Abstract
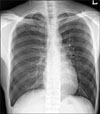
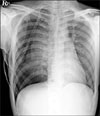
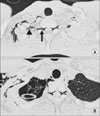
Spinal epidural emphysema is rare and has been described secondary to following medical intervention, such as lumbar puncture and epidural analgesia, pneumothorax or pneumomediastinum, degenerative disk disease, epidural abscess, and trauma. Rarely, it occurs after chest tube placement. We report a case of spinal epidural emphysema incidentally noted on HRCT after chest tube placement.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Goh BK, Yeo AW. Traumatic pneumorrhachis. J Trauma. 2005. 58:875–879.
2. Goh BK, Ng KK, Hoe MN. Traumatic epidural emphysema. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. 29:E528–E530.
3. Schneider LJ, Haller JO, Cao H. CT recognition of spinal epidural air after chest tube placement. Pediatr Radiol. 1995. 25:228.
4. Oertel MF, Korinth MC, Reinges MH, Krings T, Terbeck S, Gilsbach JM. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of pneumorrhachis. Eur Spine J. 2006. 15:Suppl 5. 636–643.
5. Nay PG, Milaszkiewicz R, Jothilingam S. Extradural air as a cause of paraplegia following lumbar analgesia. Anaesthesia. 1993. 48:402–404.
6. Kennedy TM, Ullman DA, Harte FA, Saberski LR, Greenhouse BB. Lumbar root compression secondary to epidural air. Anesth Analg. 1988. 67:1184–1186.
7. Aribas OK, Gormus N, Aydogdu Kiresi D. Epidural emphysema associated with primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001. 20:645–646.
8. Gibikote S, Wray A, Fink AM. Pneumorrhachis secondary to traumatic pneumomediastinum in a child. Pediatr Radiol. 2006. 36:711–713.
9. Tambe P, Kasat LS, Tambe AP. Epidural emphysema associated with subcutaneous emphysema following foreign body in the airway. Pediatr Surg Int. 2005. 21:721–722.
10. Baydin A, Aygun D, Nural SM, Aydin K, Nargis C. Spinal epidural air following multiple thorax trauma. Neurology India. 2007. 55:86–87.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download