Abstract
The majority of flexible bronchoscopies are performed under topical anesthesia with lidocaine being the most commonly used agent. Anaphylaxis rarely occurs after local administration of lidocaine, but can be a fatal complication. We experienced a case of unexpected anaphylaxis. A 66-year-old woman was scheduled for flexible bronchoscopy to evaluate a tracheal mass and stenosis. The oral and nasal mucosa were pretreated with lidocaine. About 2~3 minutes later, the patient developed hypotension and we treated for anaphylaxis in the emergency room. Then, we decided to perform rigid bronchoscopy in this patient, under conditions of general anesthesia. A rigid bronchoscopy was performed in this patient, safely and successfully. The tracheal mass was determined to be squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures and Tables
Figure 2
Chest computed tomography shows a tracheal stenosis by irregular hypertrophy of lower endotracheal wall.
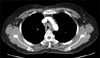
Figure 3
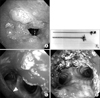
(A) Bronchoscopic finding shows a tracheal stenosis by irregular endotracheal mass in lower trachea. (B) This shows Karl Storz endoskope set. (C) This bronchoscopic finding shows that rigid bronchoscopy was performed to reestablish patency of the airway by means of mechanical removal. An arrowhead shows a tip of rigid bronchoscope. (D) Normal orifices of both main bronchi are seen.
References
1. Ikeda S, Yanai N, Ishikawa S. Flexible bronchofiberscope. Keio J Med. 1968. 17:1–16.
2. Gall H, Kaufmann R, Kalveram CM. Adverse reactions to local anesthetics: analysis of 197 cases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996. 97:933–937.
3. Fulkerson WJ. Current concepts: fiberoptic bronchoscopy. N Engl J Med. 1984. 311:511–515.
4. Credle WF Jr, Smiddy JF, Elliott RC. Complications of fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974. 109:67–72.
5. Sim SJ, Han JD, Ryu WS, Lee DW, La DJ, Park CW. Anaphylactic reaction after topical lidocaine anesthesia during bronchoscopy. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 19:219–223.
6. Ruffles SP, Gayres JG. Fatal bronchospasm after topical lignocaine before bronchoscopy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987. 294:1658–1659.
7. Prakash U. Mason RJ, Courtney Broaddus V, Murray JF, Nadel JA, editors. Chapter 22. Bronchoscopy. Murray and Nadel's textbook of respiratory medicine. 2005. 4th ed. Pennsylvania: Elsevier Saunders;617–650.
8. Niwa H, Tanahashi M, Kondo T, Ohsaki Y, Okada Y, Sato S, et al. Bronchoscopy in Japan: a survey by the Japan Society for Respiratory Endoscopy in 2006. Respirology. 2009. 14:282–289.
9. Pue CA, Pacht ER. Complications of fiberoptic bronchoscopy at a university hospital. Chest. 1995. 107:430–432.
10. British Thoracic Society Bronchoscopy Guidelines Committee, a Subcommittee of Standards of Care Committee of British Thoracic Society. British Thoracic Society guidelines on diagnostic flexible bronchoscopy. Thorax. 2001. 56:Suppl 1. i1–i21.
11. Wu FL, Razzaghi A, Souney PF. Seizure after lidocaine for bronchoscopy: case report and review of the use of lidocaine in airway anesthesia. Pharmacotherapy. 1993. 13:72–78.
12. Lee SM, Song WJ, Yang MS, Lee SH, Kwon JW, Kim TW, et al. A case of lidocaine anaphylaxis. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 26:249–253.
13. In JH, Choi JW, Joo J, Kim DW, Jung H, Park H. Intraoperative anaphylaxis after local infiltration of lidocaine for dental treatment under general anesthesia: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008. 55:395–398.
14. Birnbaum J, Porri F, Pradal M, Charpin D, Vervloet D. Allergy during anaesthesia. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994. 24:915–921.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download