Abstract
Background
Insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS-2) is a key regulator of beta cell proliferation and apoptosis. This study was aimed to investigate effect of the glucolipotoxicity on apoptosis in INS-1 cell, and the effect of Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, on IRS-2 expression in the glucolipotoxicity induced INS-1 cell. The goal was to discover the new action mechanism and function of Exendin-4 in beta cell apoptosis.
Method
INS-1 cells were cultured in glucolipotoxic condition for 2, 4 or 6 days and were categorized as G groups. Another group in which 50 nM Exendin-4 was added to INS-1 cells, cultured in glucolipotoxic condition, were named as Ex-4 groups. We investigated the expression of IRS-2 by RT-PCR, phosphorylated IRS-2 and phosphorylated Akt protein levels by western blot. We measured the apoptosis ratio of INS-1 cell in glucolipotoxic condition by TUNEL staining in both groups.
Result
IRS-2 expression of INS-1 cells decreased with correlation to the time of exposure to glucolipotoxic condition. pIRS-2 and pAkt protein levels decreased in the similar pattern in glucolipotoxicity group. However, this effect of glucolipotoxicity on INS-1 cell was inhibited by the Exendin-4 treatment. In the Ex-4 groups, IRS-2 expression, pIRS-2 and pAkt protein levels remained at the similar level to low glucose condition state. Also, apoptosis induced by glucolipotoxicity was suppressed by Exendin-4 treatment significantly.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Schematic of experimental design. A. Apoptosis measurement of isolated islet cell and INS-1 cell in glucolipotoxicity condition by AO/PI and TUNEL staining. B. Insulin gene expression of isolated islet cell in glucolipotoxicity condition. C. Confirmation of Exendin-4 concentration for INS-1 cell treatment using cAMP assay in three concentration group (Ex-4 0, 10, 100 nM). D. General scheme of INS-1 cell culture were seperated into four groups: low glucose condition, low glucose + 50 nM Exendin-4, Glucolipotoxic condition (GLTx.), GLTx + 50 nM Exendin-4. Insulin and IRS-2 gene expression was measured by RT-PCR and phosphorylated IRS-2 and Akt protein was measured by western blot. E. Apoptosis of INS-1 cell in GLTx group and GLTx + 50 nM Exendin-4 group were measured by TUNEL staining. |
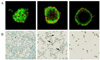 | Fig. 2Apoptosis of the isolated islet cell in glucolipotoxic condition. A. Apoptosis according to the exposure time (2, 4, 8 days) in AO/PI. B. Apoptosis of INS-1 cell in TUNEL staining (arrow: apoptotic cells). Few islet cells were survived in glucolipotoxic condition during 8 days in glucolipotoxic condition (×400). |
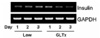 | Fig. 3Effect of the glucolipotoxic condition on insulin gene expression in isolated islet cells. Insulin was estimated by RT-PCR. GLTx: glucolipotoxicity. |
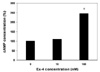 | Fig. 4Effect of exendin-4 concentration on Cyclic AMP levels in INS-1 cells. There was little difference in mean value of cAMP levels between 0 nM and 10 nM of Exendin-4 concentration. But, the mean value of cAMP levels in 100 nM of Exendin-4 was significantly higher than that of 10 nM of Exendin-4 concentration. *P < 0.05 vs. Ex-4 0 nM. |
 | Fig. 5IRS-2 and insulin gene expression on glucolipotoxic condition vs 50 nM exendin-4 treatment group in INS-1 cells. IRS-2 and insulin gene expression were increased in Exendin-4 treatment group compared with control and glucolipotoxic condition. |
 | Fig. 6Phosphorylated IRS-2 and pAkt protein levels in glucolipotoxic condition and effect of the exendin-4 on pIRS-2 and pAkt. A. pIRS-2 and pAkt were increased in Exendin-4 treatment group according to the exposure duration compared with the control group. B. Protective effect of the Exendin-4 treatment that inhibited pIRS-2 and pAkt protein reduction in glucolipotoxic condition. |
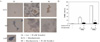 | Fig. 7The effect of Exendin-4 on apoptosis in glucolipotoxic condition. A INS-1 cell apoptosis was progressed in glucolipotoxic condition according to prolongation of exposure but, Exendin-4 treatment in the same condition inhibited apoptosis in TUNEL staining (×400). B. The apptosis rate was decreased in Exendin-4 treatment condition significantly (*P < 0.05, †P < 0.01). |
References
1. Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ, van Haeften TW. Type 2 diabetes. principles of pathogenesis and therapy. Lancet. 2005. 365:1333–1346.

2. Reaven G, Tsao PS. Insulin resistance and compensatory hyperinsulinemia: the key player between cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. 41:1044–1047.
3. Holman RR. Assessing the potential for α-glucosidase inhibitors in prediabetic states. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1998. 40:Suppl. S21–S25.

4. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998. 352:837–853.
5. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet. 1998. 352:854–865.
6. Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. β-Cell deficit and increased β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003. 52:102–110.

7. Wajchenberg BL. β-Cell Failure in Diabetes and Preservation by Clinical Treatment. Endocrine Reviews. 2007. 28:187–218.

9. Stoffers DA, Kieffer TJ, Hussain MA, Drucker DJ, Bonner-Weir S, Habener JF, Egan JM. Insulinotropic glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists stimulate expression of homeodomain protein IDX-1 and increase islet size in mouse pancreas. Diabetes. 2000. 49:741–748.

10. Rolin B, Larsen MO, Gotfredsen CF, Deacon CF, Carr RD, Wilken M, Knudsen LB. The long-acting GLP-1 derivative NN2211 ameliorates glycemia and increases beta-cell mass in diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 283:E745–E752.
11. Perfetti R, Zhou J, Doyle ME, Egan JM. Glucagon-like peptide-1 induces cell proliferation and pancreatic-duodenum homeobox-1 expression and increases endocrine cell mass in the pancreas of old, glucose-intolerant rats. Endocrinology. 2000. 141:4600–4605.

12. De Fronzo RA, Ratner RE, Han J, Kim D, Fineman MS, Baron AD. Effects of exenatide (exendin-4) on glycemic control and weight over 30 weeks in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1092–1100.

13. Giannoukakis N. Exenatide. Amylin/Eli Lilly. Curr Opin Investig Drus. 2003. 4:459–465.
14. Drucker DJ. Enhancing incretin action for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:929–940.

15. Jhala US, Canettieri G, Screaton RA, Kulkarni RN, Krajewski S, Reed J, Walker J, Lin X, White MF, Montminy M. cAMP promotes pancreatic-cell survival via CREB-mediated induction of IRS2. Genes Dev. 2003. 17:1575–1580.
16. Hennige AM, Burks DJ, Ozcan U, Kulkarni RN, Ye J, Park S, Schubert M, Fisher TL, Dow MA, Leshan R, Zakaria M, Mossa-Basha M, White MF. Upregulation of insulin receptor substrate-2 in pancreatic β cells prevents diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2003. 112:1521–1532.

18. Kjems LL, Holst JJ, Volund A, Madsbad S. The Influence of GLP-1 on Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion Effects on β-Cell Sensitivity in Type 2 and Nondiabetic Subjects. Diabetes. 2003. 52:380–386.

19. Holst JJ. Therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the actions of glucagon-like peptide-1. Diabetes Metab. Res Rev. 2002. 18:430–441.

20. Habener JF, Kemp DM. LeRoith D, Taylon SI, Olefsky JM, editors. Diabetes Mellitus. A Fundamental and Clinical Text. 2004. 3rd Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;99–113.
21. Chepurny OG, Hussain MA, Holz GG. Exendin-4 as a Stimulator of Rat Insulin I Gene Promoter Activity via bZIP/CRE Interactions Sensitive to Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase Inhibitor Ro 31-8220. Endocrinology. 2002. 143:2303–2313.

22. Holz GG. Epac: A New cAMP-Binding Protein in Support of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor-Mediated Signal Transduction in the Pancreatic β-Cell. Diabetes. 2004. 53:5–13.

23. Park SM, Dong X, Fisher TL, Dunn S, Omer AK, Weir G, White MF. Exendin-4 Uses Irs2 Signaling to Mediate Pancreatic Cell Growth and Function. J Biol Chem. 2006. 281:1159–1168.
24. Buteau J, Foisy S, Rhodes CJ, Carpenter L, Biden TJ, Prentki M. Protein Kinase C Activation Mediates Glucagon-Like Peptide-1-Induced Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation. Diabetes. 2001. 50:2237–2243.

25. Tuttle RL, Gill NS, Pugh W, Lee JP, Koeberlein B, Furth EE, Polonsky KS, Naji A, Birnbaum MJ. Regulation of pancreatic-cell growth and survival by the serine/threonine protein kinase Akt1/PKB. Nat Med. 2001. 7:1133–1137.
26. Buteau J, El Assaad W, Rhodes CJ, Rosenberg L, Joly E, Prentki M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 prevents beta cell glucolipotoxicity. Diabetologia. 2004. 47:806–815.

27. Lawlor MA, Alessi DR. PKB/Akt, a key mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J Cell Sci. 2001. 114:2903–2910.
28. Kitamura T, Nakae J, Kitamura Y, Kido Y, Biggs WH, Wright CV, White MF, Arden KC, Accili D. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 links insulin signaling to Pdx1 regulation of pancreatic β cell growth. J Clin Invest. 2002. 110:1839–1847.

29. Roche E, Maestre I, Martin F, Fuentes E, Casero J, Reig JA, Soria B. Nutrient toxicity in pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. J Physiol Biochem. 2000. 56:119–128.
30. Robertson RP. Chronic oxidative stress as a central mechanism for glucose toxicity in pancreatic islet beta cells in diabetes. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:42351–42354.

32. Jhala US, Canettieri G, Screaton RA, Kulkarni RN, Krajewski S, Reed J. cAMP promotes pancreatic beta-cell survival via CREB-mediated induction of IRS2. Genes Dev. 2003. 13:1575–1580.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download