Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop visions of nursing service, nursing strategies and key performance indicators (KPIs) for an intensive care unit (ICU) based on a Balanced Scorecard (BSC).
Methods
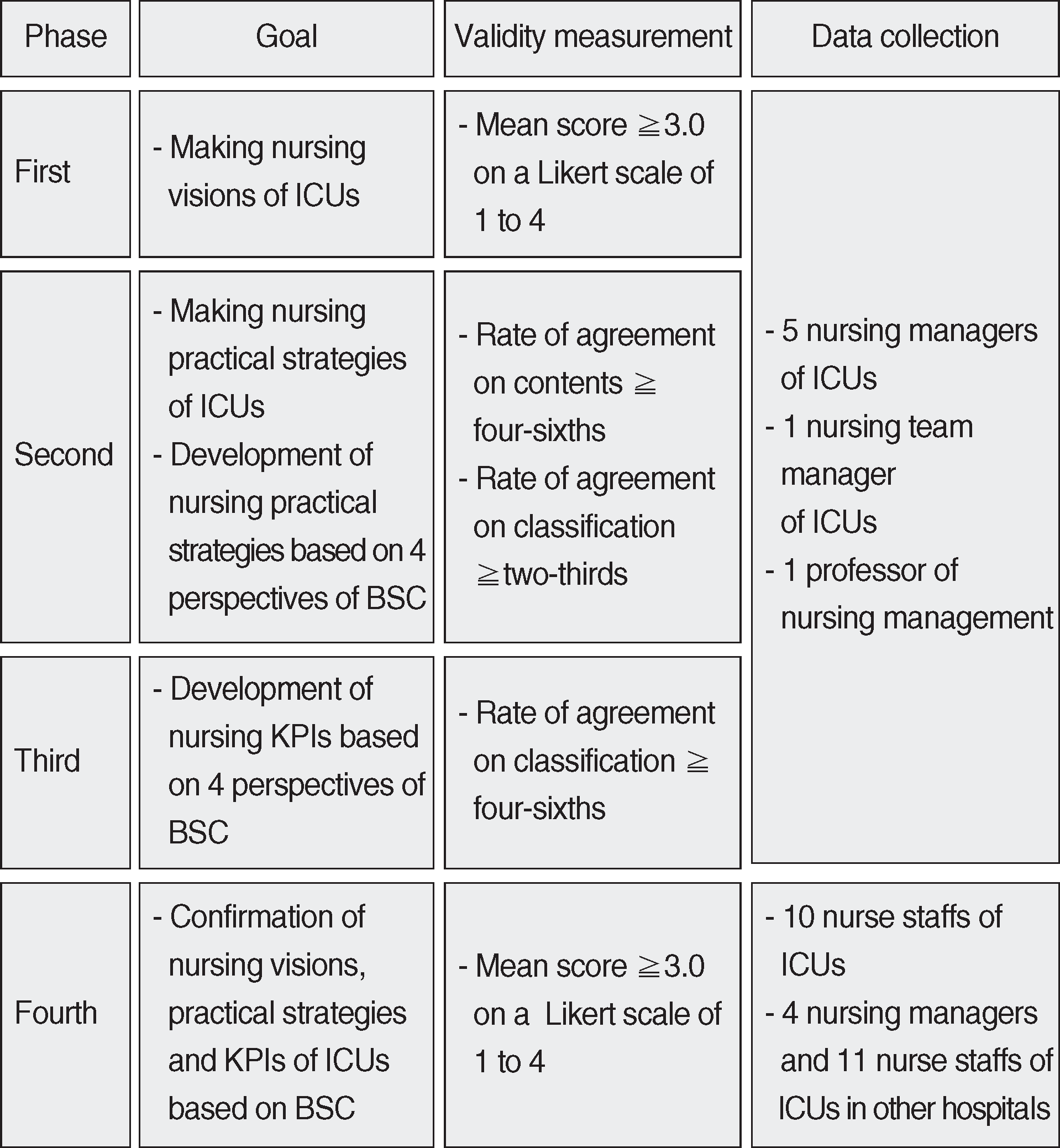
This study was undertaken by using methodological research. The development process consisted of four phases; the first phase was to develop the vision of nursing in ICUs. The second phase was to develop strategies according to 4 perspectives of a BSC. The third phase was to develop KPIs according to the 4 perspectives of BSC and the final phase was to combine the nursing visions, strategies and KPIs of ICUs.
Results
Two main visions of nursing service for ICUs were established. These were ‘realization of harmonized professional nursing with human respect’ and ‘recovery of health through specialized nursing’ respectively. In order to reach the aim of developing nursing visions, thirteen practical strategies and nineteen KPIs were developed by four perspectives of the BSC.
Go to : 
References
American Association of Critical Care Nurses. 2005. AACN standards for establishing and sustaining healthy work environments: A journey to excellence. American Journal of Critical Care. 14:187–197.
Bak W.S. 2002. The relationship between leadership, empowerment, and nursing performance. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Kyunghee University;Seoul:
Chern I. P.., Jeng H.J. 2000. Translating strategy into action. Accounting Research Monthly. 183:44–73.
Choi, B. H., & Korean BSC Research Association. 2006. BSC: Strategic performance management system. Seoul: Hangook Hak-sul Jungbo Co.
Chow C. W.., Ganulin D.., Teknica O.., Haddad K.., Williamson, J. 1998. The balanced scorecard: A potent tool for energizing and focusing health care organization management. Journal of Healthcare Management. 43:263–280.
Dixon, S. 2001. What will be the costs of a quality emergency service? Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 94:54–56.
Drucker P.., Eccles R. G.., Ness J. A.., Cucuzza T.., Simons R.., Dabila A., et al2007. Measuring corporate performance. Seoul: 21 Century Books.
Forgione D.A. 1997. Health care financial and quality measures: International call for a ‘‘balanced scorecard’’ approach. Journal of Health Care Finance. 24:55–58.
Griffith J. R.., King J.G. 2000. Championship management for health care organizations. Journal of Emergency Medicine Taiwan. 22:34–38.
Holt, T. 2001. Developing an activity-based management system for the army medical department. Journal of Health Care Finance. 27:41–46.
Hong Y. M.., Hwang K. J.., Kim M. J.., Park C.G. 2008. Balanced scorecard for performance measurement of a nursing organization in a Korean hospital. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 38:45–54.

Huang S. H.., Chen P. L.., Yang M. C.., Chang W. Y.., Lee H.J. 2004. Using a balanced scorecard to improve the performance of an emergency department. Nursing Economics. 22:140–146.
Jang B.H. 2000. A study on critical care nursing practice and development of standard for critical care nursing practice. Unpublished master’s thesis. Yonsei University;Seoul:
Jones M. L.., Filip S.J. 2000. Implementation and outcomes of a balanced scorecard model in women’s services in an academic health care institution. Quality Management in Health Care. 8:40–51.

Kang K.H. 2003. Development of performance measure indicators on hospital nursing units. Unpublished doctoral’s dissertation. Yonsei University;Seoul:
Kang S.S. 2005. A study on collaborating balanced scorecard with enterprise resource planning for hospital management performance evaluation. Unpublished doctoral’s dissertation. Dongguk University;Seoul:
Kaplan R. S.., Norton D.P. 1992. The balanced scorecard-measures that drive performance. Harvard Business Review. 70:71–79.
Kim H.J. 2006. A study on indicator development to evaluate hospital system: Based on balanced scorecard method. Unpublished master’s thesis. Yonsei University;Seoul:
Kim H. K.., Sung E.S. 2006. Strategic performance management BSC (Balanced scorecard). Seoul: Sigma Insight Com.
Kim Y.S. 2005. Development of performance measurement indicators for nursing on delivery units. Unpublished master’s thesis. Yonsei University;Seoul:
Ko Y. K.., Lee T. W.., Lim J.Y. 2007. Development of a performance measurement scale for hospital nurses. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 37:286–294.

Luttman R.J. 1998. Next generation quality, part 2: Balanced scorecards and organizational improvements. Topics in Health Information Management. 19:22–29.
Niven P.R. 2002. Balanced scorecard step by step: Maximizing and maintaining result. Seoul: Sigma Insight Com.
Oliveira, J. 2001. The balanced scorecard: An integrative approach to performance evaluation. Healthcare Financial Management. 55:42–45.
Pink G. H.., McKillop I.., Schraa E. G.., Preyra C.., Mongomery C.., Baker G.R. 2001. Creating a balanced scorecard for a hospital system. Journal of Health Care Finance. 27:1–20.
Sahney V.K. 1998. Balanced scorecard as a framework for driving performance in managed care organization. Managed Care Quarterly. 6:1–8.
Sung Y.., Song M. S.., Park, J. 2007. Estimation of nursing cost by a patient classification system(PCS) in ICU. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 37:373–380.
Voelker K. E.., Rakich J. S.., French G.R. 2001. The balanced scorecard in healthcare organization: A performance measurement and strategic planing methodology. Hospital Topics. 79.
Sung Y.., Song M. S.., Park, J. 2007. Estimation of nursing cost by a patient classification system(PCS) in ICU. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 37:373–380.
Voelker K. E.., Rakich J. S.., French G.R. 2001. The balanced scorecard in healthcare organization: A performance measurement and strategic planing methodology. Hospital Topics. 79:13–24.
Yang M. C.., Tung Y. C.2006. Using path analysis to examine causal relationships among balanced scorecard performance indicators for general hospitals: The case of a public hospital system in Taiwan. Health Care Management Review. 31:280–288.
Yoo J.I. 2001. Development of a performance measurement system for the perioperative nursing using the balanced scorecard (BSC). Unpublished maser’s thesis. Yonsei University;Seoul:
Yang M. C.., Tung Y.C. 2006. Using path analysis to examine causal relationships among balanced scorecard performance indicators for general hospitals: The case of a public hospital system in Taiwan. Health Care Management Review. 31:280–288.
Yoo J.I. 2001. Development of a performance measurement system for the perioperative nursing using the balanced scorecard (BSC). Unpublished maser’s thesis. Yonsei University;Seoul:
Sahney V.K. 1998. Balanced scorecard as a framework for driving performance in managed care organization. Managed Care Quarterly. 6:1–8.
Sung Y.., Song M. S.., Park, J. 2007. Estimation of nursing cost by a patient classification system(PCS) in ICU. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 37:373–380.
Voelker K. E.., Rakich J. S.., French G.R. 2001. The balanced scorecard in healthcare organization: A performance measurement and strategic planing methodology. Hospital Topics. 79:13–24.
Yang M. C.., Tung Y.C. 2006. Using path analysis to examine causal relationships among balanced scorecard performance indicators for general hospitals: The case of a public hospital system in Taiwan. Health Care Management Review. 31:280–288.
Yoo J.I. 2001. Development of a performance measurement system for the perioperative nursing using the balanced scorecard (BSC). Unpublished maser’s thesis. Yonsei University;Seoul:
Go to : 
Table 1.
Nursing Visions of ICUs
Table 2.
Nursing Practical Strategies of ICUs based on BSC
Table 3.
Nursing KPIs of ICUs based on BSC




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download