Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
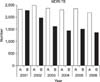 | Figure 1The number of MDR-TB patients. A method: exclusion of the patients duplicated only in a same year, B method: exclusion of any duplicated patients in whole 6 years and inclusion of the case in the first year, MDR-TB: multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. |
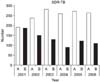 | Figure 2The number of XDR-TB patients. A method: exclusion of the patients duplicated only in a same year, B method: exclusion of any duplicated patients in whole 6 years and inclusion of the case in the first year, XDR-TB: extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. |
Table 1

DST: drug susceptibility test; INH: isoniazid; RFP: rifampicin; EMB: ethambutol; PZA: pyrazinamide; PAS: p-aminosalicylate; PTH: prothionamide; CS: cycloserine; OFX: ofloxacin; KM: kanamycin; SM: streptomycin; KIT: Korea Institute of Tuberculosis; Masan: National Masan Hospital; Mokpo: National Mokpo Hospital; Seobuk: Seobuk Hospital; SCL: Seoul Medical Science Institute; GCRL: Green Cross Reference Laboratory; NeoDIN: Neodin Medical Institute.
*Pyrazinamidase.
Table 2

The number of DST is increasing year by year (p<0.001). Statistical analysis was performed using chi-square test for trend.
KIT: Korea Institute of Tuberculosis; Masan: National Masan Hospital; Mokpo: National Mokpo Hospital; Seobuk: Seobuk Hospital; SCL: Seoul Medical Science Institute; GCRL: Green Cross Reference Laboratory; NeoDIN: Neodin Medical Institute.
Table 3

The number of patients in whom DST was performed is increasing year by year (p<0.001). Statistical analysis was performed using chi-square test for trend.
KIT: Korea Institute of Tuberculosis; Masan: National Masan Hospital; Mokpo: National Mokpo Hospital; Seobuk: Seobuk Hospital; SCL: Seoul Medical Science Institute; GCRL: Green Cross Reference Laboratory; NeoDIN: Neodin Medical Institute.
Table 5

The number of MDR-TB patients calculated by 'A' method showed decreasing trend (p<0.001). Statistical analysis was performed using chi-square test for trend. A method: exclusion of the patients duplicated only in a same year.
KIT: Korea Institute of Tuberculosis; Masan: National Masan Hospital; Mokpo: National Mokpo Hospital; Seobuk: Seobuk Hospital; SCL: Seoul Medical Science Institute; GCRL: Green Cross Reference Laboratory; NeoDIN: Neodin Medical Institute.
Table 6

The number of MDR-TB patients calculated by 'B' method showed decreasing trend (p<0.001). Statistical analysis was performed using chi-square test for trend. B method: exclusion of any duplicated patients in whole 6 years and inclusion of the case in the first year.
KIT: Korea Institute of Tuberculosis; Masan: National Masan Hospital; Mokpo: National Mokpo Hospital; Seobuk: Seobuk Hospital; SCL: Seoul Medical Science Institute; GCRL: Green Cross Reference Laboratory; NeoDIN: Neodin Medical Institute.
Table 7

The number of XDR-TB patients calculated by 'A' method showed increasing trend (p=0.002). Statistical analysis was performed using chi-square test for trend. A method: exclusion of the patients duplicated only in a same year.
KIT: Korea Institute of Tuberculosis; Masan: National Masan Hospital; Mokpo: National Mokpo Hospital; Seobuk: Seobuk Hospital; SCL: Seoul Medical Science Institute; GCRL: Green Cross Reference Laboratory; NeoDIN: Neodin Medical Institute.
Table 8

The number of XDR-TB patients calculated by 'B' method showed decreasing trend (p<0.001). Statistical analysis was performed using chi-square test for trend. B method: exclusion of any duplicated patients in whole 6 years and inclusion of the case in the first year.
KIT: Korea Institute of Tuberculosis; Masan: National Masan Hospital; Mokpo: National Mokpo Hospital; Seobuk: Seobuk Hospital; SCL: Seoul Medical Science Institute; GCRL: Green Cross Reference Laboratory; NeoDIN: Neodin Medical Institute.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download