Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
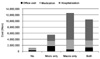 | Fig. 1Annual medical costs per patient according to the diabetic complication groups. The total medical costs increased 4.7-fold, 10.7-fold and 8.8-fold in patients with microvascular complications, macrovascular complications and both complications compared to diabetic patients without complications, respectively. Both, both microvascular and macrovascular complications; Macro only, macrovascular complications only; Micro only, microvascular complications only; Office visit, total office visit costs except medication costs. |
 | Fig. 2Proportion of sub-costs on total medical costs per patient according to the diabetic complication groups. Hospitalization costs largely increased and accounted for 65~70% of the total medical costs in patients with macrovascular complications. Micro-complication only, microvascular complications only; Macro-complication only, macrovascular complications only; Both complications, both microvascular and macrovascular complications; Micro only, microvascular complications only; Office visit, total office visit costs except medication costs. |
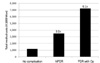 | Fig. 3Annual total medical costs per patient according to the stage of diabetic retinopathy. The total medical costs increased 3.0-fold and 6.1-fold in patients with NPDR and PDR who had been treated with operation compared to diabetic patients without complications. NPDR, non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy; PDR, proliferative diabetic retinopathy. |
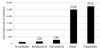 | Fig. 4Annual total medical costs per patient according to the stage of diabetic nephropathy. The total medical costs dramatically increased according to the stage of diabetic nephropathy. |
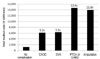 | Fig. 5Annual total medical costs per patient according to the diabetic macrovascular complications. The total medical costs increased 12.4-fold and 11.8-fold in patients with PTCA or CABG and leg amputation compared to diabetic patients without complications. CABG, coronary artery bypass graft; CAOD, coronary artery occlusive disease; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; PTCA, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. |
Table 3

Both, both microvascular and macrovascular complications; CI, confidence interval; Macro only, macrovascular complications only; Micro only, microvascular complications only; Office visit, total office visit costs except medication costs; SD, standard deviation. *P value, compared with no complication group by independent samples t-test.
Table 4

CABG, coronary artery bypass graft; CAOD, coronary artery occlusive disease; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; DM, diabetes mellitus; NPDR, non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy; Office visit, total office visit costs except medication costs; PDR, proliferative diabetic retinopathy; PTCA, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download