Abstract
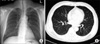
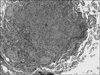
Infliximab, a TNF-α antagonist, has been used to treat refractory rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease and Behcet's disease. Tuberculosis (TB) is a well-known opportunistic infection in patients receiving infliximab. Therefore, patients should be screened and treated for latent or active TB infection before being administered infliximab. Recently, we encountered a case of military TB during infliximab therapy in a patient suffering from Behcet's disease and uveitis. We report this case with a review of the relevant literature.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Turan B, Gallati H, Erdi H, Gurler A, Michel BA, Villiger PM. Systemic levels of the T cell regulatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-12 in Bechcet's disease; soluble TNFR-75 as a biological marker of disease activity. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:128–132.
2. Niccoli L, Nannini C, Benucci M, Chindamo D, Cassara E, Salvarani C, et al. Long-term efficacy of infliximab in refractory posterior uveitis of Behcet's disease: a 24-month follow-up study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. 46:1161–1164.
3. Seong SS, Choi CB, Woo JH, Bae KW, Joung CL, Uhm WS, et al. Incidence of tuberculosis in Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA): effects of RA itself and of tumor necrosis factor blockers. J Rheumatol. 2007. 34:706–711.
4. Accorinti M, Pirraglia MP, Paroli MP, Priori R, Conti F, Pivetti-Pezzi P. Infliximab treatment for ocular and extraocular manifestations of Behcet's disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2007. 51:191–196.
5. Wallis RS, Broder MS, Wong JY, Hanson ME, Beenhouwer DO. Granulomatous infectious diseases associated with tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 38:1261–1265.
6. Balcewicz-Sablinska MK, Keane J, Kornfeld H, Remold HG. Pathogenic Mycobacterium tuberculosis evades apoptosis of host macrophages by release of TNF-R2, resulting in inactivation of TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 1998. 161:2636–2641.
7. Wagner TE, Huseby ES, Huseby JS. Exacerbation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis enteritis masquerading as Crohn's disease after treatment with a tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor. Am J Med. 2002. 112:67–69.
8. Wolfe F, Michaud K, Anderson J, Urbansky K. Tuberculosis infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and the effect of infliximab therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:372–379.
9. Lee YS, Jung JO, Hong JH, Seo YI, Eom KS, Jang SH, et al. Occurrence of tuberculous pleurisy associated with infliximab therapy. Korean J Med. 2004. 67:421–424.
10. Kim YH, Lee BJ, Park JJ, Lee WW, Han WS, Oh SN, et al. Tuberculous meningitis in a patient with Crohn's disease, which was treated with infliximab. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2007. 34:339–342.
11. British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Committee. BTS recommendations for assessing risk and for managing Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and disease in patients due to start anti-TNF-alpha treatment. Thorax. 2005. 60:800–805.
12. Sichletidis L, Settas L, Spyratos D, Chloros D, Patakas D. Tuberculosis in patients receiving anti-TNF agents despite chemoprophylaxis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006. 10:1127–1132.
13. Ruderman EM, Markenson J. Granulomatous infections and tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapies: update through. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. 48:S241.
14. Miyasaka N, Takeuchi T, Eguchi K. Proposed Japanese guidelines for the use of infliximab for rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2006. 15:4–8.
15. Wallis RS, van Vuuren C, Potgieter S. Adalimumab treatment of life-threatening tuberculosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2009. 48:1429–1432.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download