Abstract
Dieulafoy's disease of the bronchus is rare but potentially life-threatening, and should be considered in patients with massive hemoptysis, especially from unknown etiology. We report a case of a patient with massive hemoptysis due to bronchial Dieulafoy's disease. He underwent bronchial artery embolization and surgical resection, and the post-operative specimen revealed dilated and tortuous arteries in the submucosa that presented as Dieulafoy's disease of the bronchus.
Figures and Tables
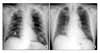
Figure 1
(A) Chest radiograph after endotracheal intubation shows fine nodular densities, mainly in the right lung parenchyma. (B) Six days later, the endotracheal tube was removed and previous parenchymal lesions are almost disappeared.
References
1. Akhras J, Patel P, Tobi M. Dieulafoy's lesion-like bleeding: an underrecognized cause of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage in patients with advanced liver disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2007. 52:722–726.
2. Regula J, Wronska E, Pachlewski J. Vascular lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2008. 22:313–328.
3. Stoopen E, Baquera-Heredia J, Cortes D, Green L. Dieulafoy's disease of the bronchus in association with a paravertebral neurilemoma. Chest. 2001. 119:292–294.
4. Savale L, Parrot A, Khalil A, Antoine M, Théodore J, Carette MF, et al. Cryptogenic hemoptysis: from a benign to a life-threatening pathologic vascular condition. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007. 175:1181–1185.
5. Alshumrani G, Almuaikeel M. Angiographic findings and endovascular embolization in Dieulafoy disease: a case report and literature review. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2006. 12:151–154.
6. Sweerts M, Nicholson AG, Goldstraw P, Corrin B. Dieulafoy's disease of the bronchus. Thorax. 1995. 50:697–698.
7. Kuzucu A, Gurses I, Soysal O, Kutlu R, Ozgel M. Dieulafoy's disease: a cause of massive hemoptysis that is probably underdiagnosed. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005. 80:1126–1128.
8. Pomplun S, Sheaff MT. Dieulafoy's disease of the bronchus: an uncommon entity. Histopathology. 2005. 46:598–599.
9. van der Werf TS, Timmer A, Zijlstra JG. Fatal haemorrhage from Dieulafoy's disease of the bronchus. Thorax. 1999. 54:184–185.
10. Martínez Ares D, Souto Ruzo J, Yáñez López J, Alonso Aguirre P, Gómez Mata C, Valbuena Ruvira L, et al. Recurrent Dieulafoy's disease with surgical management: diagnosis by endoscopic ultrasonography. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2004. 96:138–142.
11. Parrot A, Antoine M, Khalil A, Théodore J, Mangiapan G, Bazelly B, et al. Approach to diagnosis and pathological examination in bronchial Dieulafoy disease: a case series. Respir Res. 2008. 9:58.
12. Fartoukh M, Khalil A, Louis L, Carette MF, Bazelly B, Cadranel J, et al. An integrated approach to diagnosis and management of severe haemoptysis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit: a case series from a referral centre. Respir Res. 2007. 8:11.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download