Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to compare the effects of three interventions on pain, blood pressure, and pulse rate during infiltration anesthesia in patients about to undergo gamma knife surgeries.
Methods
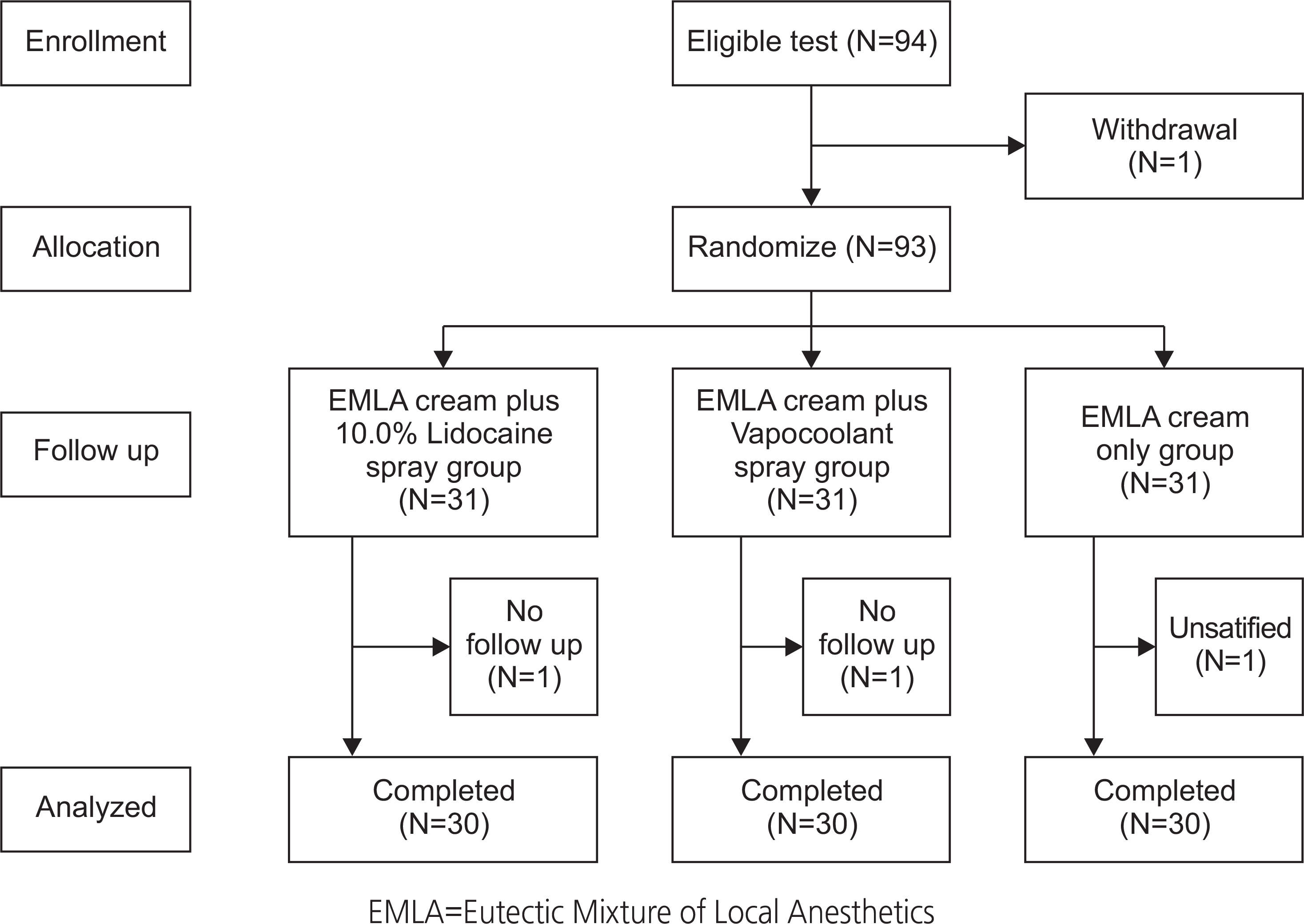
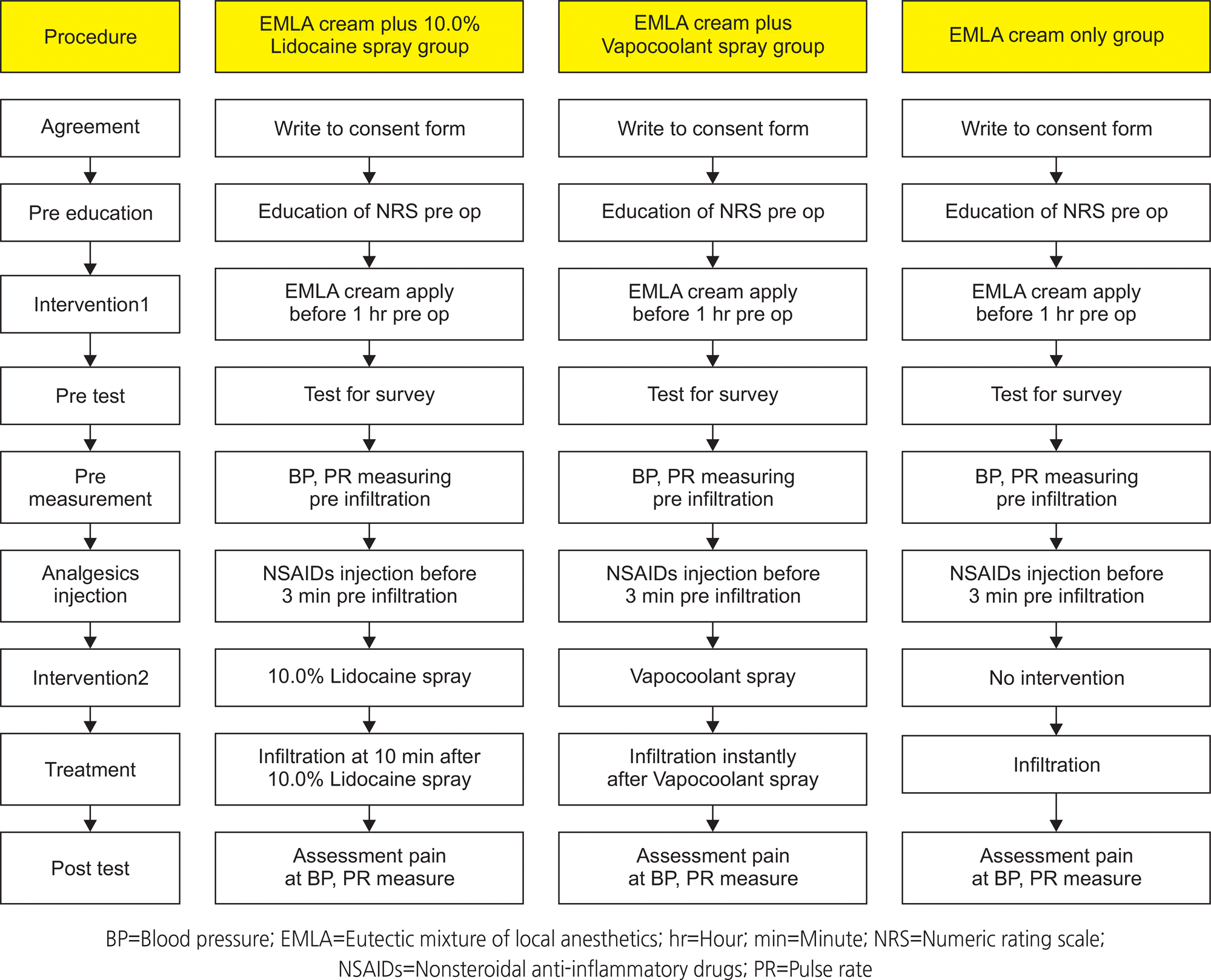
The three interventions employed in a university-affiliated Hospital in J City, South Korea were as follows: EMLA cream plus Vapocoolant spray (Vapocoolant, n=30), EMLA cream plus 10.0% Lidocaine spray (Lidocaine, n=30), and EMLA cream only (EMLA, n=30). The equivalent control-group pre test - post test study design was used. Pain was assessed subjectively using the numeric rating scale (NRS) and objectively using a Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) tester. NRS scores were assessed after infiltration anesthesia and the GSR was assessed during infiltration anesthesia. Blood pressure and pulse rate were assessed twice: before and after infiltration anesthesia. Data were collected between August 3, 2016 and March 24, 2017.
Results
NRS scores after infiltration anesthesia and the GSR during infiltration anesthesia were significantly lower in the Vapocoolant group than in the Lidocaine and EMLA groups (F=13.56, p<.001 and F=14.43, p<.001, respectively). The increase in systolic blood pressure (F=4.77, p=.011) and in pulse rates (F=4.78, p=.011) before and after infiltration anesthesia were significantly smaller in the Vapocoolant group than in the Lidocaine and EMLA groups; however, no significant differences were observed in diastolic blood pressures (F=1.51, p=.227).
Conclusion
EMLA cream plus Vapocoolant spray was the most effective intervention to relieve pain and to lower increase in systolic blood pressure and pulse rate caused by infiltration anesthesia for stereotactic frame fixation. Thus, application of Vapocoolant spray in addition to EMLA cream is highly recommended as a nursing intervention for patients undergoing gamma knife surgeries.
Go to : 
References
1. Gerosa M, Nicolato A, Foroni R. The role of gamma knife radiosurgery in the treatment of primary and metastatic brain tumors. Current Opinion in Oncology. 2003; 15(3):188–196. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001622-200305000-00002.

2. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. One out of every four was surgeried with Gamma Knife in 2016 [Internet]. Seoul: Health Insurances Review and Assessment Service;c2016. [cited 2015 Nov 26]. Available from:. http://opendata.hira.or.kr/op/opc/olapDiagBhvInfo.do.
3. Baek SY, Choi JY. Associated factors with pin-fixing & pin removal pain among patients undergoing gamma knife radiosurgery. Asian Oncology Nursing. 2012; 12(4):323–330. https://doi.org/10.5388/aon.2012.12.4.323.
4. Choi EK, Ro Y, Park SS, Park KB. The use of EMLA cream reduces the pain of skin puncture associated with caudal block in children. Korean Journal Anesthesiology. 2016; 69(2):149–154. https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2016.69.2.149.

5. Sohn KS, Lee HW, Choi SU, Lim HJ, Yoon SM, Chang SH. The effect of remifentanil on pain during local anesthetic infiltration in moderately sedated plastic surgery patients. Korean Journal of Anesthesiology. 2007; 53(3):318–324. https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2007.53.3.318.

6. Lee YH, Kim NC. The Comparison of effects of 2% lidocaine intradermal injection and 10% lidocaine spray for pain and anxiety relief on arteriovenous fistula puncture in hemodialysis patients. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2007; 13(2):169–177.
7. Hosseini Jahromi SA, Hosseini Valami SM, Hatamian S. Comparison between effect of lidocaine, morphine and ketamine spray on post-tonsillectomy pain in children. Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine. 2012; 2(1):17–21. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.4092.

8. Farion KJ, Splinter KL, Newhook K, Gaboury I, Splinter WM. The effect of vapocoolant spray on pain due to intravenous cannulation in children: A randomized controlled trial. Canadian Medical Association Journal. 2008; 179(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.070874.

9. Collado-Mesa F, Net JM, Arheart K, Klevos GA, Yepes MM. Application of a topical vapocoolant spray decreases pain at the site of initial intradermal anaesthetic injection during ultrasound-guided breast needle biopsy. Clinical Radiology. 2015; 70(9):938–942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2015.04.013.

10. Rüsch D, Koch T, Seel F, Eberhart L. Vapocoolant spray versus lidocaine infiltration for radial artery cannulation: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia. 2017; 31(1):77–83. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2016.06.008.

11. BIT Druginfo. Main homepage [Internet]. Seoul: BIT Drugin-fo;[cited 2018 Jan 25] Available from:. https://www.druginfo.co.kr/detail/product.aspx?pid=50355.
12. Han SS, Lee SC. Nursing and health statistical analysis. 2nd ed. Seoul: Fornurse;2011. p. 43.
13. Jensen MP, Karoly P, O’Riordan EF, Bland F Jr, Burns RS. The subjective experience of acute pain. An assessment of the utility of 10 indices. The Clinical Journal of Pain. 1989; 5(2):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002508-198906000-00005.

14. Shaver BA Jr, Brusilow SW, Cooke RE. Origin of the galvanic skin response. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 1962; 110(3):559–564. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-110-27579.

15. Kim JT, Shin DK. A study based on the standardization of the STAI for Korea. The New Medical Journal. 1978; 21(11):69–75.
16. Vitasari P, Wahab MNA, Herawan T, Othman A. Re-test of State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) among engineering students in Malaysia: Reliability and validity tests. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 15(2011):3843–3848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.04.383.

17. Hahn DW, Lee CH, Chon KK. Korean adaption of Spielberger’s STAI (K-STAI). Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 1996; 1(1):1–14.
18. Soriano D, Ajaj S, Chuong T, Deval B, Fauconnier A, Daraï E. Lidocaine spray and outpatient hysteroscopy: Randomized placebo controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2000; 96(5):661–664. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006250-200011000-00004.
19. World Health Organization. Cancer pain relief: With a guide to opioid availability. 2nd ed. Geneva: WHO;1996. p. 16–17.
20. Kim YS, Park HR. Effects of topical anesthetic cream on pain at venipuncture in children. Child Health Nursing Research. 2014; 20(3):142–148. https://doi.org/10.4094/chnr.2014.20.3.142.

21. Baba M, Watahiki Y, Matsunaga M, Takebe K. Sympathetic skin response in healthy man. Electromyography Clinical Neurophysiology. 1988; 28(5):277–283.
22. Maxwell C. Sensitivity and accuracy of the visual analogue scale: A psycho-physical classroom experiment. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 1978; 6(1):15–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01676.x.
23. Chesterton LS, Foster NE, Ross L. Skin temperature response to cryotherapy. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. 2002; 83(4):543–549. https://doi.org/10.1053/apmr.2002.30926.

24. Kose O, Saylan S, Ediz N, Yigit S. Effects of topical alkane vapocoolant spray on pain intensity prior to digital nerve block for ingrown nail surgery. Foot & Ankle Specialist. 2010; 3(2):73–75. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938640010363172.

25. Moon YE, Kim SH, Choi WH. Comparison of the effects of vapocoolant spray and topical anesthetic cream on pain during needle electromyography in the medial gastrocnemius. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2013; 94(5):919–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2012.12.008.

26. Waterhouse MR, Liu DR, Wang VJ. Cryotherapeutic topical analgesics for pediatric intravenous catheter placement: Ice versus vapocoolant spray. Pediatric Emergency Care. 2013; 29(1):8–12. https://doi.org/10.1097/PEC.0b013e31827b214b.
27. Choi SH, Baek KH, Lee JY, Lim HB, Kim HJ, Kim YS, et al. The effect of warm and ice application for pain control caused by arteriovenous fistula needling under hemodialysis. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2006; 12(1):179–189.
28. Choi EK, Jung JM, Sin JB. Pain reducing effect of vapocoolant spray during injection and heel stick procedure in neonates. Korean Journal of Pediatrics. 2008; 51(5):481–486. https://doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2008.51.5.481.
29. Mace SE. Prospective, randomized, double-blind controlled trial comparing vapocoolant spray vs spray in adults undergoing venipuncture. The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2016; 34(5):798–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2016.01.002.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Homogeneity Test for Characteristics between Groups (N=90)
Table 2.
Test of Differences about Pain Response after Infiltration Anesthesia according to Pain Relieving Intervention (N=90)
Table 3.
Test of Differences about Change of Physiological Response before and after Experimental Intervention (N=90)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download