Abstract
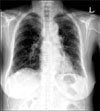
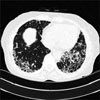
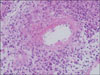
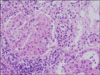
A 65-year-old woman was admitted due to poor oral intake and a dry cough over the previous 3 months. The physical examination was remarkable for bibasilar crackles, and plain chest radiography showed reticulation in both lower lung fields. A pulmonary function test demonstrated a restrictive pattern with a reduced diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. High resolution computed tomography showed reticulation and honey-combing in both peripheral lung zones, which was consistent with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern. Her skin showed livedo reticularis. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level were elevated, and hematuria was noted on urinary analysis. A serologic test for auto-antibodies showed seropositivity for Myeloperoxidase-Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (MPO-ANCA). A kidney biopsy was performed and showed focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. She was diagnosed as having pulmonary fibrosis with microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and treated with high dose steroids. Here we report a case of pulmonary fibrosis coexistent with microscopic polyangiitis.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Collins CE, Quismorio FP Jr. Pulmonary involvement in microscopic polyangiitis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2005. 11:447–451.
2. Guillevin L, Durand-Gasselin B, Cevallos R, Gayraud M, Lhote F, Callard P, et al. Microscopic polyangiitis: clinical and laboratory findings in eighty-five patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:421–430.
3. Schwarz MI, Brown KK. Small vessel vasculitis of the lung. Thorax. 2000. 55:502–510.
4. Foulon G, Delaval P, Valeyre D, Wallaert B, Debray MP, Brauner M, et al. ANCA-associated lung fibrosis: analysis of 17 patients. Respir Med. 2008. 102:1392–1398.
5. Davson J, Ball J, Platt R. The kidney in periarteritis nodosa. Q J Med. 1948. 17:175–202.
6. Jennette JC, Thomas DB, Falk RJ. Microscopic polyangiitis (microscopic polyarteritis). Semin Diagn Pathol. 2001. 18:3–13.
7. Gallagher H, Kwan JT, Jayne DR. Pulmonary renal syndrome: a 4-year, single-center experience. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002. 39:42–47.
8. Eschun GM, Mink SN, Sharma S. Pulmonary interstitial fibrosis as a presenting manifestation in perinuclear antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody microscopic polyangiitis. Chest. 2003. 123:297–301.
9. Mansi IA, Opran A, Sondhi D, Ayinla R, Rosner F. Microscopic polyangiitis presenting as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: is anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody testing indicated. Am J Med Sci. 2001. 321:201–202.
10. Homma S, Matsushita H, Nakata K. Pulmonary fibrosis in myeloperoxidase antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides. Respirology. 2004. 9:190–196.
11. Cambridge G, Williams M, Leaker B, Corbett M, Smith CR. Anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence, clinical correlates, and IgG subclass. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994. 53:24–29.
12. Braun MG, Csernok E, Schmitt WH, Gross WL. Incidence, target antigens, and clinical implications of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996. 23:826–830.
13. Hahn HS, Hwang JK, Jung HS, Song SH, Joo KW, Park GY, et al. Two Cases of Microscopic Polyangiitis with Honeycomb Lung. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2002. 52:550–556.
14. Hervier B, Pagnoux C, Agard C, Haroche J, Amoura Z, Guillevin L, et al. Pulmonary fibrosis associated with ANCA-positive vasculitides. Retrospective study of 12 cases and review of the literature. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009. 68:404–407.
15. Haegens A, van der Vliet A, Butnor KJ, Heintz N, Taatjes D, Hemenway D, et al. Asbestos-induced lung inflammation and epithelial cell proliferation are altered in myeloperoxidase-null mice. Cancer Res. 2005. 65:9670–9677.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download