Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a relapse prevention program (RPP) and examine the effects of the RPP on insight, empowerment, and treatment adherence in patients with schizophrenia.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. Participants were 54 inpatients who had a diagnosis of schizophrenia (experimental group: 26, control group: 28). The study was carried out from February 7, 2012 to February 6, 2013. Over a 10-day period prior to discharge each participant in the experimental group received three one-hour sessions of RPP a one-to-one patient-nurse interaction. Data were collected using Assess Unawareness of Mental Disorder (SUMD), Empowerment Scale, and Insight and Treatment Attitude Questionnaire (ITAQ) and analyzed using PASW 18.0 with chi-square test, independent t-test, Mann-Whitney U test, and ANCOVA.
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Session & Contents of Relapse Prevention Program for Patients with Schizophrenia
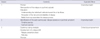
Table 2
Homogeneity Test of Socio-Demographic and Psychiatric Characteristics

Table 3
Homogeneity of Dependent Variables

Table 4
Comparison of Dependent Variables between Experimental and Control Groups

References
1. van Meijel B, Kruitwagen C, van der, Kahn RS, Grypdonck MH. An intervention study to prevent relapse in patients with schizophrenia. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2006; 38(1):42–49. DOI: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2006.00076.x.
2. Kim SH, Byeon YC, Son CK, Lee YH, Lee MK, Lee SH, et al. 2011 disabled survey report. Seoul: Ministry of Health & Welfare;Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2011. Report No.: Policy Report 2011-82.
3. Lieberman JA, Murray RM.
JS Kwon
. Comprehensive care of schizophrenia: A textbook of clinical management. London, UK: Martin Dunitz;2001. p. 37–58.
4. Almond S, Knapp M, Francois C, Toumi M, Brugha T. Relapse in schizophrenia: Costs, clinical outcomes and quality of life. Br J Psychiatry. 2004; 184(4):346–351. DOI: 10.1192/bjp.184.4.346.
5. van Meijel B, van der Gaag M, Kahn RS, Grypdonck MHF. Recognition of early warning signs in patients with schizophrenia: A review of the literature. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2004; 13(2):107–116. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-0979.2004.00314.x.
6. Abdel-Baki A, Ouellet-Plamondon C, Malla A. Pharmacotherapy challenges in patients with first-episode psychosis. J Affect Disord. 2012; 138:Suppl. S3–S14. DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2012.02.029.
7. Lee YH, Kim E. Factors on treatment compliance-illness behavior of schizophrenics under the long-term treatment. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1989; 28(2):292–305.
8. Kim BY, Lee CW, Park CW. The relationship among insight, psychopathology and drug compliance in the schizophrenic patient. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 1993; 32(3):373–380.
9. Day JC, Bentall RP, Roberts C, Randall F, Rogers A, Cattell D, et al. Attitudes toward antipsychotic medication: The impact of clinical variables and relationships with health professionals. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005; 62(7):717–724. DOI: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.7.717.
10. Goff DC, Hill M, Freudenreich O. Strategies for improving treatment adherence in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010; 71:Suppl 2. 20–26. DOI: 10.4088/JCP.9096su1cc.04.
11. Birchwood M, Spencer E, McGovern D. Schizophrenia: Early warning signs. Adv Psychiatr Treat. 2000; 6(2):93–101. DOI: 10.1192/apt.6.2.93.
12. Agius M, Oakham H, Biocina SM, Murphy S. The use of card sort exercises in the prevention of relapse in serious mental illness. Psychiatr Danub. 2006; 18(1-2):61–73.
13. Sutton DL. Relapse signatures and insight: Implications for CPNs. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2004; 11(5):569–574. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2850.2004.00762.x.
14. Smith J. Early warning signs: A self management training manual for individuals with psychosis. Worcester, UK: Worcester Community and Mental Health Trust;2003. p. 1–24.
15. Lee EO, Lim NY, Park HA, Lee IS, Kim JI, Bae J, et al. Nursing research and statistics. Paju: Soomoonsa;2009. p. 768.
16. Lincoln TM, Wilhelm K, Nestoriuc Y. Effectiveness of psychoeducation for relapse, symptoms, knowledge, adherence and functioning in psychotic disorders: A meta-analysis. Schizophr Res. 2007; 96(1-3):232–245. DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2007.07.022.
17. Amador XF, Flaum M, Andreasen NC, Strauss DH, Yale SA, Clark SC, et al. Awareness of illness in schizophrenia and schizoaffective and mood disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994; 51(10):826–836. DOI: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950100074007.
18. Song JY, Kim KT, Lee SK, Kim YH, Noh JH, Kim JW, et al. Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the scale to assessment unawareness of mental disorder (SUMD-K). J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2006; 45(4):307–315.
19. Rogers ES, Chamberlin J, Ellison ML, Crean T. A consumer-constructed scale to measure empowerment among users of mental health services. Psychiatr Serv. 1997; 48(8):1042–1047. DOI: 10.1176/ps.48.8.1042.
20. Lim JG. A study on the effect of social support on mental health disorder's empowerment: Compared with residential type [master's thesis]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;1999. 1–76.
21. McEvoy JP, Apperson LJ, Appelbaum PS, Ortlip P, Brecosky J, Hammill K, et al. Insight in schizophrenia. Its relationship to acute psychopathology. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1989; 177(1):43–47. DOI: 10.1097/00005053-198901000-00007.
22. van Meijel B, van der Gaag M, Kahn RS, Grypdonck MHF. The practice of early recognition and early intervention to prevent psychotic relapse in patients with schizophrenia: An exploratory study. Part 1. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2002; 9(3):347–355. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2850.2002.00500.x.
23. Fallon P. The role of intrusive and other recent life events on symptomatology in relapses of schizophrenia: A community nursing investigation. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2009; 16(8):685–693. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2850.2009.01451.x.
24. Choi CS, Chae JH, Woo DW, Choi YH, Hahm W, Lee KH, et al. Effects of brief symptom management module on inpatients with chronic schizophrenia: A preliminary study. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2001; 40(1):72–80.
25. Kim JE, Moon JJ, Kim MH, Kim WJ, Park MK, Song TH, et al. Effects of psychoeducation program on insight and treatment attitudes in patients with schizophrenia, schizophreniform disorder, and schizoaffective disorder. Korean J Psychopharmacol. 2010; 21(2):87–94.
26. Ko KH, Yang SH, Kim YA, Kwon MS, Bang SH, Lee JM, et al. The effects of an empowerment program for chronic schizophrenic patients on their empowerment and internalized stigma. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2008; 17(4):491–499.
27. Fishbein M, Ajzen I. Belief, attitude, intention, and behavior: An introduction to theory and research. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley;1975. p. 12–13.
28. Seo YM. Meta-analysis of psycho-social rehabilitation programs about schizophrenia patients [master's thesis]. Busan: Kyungsung University;2002. 1–90.
29. Chae JH. History and problems of concept of positive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Schizophr Clin. 2000; 2(1):53–63.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download