Abstract
Pulmonary sequestration is a rare congenital anomaly of the lung in which it is separately supplied from the aorta or one of its branches. Bilateral pulmonary sequestration is very rare, particularly in adults. In bilateral pulmonary sequestration, resection of both sides is usually recommended if both sides are infected and symptomatic. We report the case of a 37-year-old female patient with bilateral intralobar pulmonary sequestration treated by staged bilateral lower lobectomy.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
The initial chest x-ray showed cystic cavitary lesion at both lower lung field and air-fluid level with extensive consolidation in left lung base.
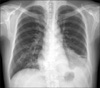
Figure 2
(A) The initial chest CT showed multiseptated cystic mass in both lower lobe with fluid collection, prominent systemic collaterals from descending thoracic aorta supply to the both lower lobe. (B) Selective aortogram showed the aberrant systemic artery supplying to sequestered lung in both lower lobe from descending thoracic aorta. CT: computed tomography.
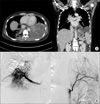
Figure 3
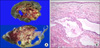
(A) Gross resected specimen of both lower lobe showed multiseptated cystic masses which filled with pus and hemorrhage (right lower lobe [upper] & left lower lobe [lower]). (B) Microscopic findings showed intralobal sequestration with cystic degeneration, with acute and chronic inflammation (H&E stain, ×200).
References
1. Roe JP, Mack JW, Shirley JH. Bilateral pulmonary sequestrations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980. 80:8–10.
2. Pryce DM. Lower accessory pulmonary artery with intralobar sequestration of lung; a report of seven cases. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1946. 58:457–467.
3. Sohn JM, Ahn KS, Hong SP, Moon KD, Yang SH, Kim YH, et al. Surgical treatment of bilateral pulmonary sequestration. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995. 28:792–796.
4. Wimbish KJ, Agha FP, Brady TM. Bilateral pulmonary sequestration: computed tomographic appearance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983. 140:689–690.
5. Chung SK, Rhie SH, Kim CS, Choi JY, Kim SH, Kim JH, et al. Bilateral pulmonary sequestrations. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992. 25:1070–1075.
6. Ransom JM, Norton JB, Williams GD. Pulmonary sequestration presenting as congestive heart failure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1978. 76:378–380.
7. Gerle RD, Jaretzki A 3rd, Ashley CA, Berne AS. Congenital bronchopulmonary-foregut malformation. Pulmonary sequestration communicating with the gastrointestinal tract. N Engl J Med. 1968. 278:1413–1419.
8. Yamamura Y, Hida Y, Kaga K, Kawada M, Niizeki H, Ichinokawa M, et al. Simultaneous resection of bilateral intralobar and extralobar pulmonary sequestrations with video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009. 87:1939–1941.
9. Wei Y, Li F. Pulmonary sequestration: a retrospective analysis of 2625 cases in China. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011. 40:e39–e42.
10. Oh KT, Kim YS, Kim BC, Moon DS, Lee DS, Lee KS, et al. A clinical features of pulmonary sequestration. Korean J Med. 1996. 51:573–580.
11. Park CB, Kim YH, Lee ES, Kim DK, Park SI, Sohnz KH. Bilateral intralobar pulmonary sequestration with horseshoe lung: a new suggestion about the treatment of pulmonary sequestration. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997. 30:226–230.
12. Park KJ, Kim ES, Kim HJ, Chang J, Ahn CM, Kim SK, et al. Clinical manifestations of 15 cases of pulmonary sequestration. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1997. 44:401–408.
13. Nam GY, Park HJ. Clinical manifestations of pulmonary sequestration. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2008. 18:54–60.
14. Ennis JT, Moule NJ, Woo-Ming M. Intralobar pulmonary sequestration in association with bilateral systemic arterialization of the lungs. Br J Radiol. 1972. 45:945–948.
15. Curros F, Chigot V, Emond S, Sayegh N, Revillon Y, Scheinman P, et al. Role of embolisation in the treatment of bronchopulmonary sequestration. Pediatr Radiol. 2000. 30:769–773.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download