Introduction
It has long been thought that health care workers (HCWs) are at an increased risk for
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection as a result of occupational exposure to patients infected with
M. tuberculosis1. Although some studies failed to show a higher estimated risk for tuberculosis (TB) among HCWs than among the corresponding local community, recent systematic analysis showed that the risk for TB among HCWs is consistently higher than the risk among the general population worldwide, irrespective of TB incidence in each country, and confirmed that TB is an occupational disease
2. HCWs working in TB-related departments (pulmonary department, medical intensive care unit, emergency room [ER], etc.), particularly nurses, have been reported to be at a higher risk of developing TB than other occupational subgroups of HCWs due to increased possibility of nosocomial transmission
3-
6.
In South Korea, an intermediate TB-burden country (92/100,000 general population), several studies have shown that the prevalence of latent TB infection (LTBI) among nurses was higher than in the general population
6,
7. In addition, one study reported that nurses working in TB-related departments had approximately five-fold higher risk for TB development than the general population
8, which indicates that LTBI remains a serious health problem among specific subgroups of HCWs in South Korea.
These findings indicate that various preventive strategies against LTBI in hospitals are still insufficient in South Korea. In order to implement stricter preventive measures, the exact prevalence of LTBI among HCWs, particularly nurses and doctors, and its risk factors should be obtained. To date, however, all studies on LTBI among HCWs have been performed at single center only
6-
9. In addition, no study has been conducted to address risk factors influencing LTBI prevalence in South Korea. Therefore, we evaluated LTBI prevalence among doctors and nurses at several tertiary care hospitals and analyzed its risk factors in South Korea.
Go to :

Materials and Methods
1. Study subjects
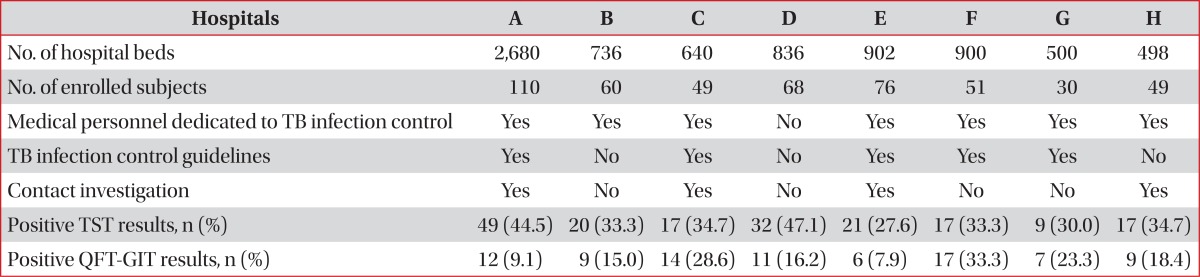
A cross sectional study to assess LTBI prevalence among doctors and nurses and its risk factors was conducted from February 2012 to May 2012 among those working at eight tertiary referral hospitals in South Korea. Doctors and nurses participated in this study voluntarily. The Institutional Review Board at each participating institution approved the clinical protocol. According to our study protocol, those HCWs who were being treated for active TB at the time of enrollment were excluded. All participants gave informed consent. They were interviewed using a standardized questionnaire. Information was obtained regarding age, gender, past history of any underlying disease, including TB, history of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination, and history of tuberculin skin test (TST). Additional information regarding risk factors of in-hospital TB infection was also gathered: duration of employment as a HCW, history of working in TB-related departments (pulmonary department, medical intensive care unit, and ER), current working department (TB-related vs. not TB-related), and degree of contact with TB-infected patients during work. The degree of contact with patients with TB infection was arbitrarily further divided into four categories and was self-selected by participants; none, mild (rare contact with TB patients), moderate (sometimes), severe (frequently).
After the completed questionnaire had been obtained, TST and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube (QFT-GIT; Cellestis Ltd., Carnegie, VIC, Australia) assay were performed at the same time and simple chest postero-anterior and left lateral radiograph (chest X-ray) were taken. Additionally, information regarding infection control measures at each hospital was obtained, specifically; 1) whether each institution had medical personnel dedicated to in-hospital TB infection control; 2) the presence or absence of its own guidelines for preventing in-hospital TB transmission; and 3) whether they conducted close contact investigation of HCWs.
2. Tuberculin skin test
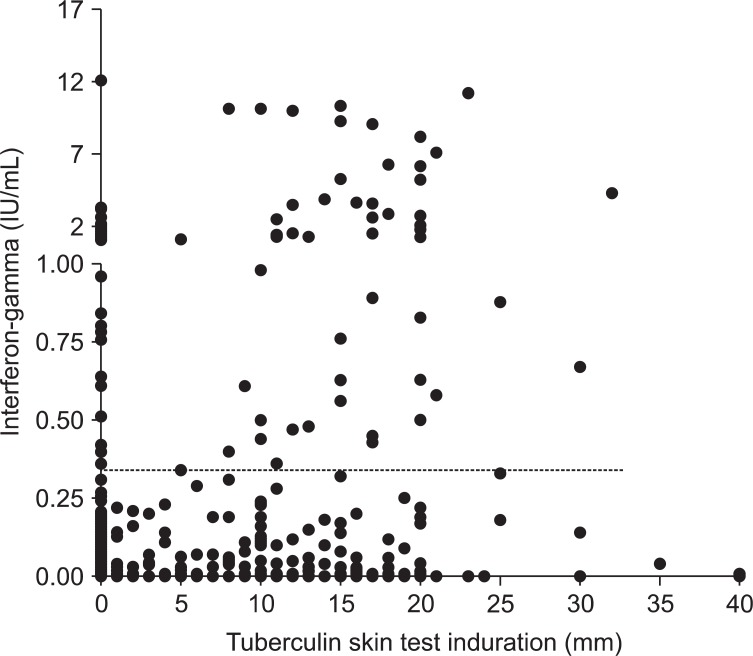
Each TST was performed by intradermal injection of 2 tuberculin units of purified protein derivative RT23 (Statens Serum Institute, Copenhagen, Denmark) into the forearm using the Mantoux technique
10. Reactions were evaluated 48 to 72 hours after injection, with a positive result defined as an induration of ≥10 mm in the transverse diameter.
3. QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube (QFT-GIT)
The QFT-GIT assay was performed in 2 stages, according to the manufacturer's instructions. One-milliliter aliquots of blood were drawn directly into three evacuated blood collection tubes, one containing heparin alone (negative control), one containing T cell mitogen (positive control), and one containing
M. tuberculosis-specific antigens, including early secreted antigenic target 6, culture filtrate protein 10, and TB7.7 (TB-antigen tube). Following overnight incubation, 200 µL of plasma was removed from each well and the concentration of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, with a positive response defined as an antigen-nil IFN-γ concentration ≥ 0.35 IU/mL
11.
4. Statistical analysis
Comparisons between groups were made using the χ
2 tests for categorical variables. Concordance between results of the TST and QFT-GIT were assessed by chance corrected proportional agreement rate; kappa (κ) coefficients, with κ>0.75 defined as excellent agreement, κ<0.4 as poor agreement, and κ between 0.4 and 0.75 as fair to good agreement
12. Odds ratio and multiple logistic regression analysis were used to calculate adjusted risk. Independent variables were selected on the basis of their statistical significance in univariate analysis and on the basis of being clinically applicable. All tests of significance were two sided; p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 12.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Go to :

Discussion
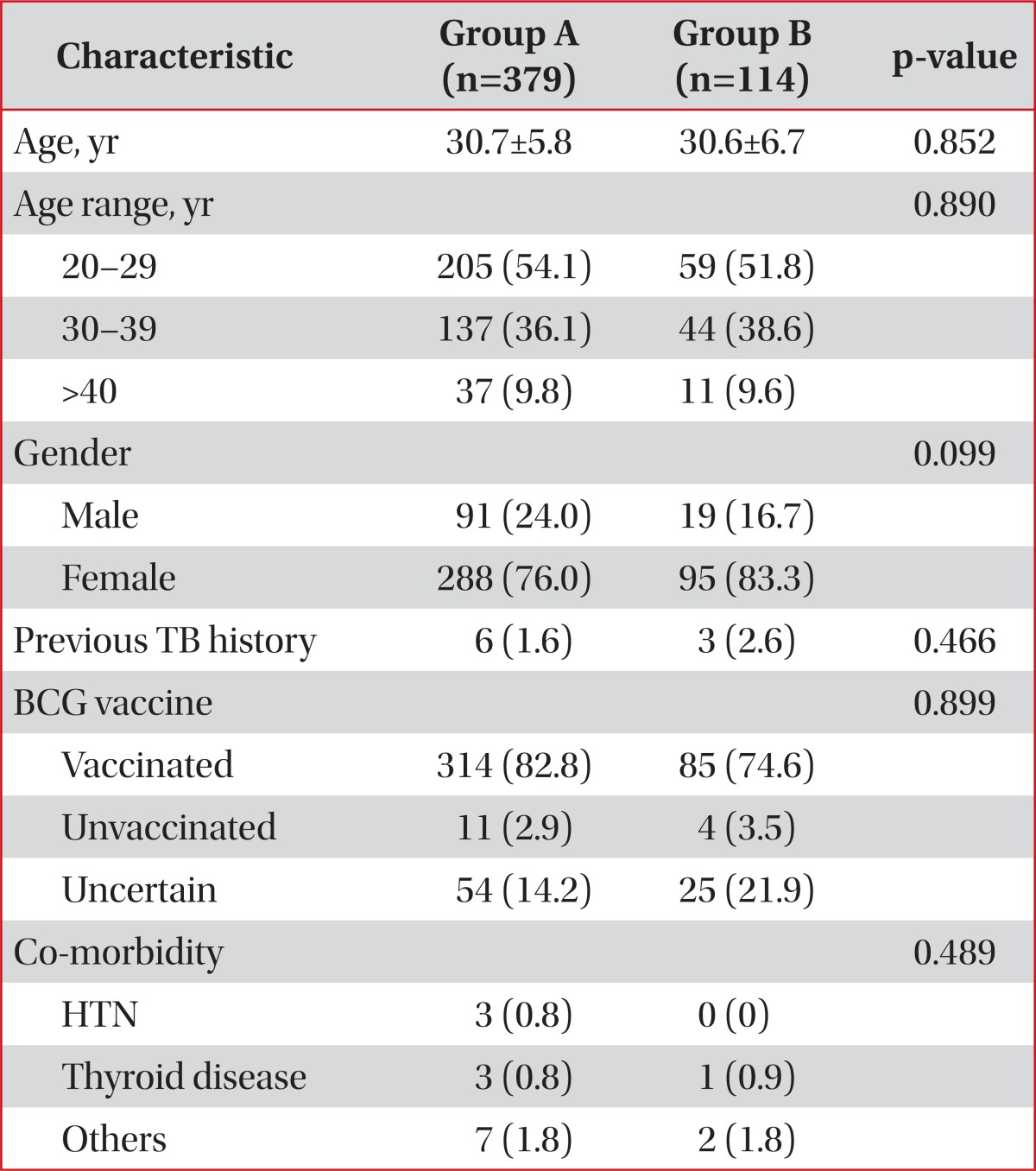
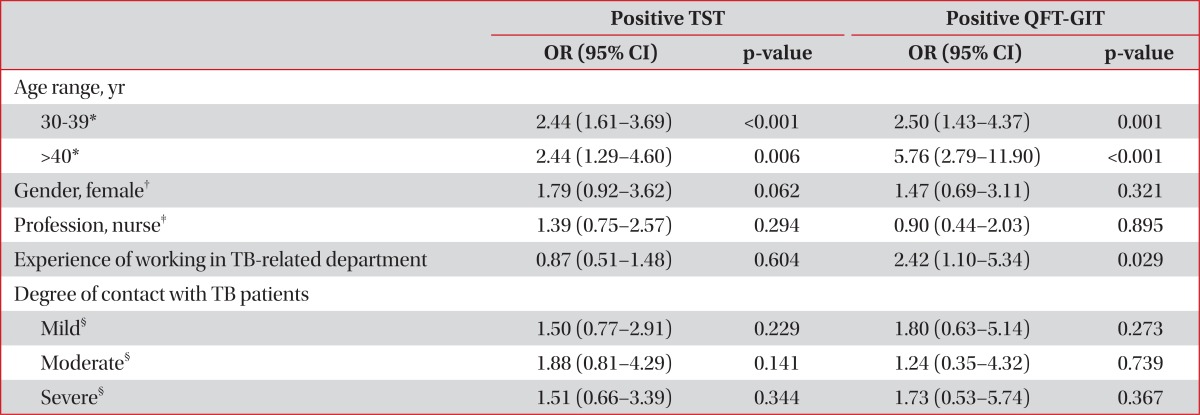
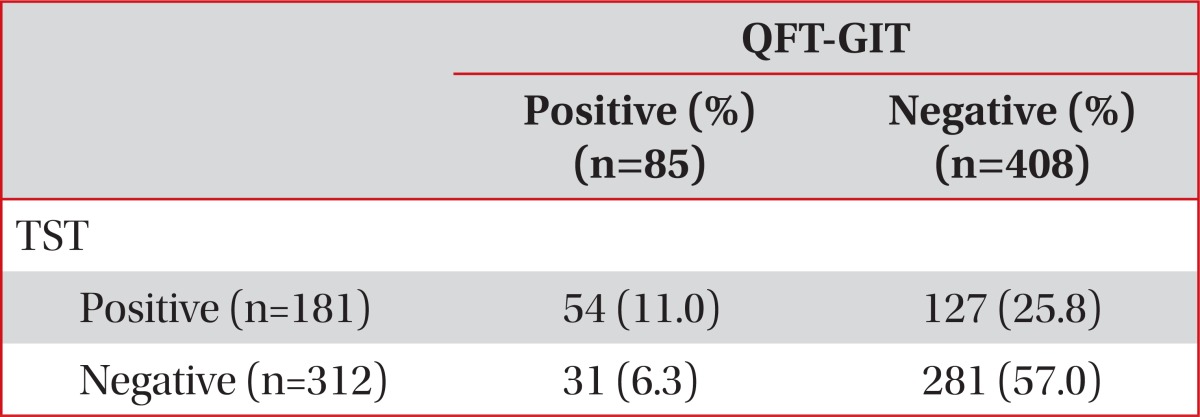
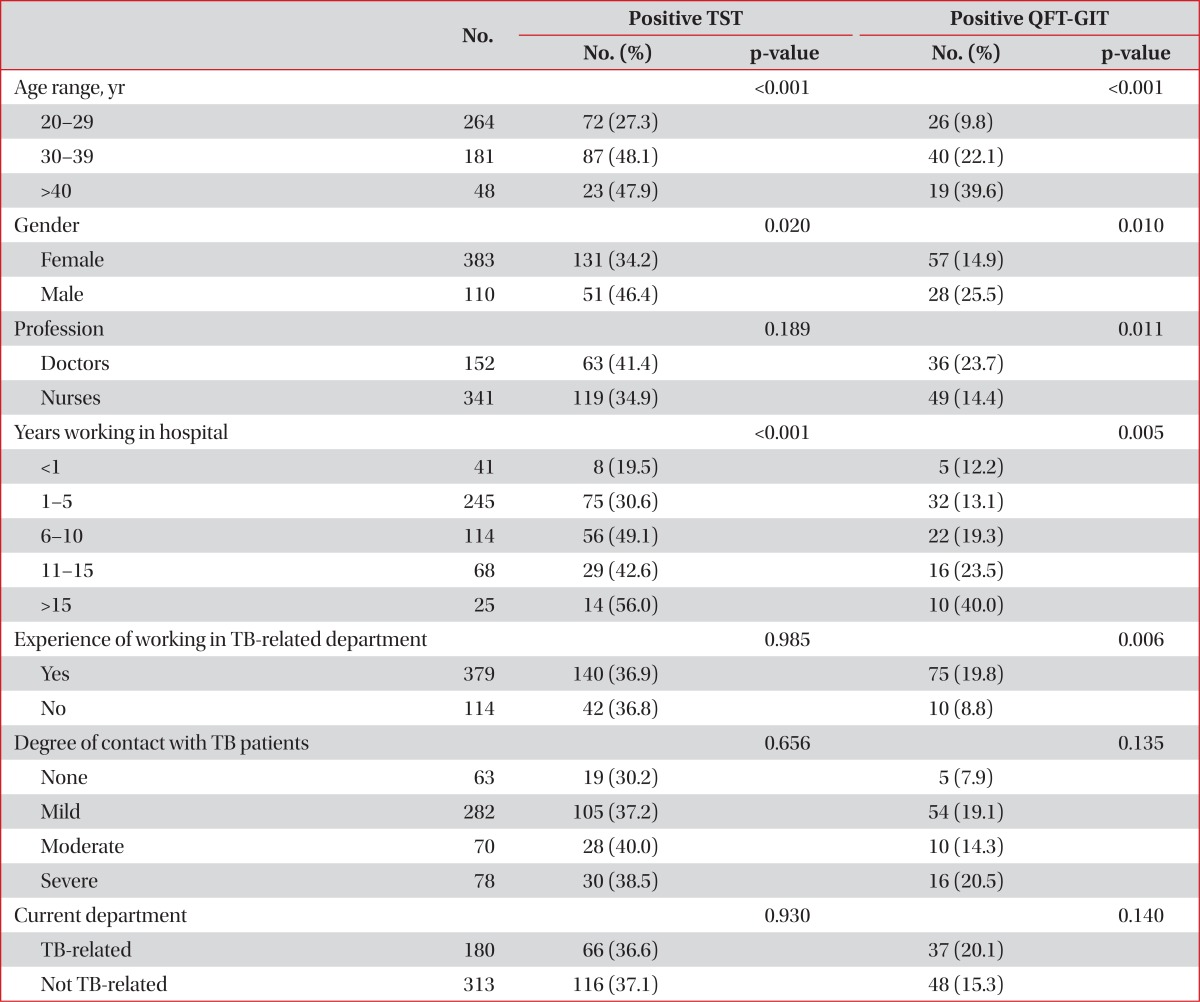
This is the first multicenter study to investigate LTBI prevalence of doctors and nurses and its risk factors in South Korea using both the TST and the QFT-GIT test. In the present multicenter study, we documented that among 152 doctors, 63 (41.4%) were positive by TST and 36 (23.7%) were positive by QTF-GIT. In addition, 119 (34.9%) had positive TST and 49 (14.4%) showed positive QFT-GIT result among 341 nurses. Two tests generally showed poor agreement. We also revealed that experience of working in TB-related departments was significantly associated with positive LTBI test results by QFT-GIT assay not by TST. This suggests that a positive QFT-GIT result may be a better indicator of LTBI than a positive TST result.
Our study showed poor agreement between the TST and the QFT-GIT, which is consistent with previous reports
6,
12. In South Korea, where BCG vaccination is mandatory, children are vaccinated with BCG at birth; until 1997, TST non-responders were revaccinated again at age 12 or 13 years
13. This BCG vaccination strategy may result in a substantial number of false-positive TST results, especially in young people. Because our participants mainly consisted of young people with a mean age of 30.6 years (82.6% of participants were younger than 35 years old), the QFT-GIT may estimate the LTBI prevalence of our population more accurately rather than the TST. The statistically significant association between the experience of working in TB-related departments and a positive LTBI result on QFT-GIT and not on TST in our study supports the above hypothesis. This assumption was also made in previous studies which were conducted in South Korea
6,
9,
12 as well as in other countries
4,
14,
15. Moreover, while the positive rate of the TST in the present study was not different from that in the general population, the positive QFT-GIT rate was significantly higher than that in general population in South Korea (unpublished data). All of these findings suggest that the QFT-GIT would be more helpful than the TST for the detection of LTBI in South Korean HCWs, especially doctors and nurses.
There have been several studies assessing the prevalence of LTBI among HCWs in South Korea. Lee et al.
7 reported that annual risk of TB infection among newly employed nurses was at least 3% on the basis of results of both the TST and QFT-GIT test. Similarly Park et al.
9 showed that a minimum of 3.3% of HCWs experienced conversion on serial QFT-GIT tests. While these studies mainly focused on the conversion rate of the TST and/or the QFT-GIT in HCWs at a single center, this was a multicenter study tried to assess the LTBI prevalence among doctors and nurses by using both tests. Our results were similar with earlier studies, which reported that the LTBI prevalence of HCWs was 37.8% on TST and 23.2% on QFT-GIT in a university hospital
6.
Since positive results on both tests are known to increase with age in usual settings, we analyzed the rates of positive results of both tests according to three age group categories in order to reduce confusing effect of age and better identify possible risk factors. As a result, we found no significant differences in the rates of positive of the two tests depending on the various risk factors. The exception to this was the experience of working in TB-related departments. A number of studies have reported various risk factors affecting the prevalence of LTBI in other nations, such as history of close contacts with individuals with active TB
4, work in a TB clinic
14, total years spent as a HCWs
15, and employment as a HCW for >5 years
16. However, these various risk factors may not be directly comparable to our study because of several factors: marked heterogeneity of the TB burden, a national program to detect patients and contacts, and characteristics (such as socioeconomic status, baseline demographics or ethics) of enrolled HCWs. We did not include the variable of current working department in the multivariate analysis because of the confounding effect of this parameter owing to rotation of HCWs, especially doctors. Similarly, although age was revealed to be independently associated with positive results of both tests, it was considered as a general feature, not only in HCWs.
In the majority of tertiary hospitals, including the eight participating hospitals in our study, infectious patients with TB are admitted to isolation rooms equipped with negative-pressure ventilation with and without ultraviolet germicidal irradiation. HCWs or visitors entering such room are required to wear N95 respirators. However, our study suggests that these measures are still insufficient and more appropriate measures should be considered. For example, despite general guidelines, many young doctors do not wear N95 respirator when they enter an isolation room, because this type of respirator is hard to wear due to its tight facial seal. Moreover, many hospitals in South Korea do not have isolation rooms for confirmed or suspected TB patients in their emergency department. Such patients can transmit TB to HCWs during their stay in the ER, which can sometimes take as long as several days. Although Korean guidelines for TB exist, it simply recommends for HCWs of high-risk group to be tested for LTBI regularly, without presenting any specific recommendations. The practical guidelines including these amendable factors need be revised to reduce TB burden of high-risk group.
We investigated whether the prevalence of LTBI among doctors and nurses differed among hospitals according to the type of management program in place to prevent nosocomial transmission of TB. Since all eight hospitals have their own isolation room and rules concerning the wearing of N95 respirators, these variables were not included in analysis. Some patients were diagnosed as having TB during their stay in general hospital wards rather than at admission to isolation rooms. Such patients may infect both HCWs and neighboring patients. Therefore, close contact investigation of HCWs who have had contact with such patients would be important in reducing the TB infection rate among HCWs. This is supported by a trend suggesting that the result of the QFT-GIT was more likely to be positive in subjects working for hospitals where contact investigation was not done. However, this trend did not have statistical significance (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.010-1.622; p=0.055).
Our study had several limitations. First, because we included only HCWs working in tertiary hospitals, the population of present study was not a representative sample of South Korean HCWs in general. Small hospitals and private clinics were not involved in this study. TB infection control measures at such institutions would most likely be inferior to larger hospitals since facilities such as isolation rooms are not well equipped in these hospitals. In addition, we were not able to objectively quantify the degree of contact with TB patients in the questionnaire. This might have resulted in no statistical differences in the positive TST or QFT-GIT rates according to the degree of contact to TB patients. Finally, because there were mostly men in the doctor's group and the majority of nurses were women, there might have been gender bias among doctors and nurses.
In conclusion, we found high prevalence of LTBI among South Korean HCWs. There was poor level of agreement between the two tests and we suggest that the QFT-GIT is a more appropriate test for the detection of LTBI in South Korean HCWs. This suggestion may be extrapolated to any other intermediate TB-burden countries where BCG vaccination is common among HCWs. Finally, given that experience of working in TB-related departments were significantly associated with TB infection in our study, stricter preventive measure should be implemented for this occupational subgroup.
Go to :





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download