Abstract
Combination treatment with pegylated interferon and ribavirin has been established as a standard therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Although interferon therapy is relatively safe, an important side effect is the induction of autoantibodies and autoimmune disease, especially autoimmune thyroid disease. Interferon associated autoimmune thyroid disease can consist of autoimmune hypothyroidism, Graves' disease, and destructive thyroiditis. Thyroid disease may lead to dose reduction or discontinuation of therapy.
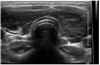
To the best of our knowledge, there are no case reports of pegylated interferon induced autoimmune hypothyroidism in Korea. We report here a case of a 26-year-old woman who developed hypothyroidism during antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C with pegylated interferon.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Baron S, Tyring SK, Fleischmann WR Jr, Coppenhaver DH, Niesel DW, Klimpel GR, Stanton GJ, Hughes TK. The interferons. Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. JAMA. 1991. 266:1375–1383.
2. Fattovich G, Giustina G, Favarato S, Ruol A. A survey of adverse events in 11,241 patients with chronic viral hepatitis treated with alfa interferon. J Hepatol. 1996. 24:38–47.
3. Prummel MF, Laurberg P. Interferon-alpha and autoimmune thyroid disease. Thyroid. 2003. 13:547–551.
4. Kozlowski A, Harris JM. Improvements in protein PEGylation: pegylated interferons for treatment of hepatitis C. J Control Release. 2001. 72:217–224.
5. Carella C, Mazziotti G, Morisco F, Rotondi M, Cioffi M, Tuccillo C, Sorvillo F, Caporaso N, Amato G. The addition of ribavirin to interferon-alpha therapy in patients with hepatitis C virus-related chronic hepatitis does not modify the thyroid autoantibody pattern but increases the risk of developing hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol. 2002. 146:743–749.
6. Jamil KM, Leedman PJ, Kontorinis N, Tarquinio L, Nazareth S, McInerney M, Connelly C, Flexman J, Burke V, Metcalf C, Cheng W. Interferon-induced thyroid dysfunction in chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 24:1017–1023.
7. Kang GH, Lee TH, Lim DM, Park KY, Kwak OS, Kwon MH, Kang MI. Peg-interferon induced autoimmune thyroiditis. Korean J Med. 2008. 74:90–93.
8. Kee KM, Lee CM, Wang JH, Tung HD, Changchien CS, Lu SN, Wang PW. Thyroid dysfunction in patients with chronic hepatitis C receiving a combined therapy of interferon and ribavirin: incidence, associated factors and prognosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 21:319–326.
9. Mandac JC, Chaudhry S, Sherman KE, Tomer Y. The clinical and physiological spectrum of interferon-alpha induced thyroiditis: toward a new classification. Hepatology. 2006. 43:661–672.
10. Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, Hannon WH, Gunter EW, Spencer CA, Braverman LE. Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 87:489–499.
11. Carella C, Mazziotti G, Morisco F, Manganella G, Rotondi M, Tuccillo C, Sorvillo F, Caporaso N, Amato G. Long-term outcome of interferon-alpha-induced thyroid autoimmunity and prognostic influence of thyroid autoantibody pattern at the end of treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001. 86:1925–1929.
12. Huang MJ, Tsai SL, Huang BY, Sheen IS, Yeh CT, Liaw YF. Prevalence and significance of thyroid autoantibodies in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: a prospective controlled study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1999. 50:503–509.
13. Deutsch M, Dourakis S, Manesis EK, Gioustozi A, Hess G, Horsch A, Hadziyannis S. Thyroid abnormalities in chronic viral hepatitis and their relationship to interferon alfa therapy. Hepatology. 1997. 26:206–210.
14. Dalgard O, Bjøro K, Hellum K, Myrvang B, Bjøro T, Haug E, Bell H. Thyroid dysfunction during treatment of chronic hepatitis C with interferon alpha: no association with either interferon dosage or efficacy of therapy. J Intern Med. 2002. 251:400–406.
15. Deutsch M, Koskinas J, Tzannos K, Vassilopoulos D, Mailis A, Tolis G, Hadziyannis S. Hashimoto encephalopathy with pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin. Ann Pharmacother. 2005. 39:1745–1748.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download