Abstract
Paraneoplastic neurologic syndrome is a group of assorted disorders resulting from damage to the nervous system in cancer, remote from primary site, and not related to metastasis, infection, or metabolic disorder associated with cancer. Patient with small cell lung cancer sometimes shows various neurological syndromes, but patient with non-small cell lung cancer rarely shows neurologic syndromes and few antineuronal antibodies have been found. Here, we report a case of 53-year-old male patient who developed ptosis and extraocular muscular limitation of left eye due to third and forth cranial nerve palsy in non-small cell lung cancer without brain metastasis. These neurologic symptoms improved after lobectomy without any other treatment immunotherapy.
Figures and Tables
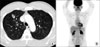
Figure 1
Ptosis of left eye improve after removal of lung cancer in eye opening (before [A] and after [E]) and EOM limitation of vertical and medial gaze (B~D are before, and F~H are after of frontal gaze, up gaze and right up gaze).

References
1. Darnell RB, Posner JB. Paraneoplastic syndromes involving the nervous system. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349:1543–1554.
2. Toothaker TB, Rubin M. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: a review. Neurologist. 2009. 15:21–33.
3. Graus F, Delattre JY, Antoine JC, Dalmau J, Giometto B, Grisold W, et al. Recommended diagnostic criteria for paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004. 75:1135–1140.
4. Honnorat J, Antoine JC. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007. 2:22.
5. Seute T, Leffers P, ten Velde GP, Twijnstra A. Neurologic disorders in 432 consecutive patients with small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2004. 100:801–806.
6. Hiasa Y, Kunishige M, Mitsui T, Kondo S, Kuriwaka R, Shigekiyo S, et al. Complicated paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: a report of two patients with small cell or non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2003. 106:47–49.
7. Fujimoto S, Kumamoto T, Ito T, Sannomiya K, Inuzuka T, Tsuda T. A clinicopathological study of a patient with anti-Hu-associated paraneoplastic sensory neuronopathy with multiple cranial nerve palsies. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2002. 104:98–102.
8. Dalmau J, Graus F, Rosenblum MK, Posner JB. Anti-Hu--associated paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy. A clinical study of 71 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1992. 71:59–72.
9. Reddy RV, Vakili ST. Midbrain encephalitis as a remote effect of a malignant neoplasm. Arch Neurol. 1981. 38:781–782.
10. Pillay N, Gilbert JJ, Ebers GC, Brown JD. Internuclear ophthalmoplegia and "optic neuritis": paraneoplastic effects of bronchial carcinoma. Neurology. 1984. 34:788–791.
11. Vedeler CA, Antoine JC, Giometto B, Graus F, Grisold W, Hart IK, et al. Management of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol. 2006. 13:682–690.
12. Darnell RB. Onconeural antigens and the paraneoplastic neurologic disorders: at the intersection of cancer, immunity, and the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996. 93:4529–4536.
13. Furneaux HF, Reich L, Posner JB. Autoantibody synthesis in the central nervous system of patients with paraneoplastic syndromes. Neurology. 1990. 40:1085–1091.
14. Vernino S, O'Neill BP, Marks RS, O'Fallon JR, Kimmel DW. Immunomodulatory treatment trial for paraneoplastic neurological disorders. Neuro Oncol. 2004. 6:55–62.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download