Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of pelvic floor muscle exercise using electric stimulation and biofeedback on maximum pressure of vaginal contraction, vaginal contraction duration and sexual function in women who have had vaginal rejuvenation.
Methods
The research design was a non-equivalent control group non-synchronized design study. Participants in this study were women who had vaginal rejuvenation at C obstetrics and gynecology hospital. The 15 participants in the experimental group were given pelvic floor muscle exercise using electric stimulation and biofeedback and the 15 participants in the control group received self pelvic floor muscle exercise.
Results
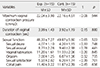
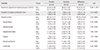
For maximum pressure of vaginal contraction, the experimental group showed a statistically significant increase compared to than the control group (t=5.96, p<.001). For vaginal contraction duration, the experimental group also showed a statistically significant increase compared to the control group (t=3.23, p=.003). For women's sexual function, the experimental group showed a significant increase when compared to the control group in total sexual function scores (t=3.41, p=.002).
Figures and Tables
References
1. Min KS. Update of female sexual dysfunction. Korean J Womens Health. 2004; 5(1):81–90.
2. Kim HY, Lee ES. Sexual dysfunction and related factors in married Korean women. J Korean Acad Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2010; 19(3):329–338.
3. Hong JY. The book for female written by male urologist. Seoul: BugeonBio;2002.
4. Won C. Gyneco-plastic surgery. Seoul: Gabon;2007.
5. Bae JY, Yun HJ, We JS, Choe JH, Song MJ, Cho HJ, et al. The effect of colpoperineoplasty on female sexual function. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2005; 48(6):1513–1520.
6. Park WK. Well-being. Seoul: Yuna Media;2004.
7. Helström L, Nilsson B. Impact of vaginal surgery on sexuality and quality of life in women with urinary incontinence or genital descensus. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2005; 84(1):79–84. DOI: 10.1111/j.0001-6349.2005.00668.x.
8. Kim KS. Sexual health care. Seoul: Koonja;2013.
9. So H, Cho I, Chae M, Min S. Effects of pelvic floor muscle exercise and electric stimulation therapy for stress urinary incontinence among middle-aged women. J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2011; 15(2):216–229.
10. Bae YK, Lee DH, Park SC, Jin SH, Koh MW, Lee TH. The efficacy of biofeedback and electrical stimulation by kontinence HMT2000 in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence patients. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2003; 20(1):36–44.
11. Kim TH. Comparative effects of pelvic floor muscle exercise training for stress urinary incontinence women [dissertation]. Daegu: Keimyung University;2004.
12. Min HJ, Byeon JS, Myung SJ, Yang SK, Yoon IJ, Kwon OR, et al. Combined therapy with electrical stimulation and biofeedback for treating pelvic floor dyssynergia. Korean J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2006; 12(2):108–116.
13. Beji NK, Yalcin O, Erkan HA. The effect of pelvic floor training on sexual function of treated patients. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2003; 14(4):234–238. DOI: 10.1007/s00192-003-1071-2.
14. Lee YC, Yoon H, Park YY. The effect of functional electrical stimulation(FES) - Biofeedback on sexual activity and quality of life in female stress urinary incontinence. Korean J Urol. 2003; 44(10):999–1005.
15. Pardo JS, Solà VD, Ricci PA, Guiloff EF, Freundlich OK. Colpoperineoplasty in women with a sensation of a wide vagina. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2006; 85(9):1125–1127. DOI: 10.1080/00016340600622544.
16. Rosen R, Brown C, Heiman J, Leiblum S, Meston C, Shabsigh R, et al. The Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI): A multidimensional self-report instrument for the assessment of female sexual function. J Sex Marital Ther. 2000; 26(2):191–208. DOI: 10.1080/009262300278597.
17. Kim HY, So H, Park K, Jeong SJ, Lee JY, Ryu SB. Development of the Korean-version of female sexual function index (FSFI). Korean J Androl. 2002; 20(1):50–56.
18. Chae MJ. Effect of pelvic floor muscle exercise by electrical stimulation on pelvic floor muscle contraction and sexual function in married female [master's thesis]. Gwangju: Chonnam National University;2005.
19. Choi ES, Park CS, Lee IS, Oh JA. Effects of intensive pelvic floor muscle exercise on recovery of genitourinary system, sexual life and daily life after normal delivery. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2002; 8(3):412–423.
20. Jeong H. The effect of conservative therapy for urinary incontinence on the improvement of women's sexual dysfunction [dissertation]. Seongnam: Kyungwon University;2008.
21. Jeong NO. Effects of an incontinence prevention program on postpartum women. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2009; 15(3):177–185. DOI: 10.4069/kjwhn.2009.15.3.177.
22. Rivalta M, Sighinolfi MC, Micali S, De Stefani S, Bianchi G. Sexual function and quality of life in women with urinary incontinence treated by a complete pelvic floor rehabilitation program (biofeedback, functional electrical stimulation, pelvic floor muscles exercises, and vaginal cones). J Sex Med. 2010; 7(3):1200–1208. DOI: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01676.x.
23. Lúcio AC, D'Ancona CA, Lopes MH, Perissinotto MC, Damasceno BP. The effect of pelvic floor muscle training alone or in combination with electrostimulation in the treatment of sexual dysfunction in women with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2014; 20(13):1761–1768. DOI: 10.1177/1352458514531520.
24. Bø K, Talseth T, Vinsnes A. Randomized controlled trial on the effect of pelvic floor muscle training on quality of life and sexual problems in genuine stress incontinent women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2000; 79(7):598–603.
25. Iglesia CB, Yurteri-Kaplan L, Alinsod R. Female genital cosmetic surgery: A review of techniques and outcomes. Int Urogynecol J. 2013; 24(12):1997–2009. DOI: 10.1007/s00192-013-2117-8.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download