Abstract
Intussusception primarily occurs in children and is uncommon in adults. Moreover, intussusception caused by intestinal tuberculosis is very rare. We report a case of intussusception induced by intestinal tuberculosis. A 53-year-old man presented to our hospital with complaints of cough and sputum for 2 weeks. We started anti-tuberculosis medication as the patient's sputum acid-fast staining was positive. After 4 days of treatment, the patient developed abdominal cramping pain. Imaging studies showed ileo-ileal type intussusception. The patient underwent segmental resection of the small bowel and intestinal tuberculosis was confirmed on histological examination. He recovered after surgery and was discharged on anti-tuberculosis medication.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Chest X-ray shows multiple nodules and fibrotic scars in the left and right upper lungs with fluid collection in the right hemithorax.
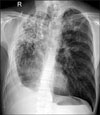
Figure 2
Abdomen plain X-ray shows multiple air-fluid levels in the dilated loops suggesting small bowel obstruction.
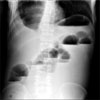
Figure 3
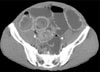
Computed tomography scan of the abdomen shows invagination of ileum to ileum with multiple fluid-filled and dilated loops of the small bowel. Collapse of the terminal ileum and colon is also shown.
References
1. Marinis A, Yiallourou A, Samanides L, Dafnios N, Anastasopoulos G, Vassiliou I, et al. Intussusception of the bowel in adults: a review. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. 15:407–411.
2. Pollack CV Jr, Pender ES. Unusual cases of intussusception. J Emerg Med. 1991. 9:347–355.
3. Nakamura S, Yanagihara K, Izumikawa K, Seki M, Kakeya H, Yamamoto Y, et al. Severe pulmonary tuberculosis complicating Ileocecal intussusception due to intestinal tuberculosis: a case report. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2008. 7:16.
4. Wang N, Cui XY, Liu Y, Long J, Xu YH, Guo RX, et al. Adult intussusception: a retrospective review of 41 cases. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. 15:3303–3308.
5. Hong ES, Kwon KS, Jeong S, Kim SH, Cho HG, Kim PS, et al. A case of intussusception induced by intestinal tuberculosis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 18:99–105.
6. Kim AR, Kim SN, Lee YH, Oh CK. A case of intestinal tuberculosis associated with intussusception. New Med J. 1990. 33:83–86.
7. Yang WJ, Yoon DS, Lee JJ, Park CJ, Kim DH. Clinical review of the intussusception in adults. J Korean Surg Soc. 1998. 55:388–393.
8. Park SH, Moon HY. Adult intussusception in Korea. J Korean Surg Soc. 1992. 43:829–837.
9. Chang CC, Chen YY, Chen YF, Lin CN, Yen HH, Lou HY. Adult intussusception in Asians: clinical presentations, diagnosis, and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 22:1767–1771.
10. McKay R. Ileocecal intussusception in an adult: the laparoscopic approach. JSLS. 2006. 10:250–253.
11. Lee YJ, Yang SK, Myung SJ, Byeon JS, Park IG, Kim JS, et al. The usefulness of colonoscopic biopsy in the diagnosis of intestinal tuberculosis and pattern of concomitant extra-intestinal tuberculosis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004. 44:153–159.
12. Ha HK, Ko GY, Yu ES, Yoon K, Hong WS, Kim HR, et al. Intestinal tuberculosis with abdominal complications: radiologic and pathologic features. Abdom Imaging. 1999. 24:32–38.
13. Pettengell KE, Larsen C, Garb M, Mayet FG, Simjee AE, Pirie D. Gastrointestinal tuberculosis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Q J Med. 1990. 74:303–308.
14. Sharma MP, Bhatia V. Abdominal tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res. 2004. 120:305–315.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download