References
1. Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 282:1523–1529. 1999.

2. Shaw DI, Hall WL, Williams CM. Metabolic syndrome: what is it and what are the implications? Proc Nutr Soc. 64:349–357. 2005.

3. Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA. 295:1549–1555. 2006.

4. Kim SG, Choi DS. The present state of diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 51:791–799. 2008.

5. Young ME, Guthrie PH, Razeghi P, Leighton B, Abbasi S, Patil S, Youker KA, Taegtmeyer H. Impaired long-chain fatty acid oxidation and contractile dysfunction in the obese Zucker rat heart. Diabetes. 51:2587–2595. 2002.

6. Zhou YT, Grayburn P, Karim A, Shimabukuro M, Higa M, Baetens D, Orci L, Unger RH. Lipotoxic heart disease in obese rats: implications for human obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 97:1784–1789. 2000.

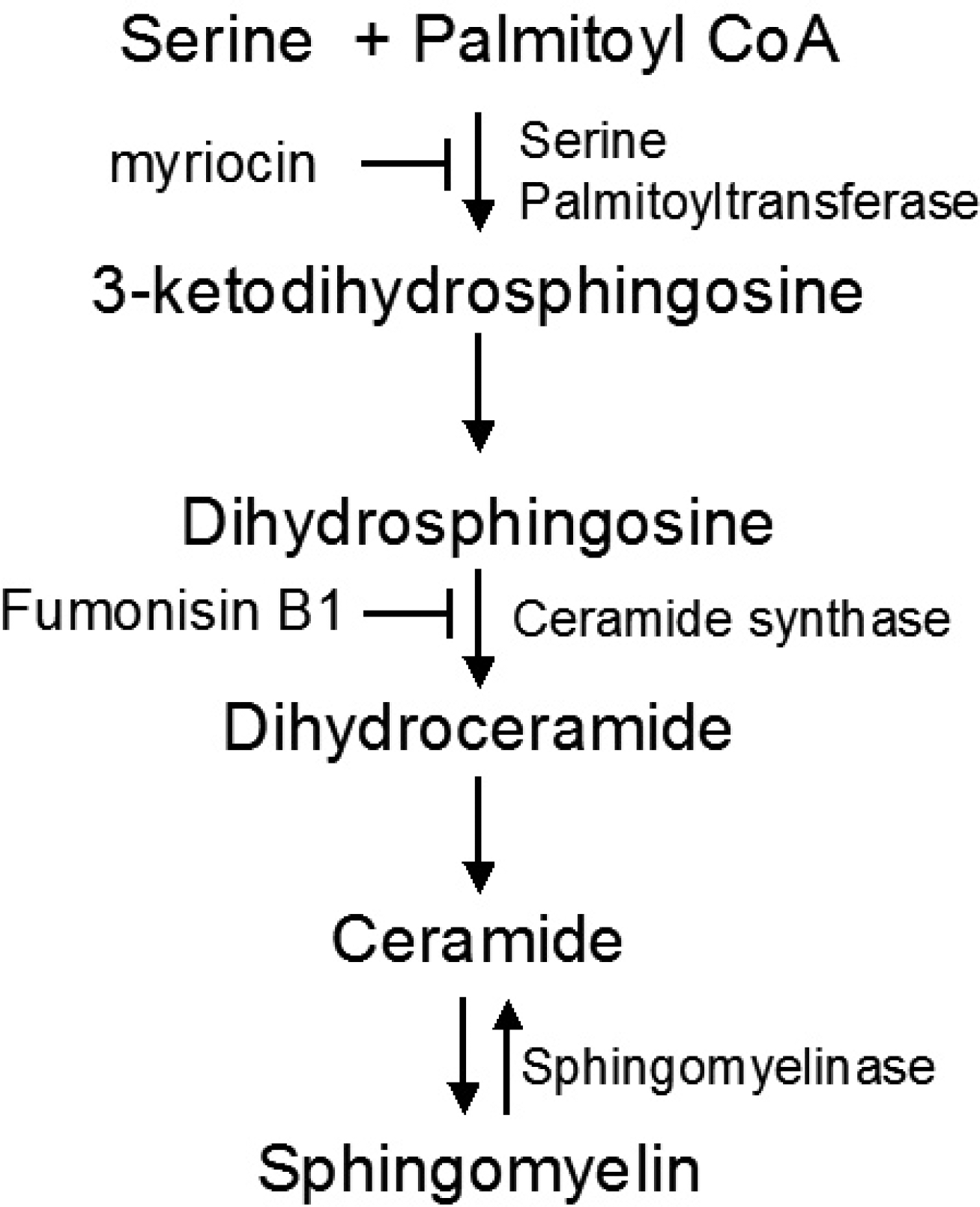
7. Merrill AH Jr. De novo sphingolipid biosynthesis: a necessary, but dangerous, pathway. J Biol Chem. 277:25843–25846. 2002.

8. Shimabukuro M, Higa M, Zhou YT, Wang MY, Newgard CB, Unger RH. Lipoapoptosis in beta-cells of obese prediabetic fa/fa rats. Role of serine palmitoyltransferase overexpression. J Biol Chem. 273:32487–32490. 1998.
10. Hanada K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1632:16–30. 2003.

11. Clarke CJ, Snook CF, Tani M, Matmati N, Marchesini N, Hannun YA. The extended family of neutral sphingomyelinases. Biochemistry. 45:11247–11256. 2006.

12. Pettus BJ, Chalfant CE, Hannun YA. Ceramide in apoptosis: an overview and current perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1585:114–125. 2002.

13. Spiegel S, Milstien S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:397–407. 2003.

14. Hui H, Dotta F, Di Mario U, Perfetti R. Role of caspases in the regulation of apoptotic pancreatic islet beta-cells death. J Cell Physiol. 200:177–200. 2004.

15. Buchanan TA. Pancreatic beta-cell loss and preservation in type 2 diabetes. Clin Ther. 25:B32–B46. 2003.

16. Shimizu H, Okajima F, Kimura T, Ohtani K, Tsuchiya T, Takahashi H, Kuwabara A, Tomura H, Sato K, Mori M. Sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates insulin secretion in HIT-T 15 cells and mouse islets. Endocr J. 47:261–269. 2000.

17. Holland WL, Brozinick JT, Wang LP, Hawkins ED, Sargent KM, Liu Y, Narra K, Hoehn KL, Knotts TA, Siesky A, Nelson DH, Karathanasis SK, Fontenot GK, Birnbaum MJ, Summers SA. Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 5:167–179. 2007.

18. Kelpe CL, Moore PC, Parazzoli SD, Wicksteed B, Rhodes CJ, Poitout V. Palmitate inhibition of insulin gene expression is mediated at the transcriptional level via ceramide synthesis. J Biol Chem. 278:30015–30021. 2003.

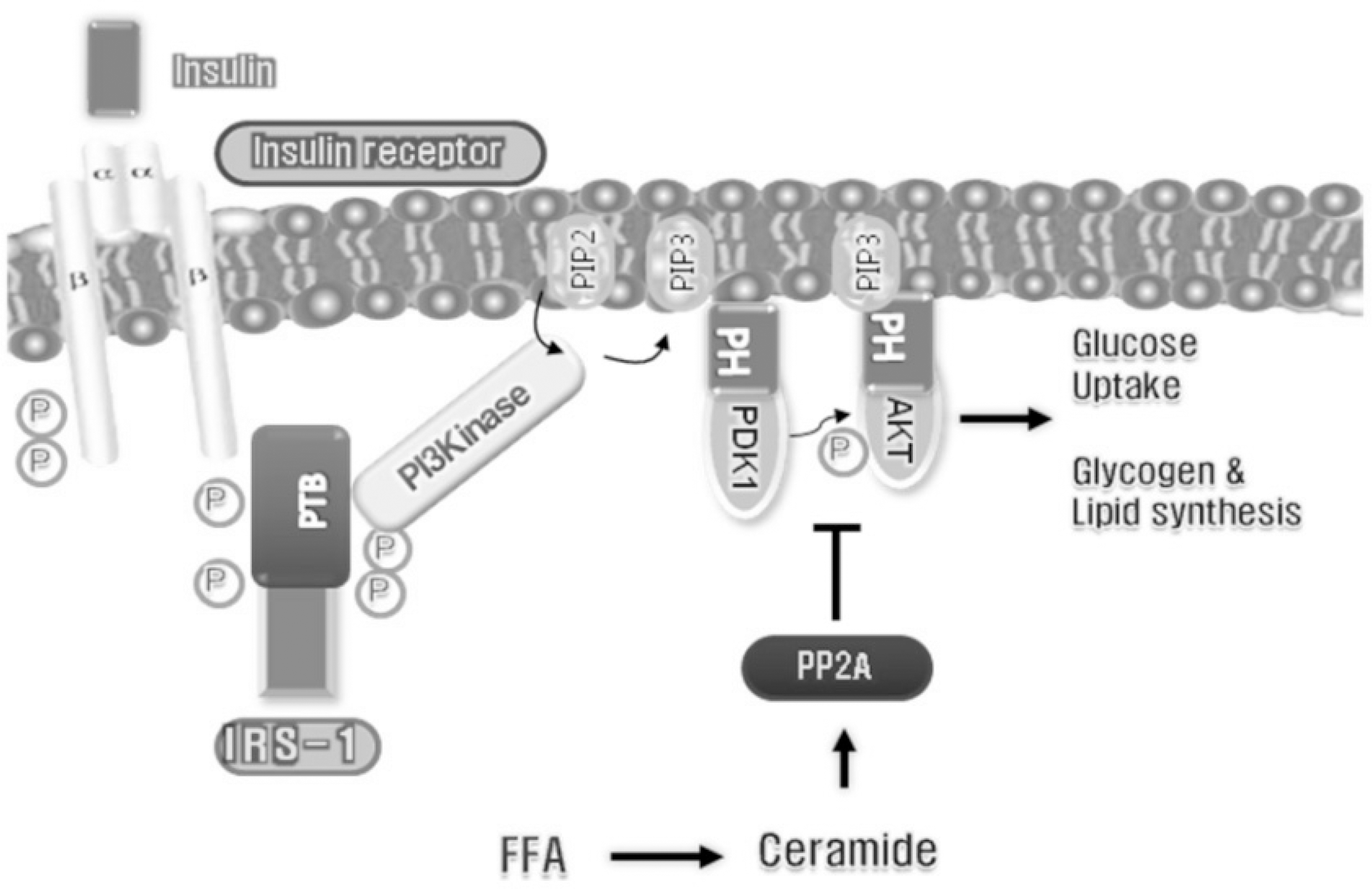
19. Keller SR, Lienhard GE. Insulin signalling: the role of insulin receptor substrate 1. Trends Cell Biol. 4:115–119. 1994.

20. Savage DB, Petersen KF, Shulman GI. Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Physiol Rev. 87:507–520. 2007.

21. Yamashita T, Hashiramoto A, Haluzik M, Mizukami H, Beck S, Norton A, Kono M, Tsuji S, Daniotti JL, Werth N, Sandhoff R, Sandhoff K, Proia RL. Enhanced insulin sensitivity in mice lacking ganglioside GM3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100:3445–3449. 2003.

22. Park TS, Hu Y, Noh HL, Drosatos K, Okajima K, Buchanan J, Tuinei J, Homma S, Jiang XC, Abel ED, Goldberg IJ. Ceramide is a cardiotoxin in lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. J Lipid Res. 49:2101–2112. 2008.

23. Dyntar D, Eppenberger-Eberhardt M, Maedler K, Pruschy M, Eppenberger HM, Spinas GA, Donath MY. Glucose and palmitic acid induce degeneration of myofibrils and modulate apoptosis in rat adult cardiomyocytes. Diabetes. 50:2105–2113. 2001.

24. Jiang XC, Paultre F, Pearson TA, Reed RG, Francis CK, Lin M, Berglund L, Tall AR. Plasma sphingomyelin level as a risk factor for coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:2614–2618. 2000.

25. Schissel SL, Tweedie-Hardman J, Rapp JH, Graham G, Williams KJ, Tabas I. Rabbit aorta and human atherosclerotic lesions hydrolyze the sphingomyelin of retained low-density lipoprotein. Proposed role for arterial-wall sphingomyelinase in subendothelial retention and aggregation of atherogenic lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 98:1455–1464. 1996.

26. Hoff HF, Morton RE. Lipoproteins containing apo B extracted from human aortas. Structure and function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 454:183–194. 1985.
27. Park TS, Panek RL, Mueller SB, Hanselman JC, Rosebury WS, Robertson AW, Kindt EK, Homan R, Karathanasis SK, Rekhter MD. Inhibition of sphingomyelin synthesis reduces atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Circulation. 110:3465–3471. 2004.

28. Hojjati MR, Li Z, Zhou H, Tang S, Huan C, Ooi E, Lu S, Jiang XC. Effect of myriocin on plasma sphingolipid metabolism and atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 280:10284–10289. 2005.

29. Holopainen JM, Lemmich J, Richter F, Mouritsen OG, Rapp G, Kinnunen PK. Dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/C16: 0-ceramide binary liposomes studied by differential scanning calorimetry and wide- and small-angle x-ray scattering. Biophys J. 78:2459–2469. 2000.
30. Holopainen JM, Lehtonen JY, Kinnunen PK. Lipid microdomains in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-ceramide liposomes. Chem Phys Lipids. 88:1–13. 1997.

31. AugéN. Nikolova-Karakashian M, Carpentier S, Parthasarathy S, Nègre-Salvayre A, Salvayre R, Merrill AH Jr, Merrill AH Jr, Levade T. Role of sphingosine 1-phosphate in the mitogenesis induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein in smooth muscle cells via activation of sphingomyelinase, ceramidase, and sphingosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 274:21533–21538. 1999.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download