Abstract
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related autoimmune diseases are characterized by high serum IgG4 concentrations, sclerosing inflammation of numerous IgG4-positive lymphoplasma cells of varying origin, and a positive response to steroid treatment. Autoimmune pancreatitis, sclerosing cholangitis, and retroperitoneal fibrosis are representative presentations of IgG4 related autoimmune disease. Herein, we describe 2 patients (40-years-old woman and 47-years-old man) diagnosed with pulmonary involvement of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. The patients were admitted for an evaluation of the lung mass or multiple lung nodules found on chest radiography. Surgical lung biopsies were performed and pathologic finding revealed lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing inflammation with numerous IgG4 positive cells. The patients had elevated serum total IgG and IgG4 levels. Treatment consisted of high dose methylpredinisolone (1 mg/kg/day) and demonstrated good responsiveness. However, one patient experienced 2 relapses while being tapered off of steroid treatment.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Patient 1. (A) Chest radiography showed multiple ill-defined nodular opacity in right lung field and fibrostreak lesion in left upper lung field. (B) Chest CT scan showed multiple irregular nodule in right upper lung. Patient 2. (C) Chest radiography shows ill-defined consolidative lesion on right middle lung. (D) Chest CT shows mass-like opacity and ill-defined nodular opacity in right middle lobe and right lower lobe.
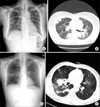
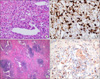
Figure 2
Patient 1. (A), (B) Lung biopsy showed lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing inflammation with numerous IgG4 positive plasma cells (H&E stain, ×400, IgG4 immunostaining). Patient 2. (C) Lung biopsy reveals inflammatory cell infiltration such as lymphocytes and plasma cells (H&E stain, ×100 ). (D) IgG4 immunostaining showed immunoreactive plasma cells (×100).
References
1. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003. 38:982–984.
2. Zen Y, Kitagawa S, Minato H, Kurumaya H, Katayanagi K, Masuda S, et al. IgG4-positive plasma cells in inflammatory pseudotumor (plasma cell granuloma) of the lung. Hum pathol. 2005. 36:710–717.
3. Hamed G, Tsushima K, Yasuo M, Kubo K, Yamazaki S, Kawa S, et al. Inflammatory lesions of the lung, submandibular gland, bile duct and prostate in a patient with IgG4-associated multifocal systemic fibrosclerosis. Respirology. 2007. 12:455–457.
4. Takato H, Yasui M, Ichikawa Y, Fujimura M, Nakao S, Zen Y, et al. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia with abundant IgG4-positive cells infiltration, which was thought as pulmonary involvement of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. Intern Med. 2008. 47:291–294.
5. Duvic C, Desrame J, Lévêque C, Nedelec G. Retroperitoneal fibrosis, sclerosing pancreatitis and bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004. 19:2397–2399.
6. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:732–738.
7. Hirano K, Kawabe T, Komatsu Y, Matsubara S, Togawa O, Arizumi T, et al. High-rate pulmonary involvement in autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern Med J. 2006. 36:58–61.
8. Taniguchi T, Ko M, Seko S, Nishida O, Inoue F, Kobayashi H, et al. Interstitial pneumonia associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2004. 53:770. author reply 770-1.
9. Inoue D, Zen Y, Abo H, Gabata T, Demachi H, Kobayashi T, et al. Immunoglobulin G4-related lung disease: CT findings with pathologic correlations. Radiology. 2009. 251:260–270.
10. Kobayashi H, Shimokawaji T, Kanoh S, Motoyoshi K, Aida S. IgG4-positive pulmonary disease. J Thorac Imaging. 2007. 22:360–362.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download