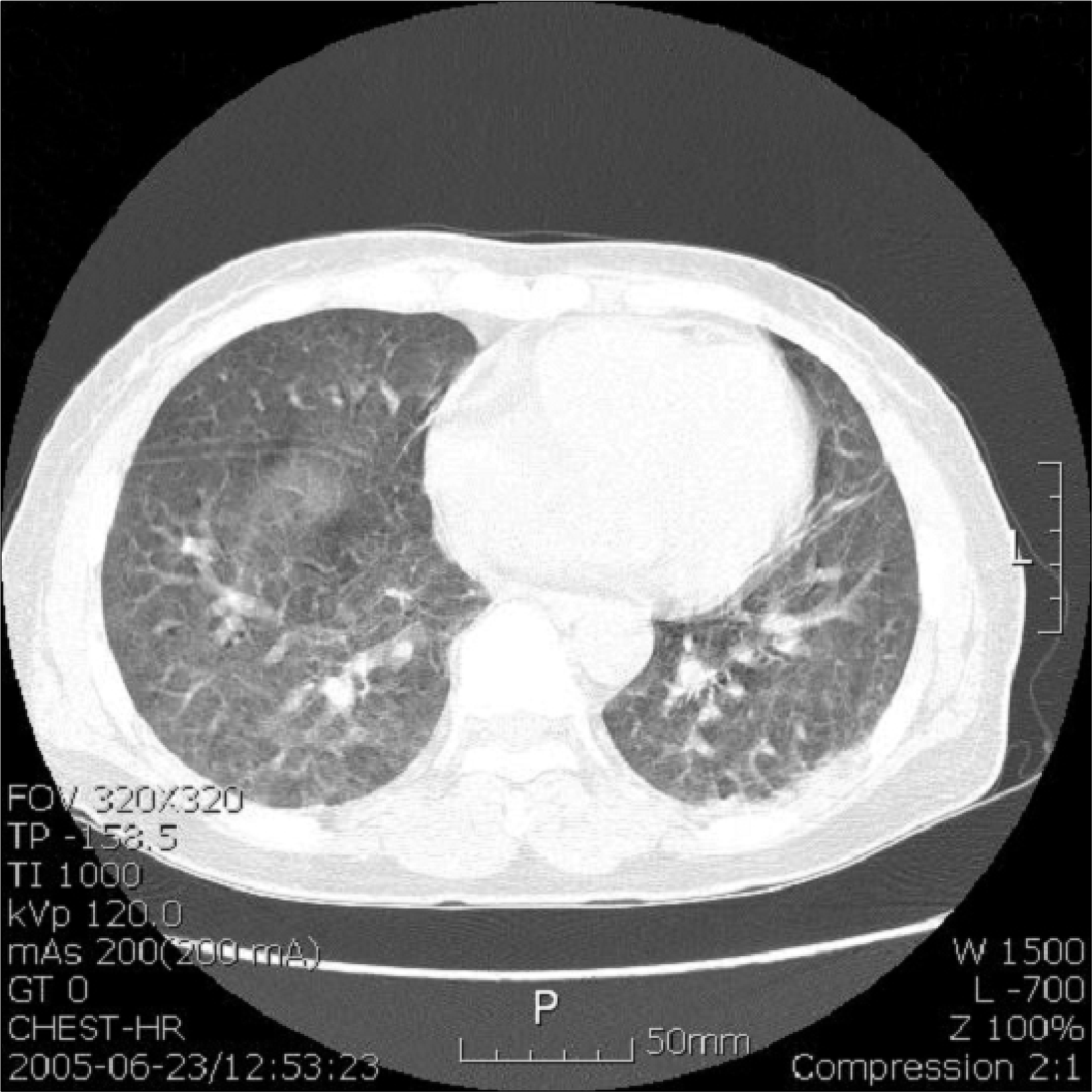
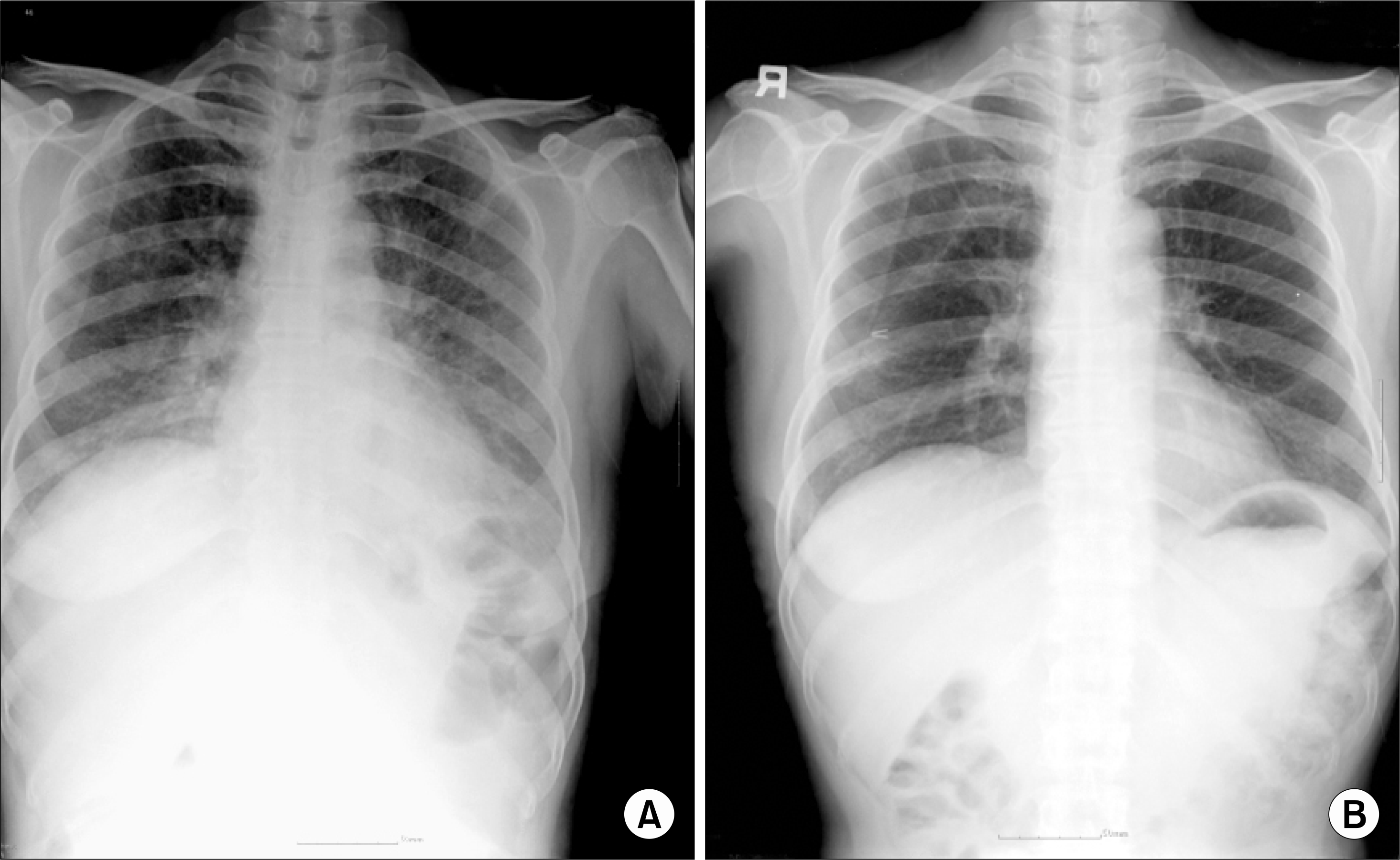
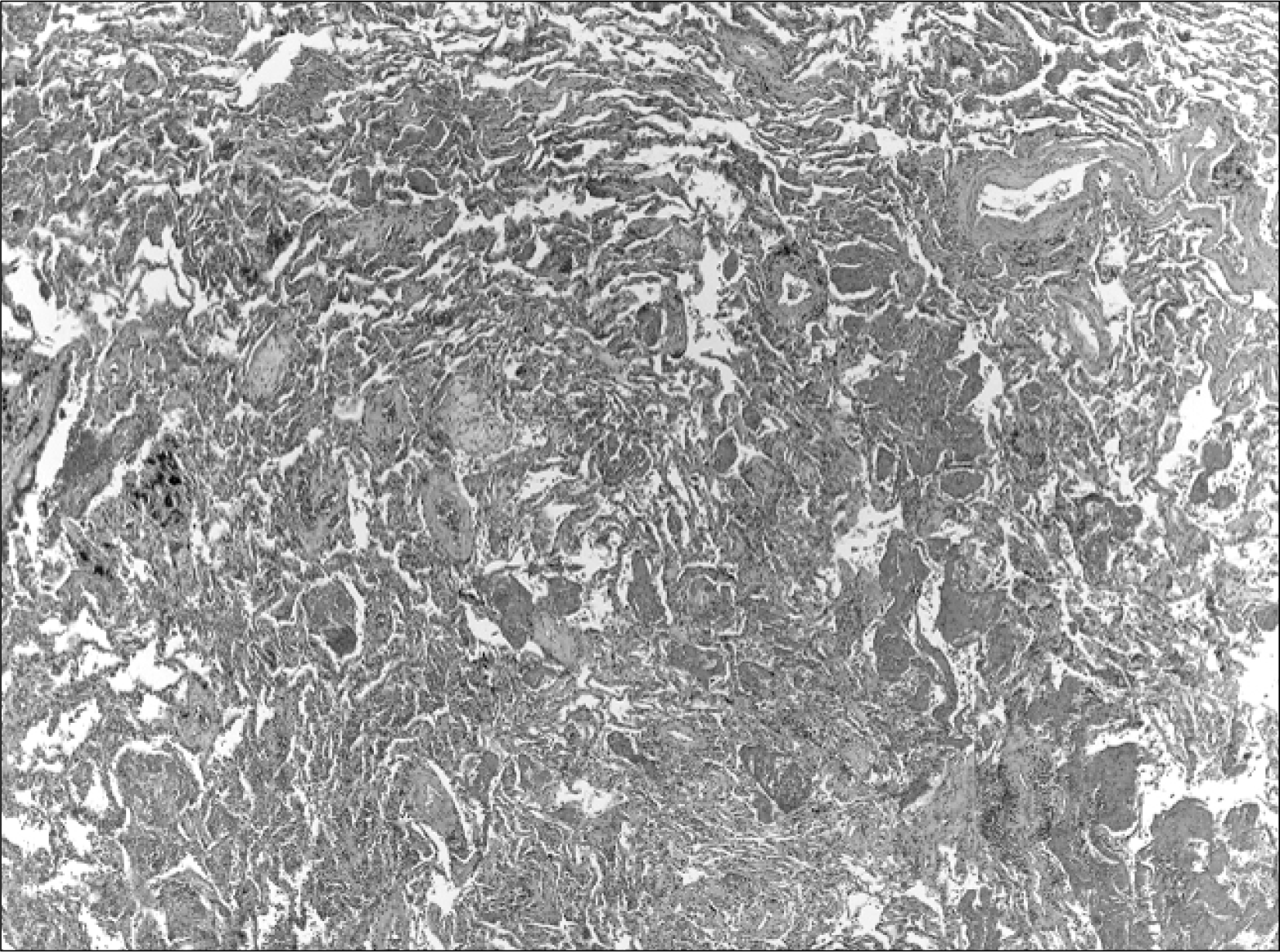
Leflunomide is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug that has been available in Korea since 2003. Leflunomide induced interstitial pneumonitis has been reported as an adverse effect in other countries but not in Korea. A 57-year-old woman was treated with leflunomide since she had been resistant to methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine. She developed high fever, dyspnea, and non-productive cough 3 months after the administration of leflunomide. She was diagnosed leflunomide-induced interstitial pneumonitis based on history, physical, laboratory, radiologic and pathologic findings. The patient was treated by prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day with cholestyramine 24 g/day, resulting in dramatic improvement. Here we report a case of leflunomide induced pneumonitis treated successfully with high dose steroid.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). 박용범: 이수곤. Leflunomide: 새로운항류마티스약제. 대한류마티스학회지. 2000. 4:323–32.
2). Cohen S., Cannon GW., Schiff M., Weaver A., Fox R., 이sen N, et al. Two-year, blinded, randomized, controlled trial of treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide compared with methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. 44:1984–92.

3). Li EK., Tam LS., Tomlinson B. Leflunomide in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther. 2004. 26:447–59.

4). Ito S., Sumida T. Interstitial lung disease associated with leflunomide. Intern Med. 2004. 43:1103–4.

5). Takeishi M., Akiyama Y., Akiba H., Adachi D., Hirano M., Mimura T. Leflunomide induced acute interstitial pneumonia. J Rheumatol. 2005. 32:1160–3.
6). Vallbracht II., Popper HH., Rieber J., Nowak F., Gallenberger S., Piper B, et al. Lethal pneumonitis under leflunomide therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. 44:1580–1.

7). Hirabayashi Y., Shimizu H., Kobayashi N., Kudo K. Leflunomide-induced pneumonitis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med. 2006. 45:689–91.

8). Savage RL., Highton J., Boyd IW., Chapman P. Pneumonitis associated with leflunomide: a profile of New Zealand and Australian reports. Intern Med J. 2006. 36:162–9.

9). Kremer JM., Genovese MC., Cannon GW., Caldwell JR., Cush JJ., Furst DE, et al. Concomitant leflunomide therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite stable doses of methotrexate. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2002. 137:726–33.
10). Combe B. Leflunomide combined with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or biologics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2006. 73:587–90.
11). Kim DS. Interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: recent advances. Curr ᄋpin Pulm Med. 2006. 12:346–53.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download