Abstract
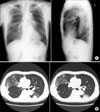
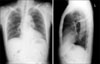
The combination therapy of pegylated interferon and ribavirin is the mainstay of treatment for chronic hepatitis C patients. Anti-viral therapy is commonly associated with side effects such as headache, fever, myalgia, and arthralgia. However, anti-viral therapy can continue because these side effects are mostly mild and can be improved with supportive management. Anti-viral therapy should be stopped promptly if serious side effects, such as interstitial pneumonitis or hemolytic anemia occur, although those serious side effects are rare. There were a few case reports of interferon-related interstitial pneumonitis worldwide. In Korea, one atypical case report of interstitial pneumonitis has been reported, which followed the combination therapy of interferon-alpha and ribavirin in a patient with chronic hepatitis C. We present a case of interstitial pneumonitis and pancytopenia following the combination therapy of pegylated interferon and ribavirin in a patient with chronic hepatitis C.
Figures and Tables
References
1. NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002. 19:1–46.
2. Strader DB, Wright T, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2004. 39:1147–1171.
3. Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001. 358:958–965.
4. Hwang SY, Lee HJ, Park KT, Kim KY, Lee SM, Park CW, et al. Effectiveness and complications of combination therapy with interferon alpha and ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007. 49:166–172.
5. Chin K, Tabata C, Sataka N, Nagai S, Moriyasu F, Kuno K. Pneumonitis associated with natural and recombinant interferon alfa therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Chest. 1994. 105:939–941.
6. Abi-Nassif S, Mark EJ, Fogel RB, Hallisey RK Jr. Pegylated interferon and ribavirin-induced interstitial pneumonitis with ARDS. Chest. 2003. 124:406–410.
7. Okanoue T, Sakamoto S, Itoh Y, Minami M, Yasui K, Sakamoto M, et al. Side effects of high-dose interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1996. 25:283–291.
8. Jeong HS, Oh JY, Jeon J, Seo MJ, Moon SH, Kim HS, et al. A case of interstitial pneumonitis after interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 34:698–703.
9. Son BK, Sohn JH, Kim TY, Park YK, Jeon YC, Han DS. Pulmonary Toxicity by Pegylated Interferon α-2a in a Patient with Chronic Hepatitis C. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:103–107.
10. Kang MJ, Jung EU, Park SW, Choi P, Kim JH, Park SJ, et al. Effects of pegylated interferon and ribavirin in Korean patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Korean J Hepatol. 2008. 14:318–330.
11. Cheong HR, Woo HY, Heo J, Yoon KT, Kim DU, Kim GH, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of the combination therapy of peginterferon alpha and ribavirin in cirrhotic patients with HCV infection. Korean J Hepatol. 2010. 16:38–48.
12. Hoffmann RM, Jung MC, Motz R, Gössl C, Emslander HP, Zachoval R, et al. Sarcoidosis associated with interferon-alpha therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1998. 28:1058–1063.
13. Ogata K, Koga T, Yagawa K. Interferon-related bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Chest. 1994. 106:612–613.
14. Camus P, Fanton A, Bonniaud P, Camus C, Foucher P. Interstitial lung disease induced by drugs and radiation. Respiration. 2004. 71:301–326.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download