Abstract
Objecti
To investigate the effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α on the production of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), which might have important roles in the immune mediated inflammatory response of Behcet's syndrome.
Methods
Sixty two patients with Behcet's syndrome and thirty healthy controls were included in this study. The concentrations of TNF-α in sera were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from eleven patients with Behcet's syndrome were cultured for 48 hours with various concentration of TNF-α. The concentrations of MIF in sera and culture supernatants were determined by ELISA.
Results
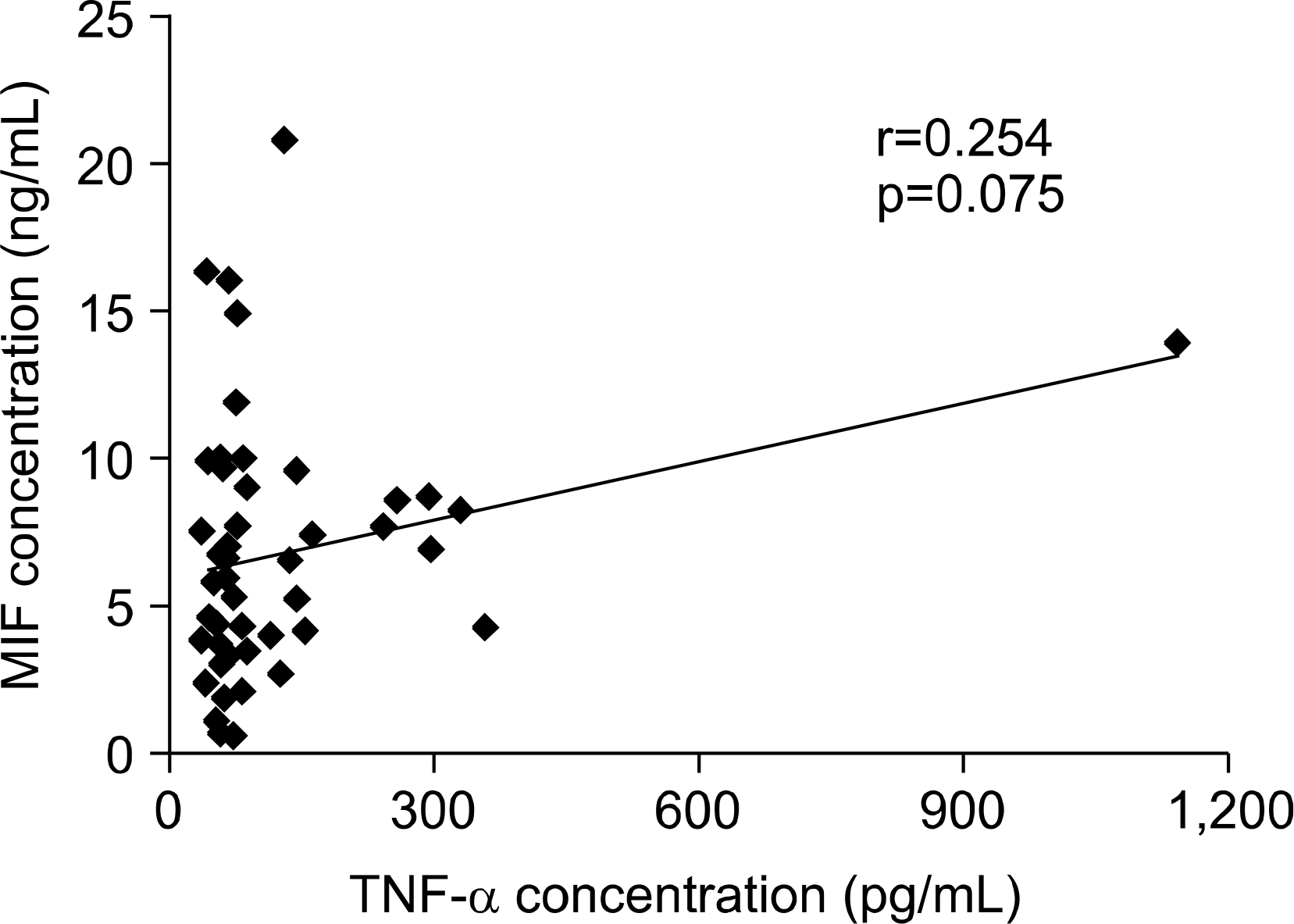
Serum levels of TNF-α were significantly higher in patients with Behcet's syndrome than in healthy controls. TNF-α dose-dependently increased MIF production from PBMCs in patients with Behcet's syndrome. Serum levels of TNF-α tended to correlate with serum levels of MIF, although did not reach statistical significance.
REFERENCES
1). Sakane T., Takeno M., Suzuki N., Inaba G. Behcet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1284–91.
2). Hirohata S., Kikuchi H. Behcet's disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003. 5:139–46.
3). Evereklioglu C., Er H., Turkoz Y., Cekmen M. Serum levels of TNF-alpha, sIL-2R, IL-6, and IL-8 are increased and associated with elevated lipid peroxidation in patients with Behcet's disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2002. 11:87–93.
4). Akdeniz N., Esrefoglu M., Keles MS., Karakuzu A., Atasoy M. Serum interleukin-2, interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and nitric oxide levels in patients with Behcet's disease. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2004. 33:596–9.
5). Katsantonis J., Adler Y., Orfanos CE., Zouboulis CC. Adamantiades-Behcet's disease: serum IL-8 is a more reliable marker for disease activity than C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Dermatology. 2000. 201:37–9.
6). Oztas MO., Onder M., Gurer MA., Bukan N., Sancak B. Serum interleukin 18 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha levels are increased in Behcet's disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005. 30:61–3.

7). Cekmen M., Evereklioglu C., Er H., Inaloz HS., Doganay S., Turkoz Y, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor levels are increased and associated with disease activity in patients with Behcet's syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2003. 42:870–5.
8). Erdem F., Gundogdu M., Kiki I., Ali Sari R., Kiziltunc A. Vascular endothelial and basic fibroblast growth factor serum levels in patients with Behcet's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2005. 25:599–603.
9). Bozoglu E., Dinc A., Erdem H., Pay S., Simsek I., Kocar IH. Vascular endothelial growth factor and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in Behcet's patients with venous thrombosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005. 23((4 Suppl 38):):S42–8.
10). 홍지현: 김현숙: 김해림: 박미경: 윤종현: 이상헌등. 베체트증후군환자에서혈관내피성장인자(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor, VEGF)의상승. 대한류마티스학회지. 2005. 12:189–96.
11). Ozer HT., Erken E., Gunesacar R., Kara ᄋ. Serum RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MCP-1 levels in Behcet's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2005. 25:487–8.
12). Kotake S., Kitaichi N., ᄋhno S. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in uveitis. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2002. 42:99–103.

13). 김성동: 김상현: 김해림: 박미경: 윤종현: 김완욱등. 베체트병환자에서혈청대식세포유주억제인자(Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor, MIF)의상승. 대한류마티스학회지. 2004. 11:205–11.
14). Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet's disease. International Study Group for Behcet's Disease. Lancet. 1990. 335:1078–80.
15). Yurdakul S., Hamuryudan V., Yazici H. Behcet syndrome. Curr ᄋpin Rheumatol. 2004. 16:38–42.
16). Nathan CF., Remold HG., David JR. Characterization of a lymphocyte factor which alters macrophage functions. J Exp Med. 1973. 137:275–90.

17). Morand EF. New therapeutic target in inflammatory disease: macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Intern Med J. 2005. 35:419–26.

18). Morand EF., Leech M., Bernhagen J. MIF: a new cytokine link between rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006. 5:399–410.

19). Morand EF., Leech M., Weedon H., Metz C., Bucala R., Smith MD. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical correlations. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002. 41:558–62.

20). Morand EF., Bucala R., Leech M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: an emerging therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:291–9.

21). Anderson PJ. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: clinical implications of their different immunogenicity profiles. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 34:19–22.

22). Chatzantoni K., Mouzaki A. Anti-TNF-alpha antibody therapies in autoimmune diseases. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. 6:1707–14.
23). Sarwar H., McGrath H Jr., Espinoza LR. Successful treatment of long-standing neuro-Behcet's disease with infliximab. J Rheumatol. 2005. 32:181–3.
24). Giansanti F., Barbera ML., Virgili G., Pieri B., Emmi L., Menchini U. Infliximab for the treatment of posterior uveitis with retinal neovascularization in Behcet disease. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2004. 14:445–8.
25). Ju JH., Kwok SK., Seo SH., Yoon CH., Kim HY., Park SH. Successful treatment of life-threatening intestinal ulcer in Behcet's disease with infliximab: rapid healing of Behcet's ulcer with infliximab. Clin Rheumatol 2006 Oct 13.
Fig. 1.
Serum levels of TNF- ff in patients with Behcet's syndrome and healthy controls. Serum levels of TNF- ff were significantly higher in patients with Behcet's syndrome than in healthy controls. ∗p <0.01 versus healthy controls. Serum levels of TNF- ff were higher in patients with active Behcet's syndrome than in patients with inactive Behcet's syndrome, although statistically insignificant (p>0.05).
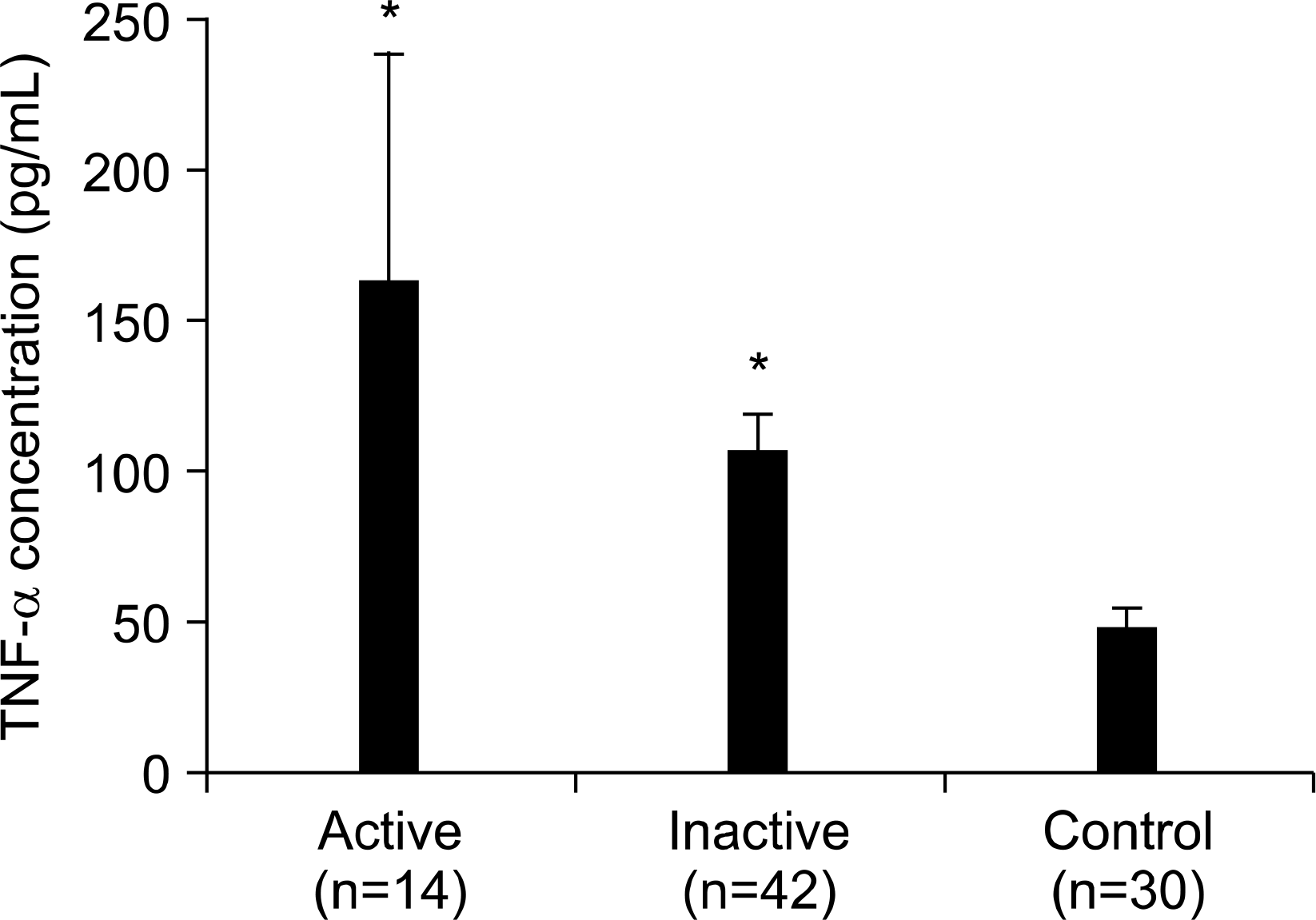
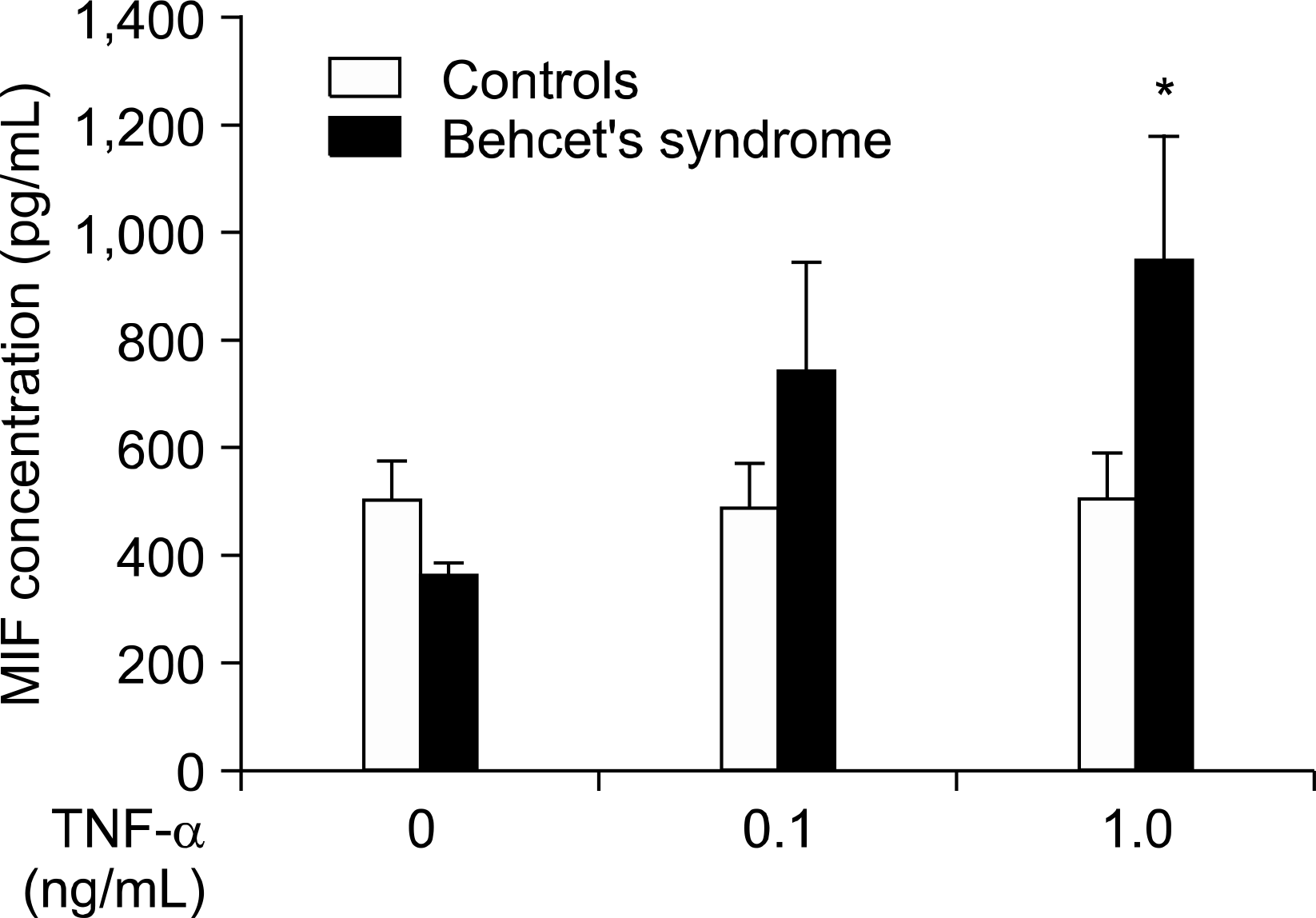
Fig. 2.
Effect of TNF- ff on macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in patients with Behcet's syndrome (n=4) and healthy controls (n=10). PBMCs were cultured in duplicate for 48 hours with medium alone or in the presence of TNF- σ (0.1 to 1.0 ng/mL). The concentrations of MIF in the culture supernatant were determined by ELISA. TNF- ff dose-dependently increased MIF production from PBMCs in patients with Behcet's syndrome not in healthy controls. ∗p<0.05 versus untreated cells.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download