Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to develop and measure the effect of a movie-based-nursing intervention program designed to enhance motivation for rehabilitation and reduce depression levels in stroke patients.
Methods
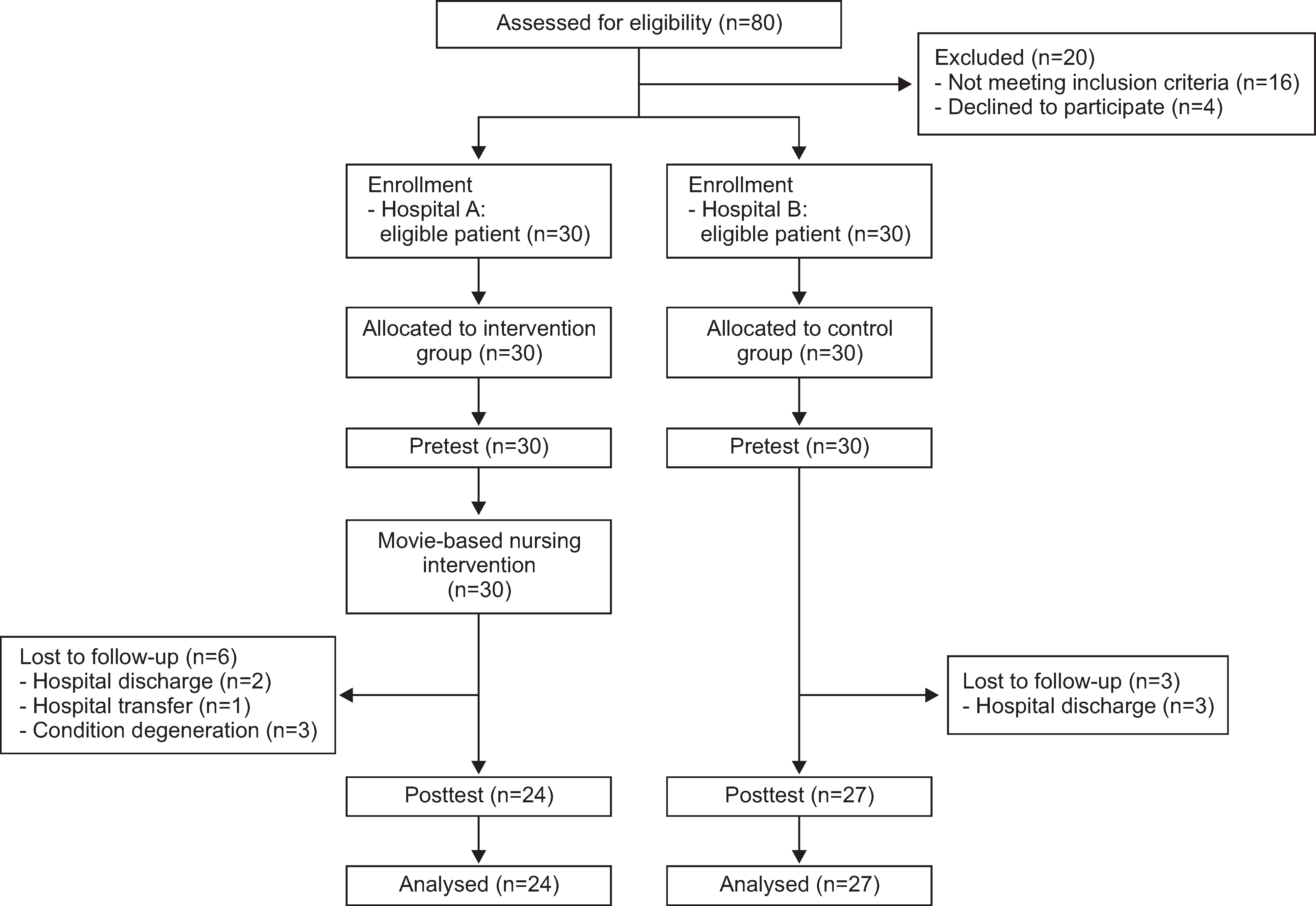
The study used a quasi-experimental, nonequivalent control group and a pretest-posttest design. The 60 research subjects were assigned to the experimental (n=30) or control group (n=30). The movie-based nursing intervention program was provided for the experimental group during 60-minute sessions held once per week for 10 weeks. The program consisted of patient education to strengthen motivation for rehabilitation and reduce depression, watching movies to identify role models, and group discussion to facilitate therapeutic interaction.
Results
After 10 weeks of participation in the movie-based nursing intervention program, the experimental group's rehabilitation motivation score was significantly higher, F=1161.54 (within groups df=49, between groups df=1), p<.001, relative to that observed in the control group. In addition, the experimental group's depression score was significantly lower relative to that observed in the control group, F=258.97 (within groups df=49, between groups df=1), p<.001.
References
1. Clinical Research Center for Stroke. Clinical practice guidelines for stroke [Internet]. Seoul: Author;2015. [cited 2016 July 12]. Available from:. http://stroke-crc.or.kr/뇌졸중_요약_영문%20150224.pdf.
2. Égi C, Horv th J, Hahn K, Kalman B, Betlehem J, Nagy L. Improving outcomes achieved by a new stroke program in Hungary. Cerebrovascular Diseases Extra. 2015; 5(3):132–138. http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000441479.

3. Robinson RG, Spalletta G. Poststroke depression: A review. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 2010; 55(6):341–349. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/070674371005500602.

4. Son MK. Poststroke depression. Brain & Neurorehabilitation. 2015; 8(2):65–72. http://dx.doi.org/10.12786/bn.2015.8.2.65.

5. Park YS, Kweon SS. Factors affecting stroke patients' rehabilitation motivation. Korean Public Health Research. 2002; 28(1):21–30.
6. Zhang XF, Zou W, Yang Y. Effects of IL-6 and cortisol fluctuations in post-stroke depression. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. 2016; 36(5):732–735. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11596-016-1653-0.

7. Kwon EH. A study on the relation of senile patients’s family support and rehabilitation motive: Focused on implications to social welfare practice and policy in rehabilitation care. Journal of Korean Local Government & Administration Studies. 2005; 19(3):19–47.
8. Kim HS, Hwang YO, Yu JH, Jung JH, Woo HS, Jung HS. The correlation between depression, motivation for rehabilitation, activities of daily living, and quality of life in stroke patients. The Journal of Korean Society of Occupational Therapy. 2009; 17(3):41–53.
9. Han HS, Lim NY. On the test of the reliability and validity of the disabled’s motivation scale for rehabilitation. The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing. 2002; 5(2):124–133.
10. Yoon HS, Nam HJ, Park SY, Han JH, Jang SJ, Seong IS, et al. Posttraumatic stress symptoms, anxiety, and depression after stroke. Journal of Korea Academy Society of Home care Nursing. 2008; 15(1):5–13.
11. Kim MH. Factors influencing depression of the elderly with post stroke hemiplegia. Journal of the Korean Gerontological Society. 2006; 26(4):911–927.
12. Park EY, Shin IS, Kim JH. A meta-analysis of the variables related to depression in Korean patients with a stroke. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2012; 42(4):537–548. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.4.537.

13. Hong MS, Jo HS, Yom YH, Kim GM. The analysis of trends and contents of nursing intervention research for stroke patients in Korea. Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing. 2012; 19(1):109–121. http://dx.doi.org/10.7739/jkafn.2012.19.1.109.

14. Jeong SH, Suh MJ. The need for rehabilitation day care program service of stroke survivors. The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing. 1999; 2(1):29–44.
15. Shim YS. The theory & practice of cinematherapy. Seoul: Hakjisa Corp.;2011. p. 24–147.
16. Lee SE, Ko SH. The effects of cinema therapy on depression and self-esteem in people with schizophrenia. Journal of Digital Convergence. 2013; 11(10):585–592.
17. Sim CS, Park MH, Kim YM, Kim HG. The development of interactive cinema therapy program for old people’s depression: Reminiscence method. Studies in Humanities. 2011; 31:389–412.
18. Kim HG. Effects of a cinema therapy-based group reminiscence program on depression and ego integrity of nursing home elders. Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. 2014; 23(4):233–241. http://dx.doi.org/10.12934/jkpmhn.2014.23.4.233.

19. Dumtrache SD. The effects of a cinema-therapy group on diminishing anxiety in young people. Procedia - Social and Be- havioral Sciences. 2014; 124:717–721. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.03.342.

20. Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates;1988.
21. Kong HK, Lee H. Effect of empowerment program on rehabilitation motivation, depression, activities of daily living among the patients with stroke. Journal of Korean Academy of Adult Nursing. 2008; 20(3):406–417.
22. Chong YS, Lee YH. The effect of group counseling on depression and psychological well-geing of elderly stroke patients. Catholic Journal of Social Science. 2007; 23:57–75.
23. Jeon SH. The effect of rehabilitation motivation reinforcement nursing intervention for social re-adjustment of elderly people with hemiplegia living in the community [master’s thesis]. Seoul: Korea University;2013. p. 1–179.
24. Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, Lum O, Huang V, Adey M, et al. Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: A preliminary report. Journal of Psychiatric Research. 1982; 17(1):37–49. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-3956(82)90033-4.

25. Cho MJ, Bae JN, Suh GH, Hahm BJ, Kim JK, Lee DW, et al. Validation of geriatric depression scale, Korean version(GDS) in the assessment of DSM-III-R major depression. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1999; 38(1):48–63.
26. Yeo HN, Kim YK. Effects of a group rehabilitation exercise program for stroke patients on their depression and motivation of rehabilitation. Journal of Korean Clinical Nursing Research. 2012; 18(3):424–434. http://dx.doi.org/10.22650/JKCNR.2012.18.3.424.
27. Niemiec RM, Wedding D. Positive psychology at the movies: Using films to build virtues and character strengths. Baek SH, Choi HJ, Han YO, Jo D, translator. Gottingen, DE: Hogrefe & Huber Publishing;2008.
28. Park MG, Ha Y. Effectiv eness of a self-management program using goal setting based on a G-AP for patients after a stroke. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2014; 44(5):581–591. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.5.581.
Table 1.
Movie-Based Nursing Intervention Program for Stroke Patients
Table 2.
Homogeneity Test for General Characteristics between the Two Groups (N=51)
Table 3.
Homogeneity Test for Outcome Variables between the Two Groups (N=51)
| Variables | Exp.(n=24) | Cont.(n=27) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean±SD | Mean±SD | |||
| Rehabilitation motivation | 55.33±5.67 | 57.78±5.99 | -1.49 | .143 |
| Depression | 9.96±1.94 | 9.59±2.32 | 0.60 | .548 |
Table 4.
Changes in Rehabilitation Motivation and Depression with Implementation of the Movie-Based Nursing Intervention Program (N=51)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download