Abstract
Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia is a very rare benign disease and usually shows consolidation on chest X-ray with symptoms of pneumonia due to the proliferation of lymphoid cells in the lung parenchyma. It is common for patients to be diagnosed with pneumonia and treated with antibiotics, but patients often enter a cycle of repeated improvement, followed by aggravation of symptoms. At this point, surgical diagnostic tools are considered in order to differentiate between malignant disease and interstitial lung disease. Here, we report 2 cases of patients with nodular lymphoid hyperplasia and review the associated references.
Figures and Tables
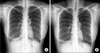
Figure 1
Preoperative chest X-ray. Right middle lobe infiltration had increased after 1 year later. (A) April 17, 2007. (B) June 25, 2008.
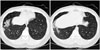
Figure 2
Multifocal homogenous ground glass opacities and consolidations with air-bronchogram at right middle lobe and right lower lobe were shown at preoperative chest CT (June 25, 2008).

Figure 3
(A) Multifocal lymphoid follicles were shown in peribronchiolar area and alveolar wall with interstitial fibrosis (hematoxylin-eosin ×100), (B) CD3 positive (CD3 immunohistochemical staining ×100), (C) CD20 positive (CD20 immunohistochemical staining ×100).
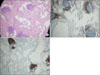
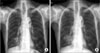
Figure 4
Preoperative chest X-ray. Right lower lobe infiltration had increased after 1 year later. (A) July 30, 2009. (B) June 1, 2010.
References
1. Abbondanzo SL, Rush W, Bijwaard KE, Koss MN. Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia of the lung: a clinicopathologic study of 14 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000. 24:587–597.
2. Nicholson AG. Pulmonary lymphoprolliferative disorders. Curr Diagn Pathol. 2000. 6:130–139.
3. Saltzstein SL. Pulmonary malignant lymphomas and pseudolymphomas: classification, therapy, and prognosis. Cancer. 1963. 16:928–955.
4. Koss MN. Pulmonary lymphoid disorders. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1995. 12:158–171.
5. Li G, Hansmann ML, Zwingers T, Lennert K. Primary lymphomas of the lung: morphological, immunohistochemical and clinical features. Histopathology. 1990. 16:519–531.
6. Guinee DG Jr. Update on nonneoplastic pulmonary lymphoproliferative disorders and related entities. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010. 134:691–701.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download