Abstract
Background
TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand) is a newly identified member of the TNF gene family which appears to have tumor-selective cytotoxicity due to the distinct decoy receptor system. TRAIL has direct access to caspase machinery and induces apoptosis regardless of p53 phenotype. Therefore, TRAIL has a therapeutic potential in lung cancer which frequently harbors p53 mutation in more than 50% of cases. However, it was shown that TRAIL also could activates NF-κB in some cell lines which might inhibit TRAIL-induced apoptosis. This study was designed to investigate whether TRAIL can activate NF-κB in lung cancer cell lines relatively resistant to TRAIL-induced apoptosis and inhibition of NF-κB activation using proteasome inhibitor MG132 which blocks IκBα degradation can sensitize lung cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
Methods
A549 (wt p53) and NCI-H1299 (null p53) lung cancer cells were used and cell viability test was done by MTT assay. Apoptosis was confirmed with Annexin V assay followed by FACS analysis. To study NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activation, a luciferase reporter gene assay was used after making A549 and NCI-H1299 cells stably transfected with IgGκ-NF-κB luciferase construct. To investigate DNA binding of NF-κB activated by TRAIL, electromobility shift assay was used and supershift assay was done using anti-p65 antibody. Western blot was done for the study of IκBα degradation.
Results
A549 and NCI-H1299 cells were relatively resistant to TRAIL-induced apoptosis showing only 20~30% cell death even at the concentration 100 ng/ml, but MG132 (3µM) pre-treatment 1 hour prior to TRAIL addition greatly increased cell death more than 80%. Luciferase assay showed TRAIL-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity in both cell lines. Electromobility shift assay demonstrated DNA binding complex of NF-κB activated by TRAIL and supershift with p65 antibody. IκBα degradation was proven by western blot. MG132 completely blocked both TRAIL-induced NF-κB dependent luciferase activity and DNA binding of NF-κB.
Figures and Tables
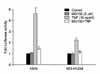 | Figure 1MG132 inhibits TNF-α induced NF-κB dependent transcriptional activation in both A549 and NCI-H1299 cells. A549 and NCI-H1299 cells which stably expressed an IgGκ-NF-κB luciferase reporter gene construct were pretreated with MG132 (3 uM) for 1 h followed by the addition of TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 6 h. The cells were then harvested for analysis of luciferase activity. Values are mean of three experiments±SD. |
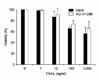 | Figure 2Dose-dependent TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity in A549 and NCI-H1299 lung cancer cells. Cells were incubated with TRAIL for 24 h followed by analysis of cell viability by an MTT assay. Values are mean of three experiments±SD. |
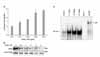 | Figure 3TRAIL induces NF-κB activation in A549 cells. (A) Luciferase assay: Stable A549 IgGκ-NF-κB luciferase cells were treated with TRAIL (100 ng/ml) for different time points. Cells were harvested for luciferase assay. The fold luciferase activation was calculated relative to a normalized value of one given to control (untreated) cells. Data represent the mean luciferase value from triplicates in one experiment, which was used to calculate the mean+SD. from two experiments. (B) Western blot for IκBα degradation: A549 cells were treated with TRAIL (100 ng/ml) for various times and cellular proteins was harvested followed by loading of equal amounts of protein on an SDS-PAGE gel which was probed with an anti-IκBα antibody after transfer to nitrocellulose. (C) EMSA with supershift. A549 cells were treated with TRAIL (100 ng/ml) for various times and harvested for nuclear extraction. Electromobility shift assay was done with a radiolabeled IgGκ-NF-κB probe. Equal amounts (7.5 ug) of nuclear protein was loaded in each lane. In 5th lane, an 100x excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide was added 5 min before the addition of radiolabeled probe. In 6th lane, a rabbit polyclonal antibody p65 was added to the nuclear extract 10 min before the addition of radiolabeled probe. |
 | Figure 4(A) MG132 sensitizes A549 and NCI-H1299 cells to TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity. MG132 (3 uM) was pretreated 1 h before the addition of TRAIL (100 ng/ml) and after 24 h incubation cell viability test by an MTT assay was done. Values are mean of three experiments±SD. (B) Annexin V assay shows the sensitization effect of MG132 to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in A549 cells. Treatment schedule was the same with Figure 3A. and cells were harvested and followed by the analysis of apoptosis by FACS scan. (a: control, b: MG132 3µM, c: TRAIL 100 ng/ml, d: MG132 1 hr pre-treatment+TRAIL). |
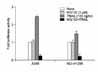 | Figure 5MG132 inhibits TRAIL-induced NF-κB transcriptional activity in A549 and NCI-H1299 cells. A549 and NCI-H1299 cells which stably expressed an IgGκ-NF-κB luciferase reporter gene construct were pretreated with MG132 (3 uM) for 1 h followed by the addition of TRAIL (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. The cells were then harvested for analysis of luciferase activity. Values are mean of three experiments±SD. |
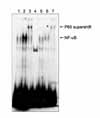 | Figure 6MG132 inhibits TRAIL-induced DNA binding of NF-κB in A549 cells and supershift assay shows NF-κB complex containing p65. A549 cells were treated with TRAIL (100 ng/ml) for various times and harvested for nuclear extraction. Electromobility shift assay was done with a radiolabeled IgGκ-NF-κB probe. Equal amounts (7.5 ug) of nuclear protein was loaded in each lane. In 4th lane, an 100x excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide was added 5 min before the addition of radiolabeled probe. In 3rd and 7th lanes, a rabbit polyclonal antibody p65 was added to the nuclear extract 10 min before the addition of radiolabeled probe (lane 1: control, lane 2: TRAIL 100 ng/ml for 2 hr, lane 3: TRAIL+p65 Ab, lane 4: TRAIL+x100 (cold competition), lane 5: MG132 3µM, lane 6: MG132+TRAIL, lane 7: MG132+TRAIL+p65 Ab). |
References
1. Lee KY, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Yoo KH. Immunohistochemical analysis for the expression of DR5 TRAIL receptor and p53 in non-small cell lung cancer. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2008. 64:278–284.
2. Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995. 3:673–682.
3. Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:12687–12690.
4. Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Apoptosis control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999. 11:255–260.
5. Lee KY, Park JS, Jee YK, Rosen GD. Triptolide sensitizes lung cancer cells to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. Exp Mol Med. 2002. 34:462–468.
6. Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Anderson KC. Proteasome inhibition in multiple myeloma: therapeutic implication. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005. 45:465–476.
7. Almond JB, Cohen GM. The proteasome: a novel target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia. 2002. 16:433–443.
8. Fribley A, Zeng Q, Wang CY. Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress-reactive oxygen species in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. 24:9695–9704.
9. Ishii Y, Waxman S, Germain D. Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007. 7:359–365.
10. Voortman J, Resende TP, Abou El Hassan MA, Giaccone G, Kruyt FA. TRAIL therapy in non-small cell lung cancer cells: sensitization to death receptor-mediated apoptosis by proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. 6:2103–2112.
11. Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, et al. TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J. 1997. 16:5386–5397.
12. Golstein P. Cell death: TRAIL and its receptors. Curr Biol. 1997. 7:R750–R753.
13. Schneider P, Bodmer JL, Thome M, Hofmann K, Holler N, Tschopp J. Characterization of two receptors for TRAIL. FEBS Lett. 1997. 416:329–334.
14. Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, et al. Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science. 1997. 277:818–821.
15. Degli-Esposti MA, Smolak PJ, Walczak H, Waugh J, Huang CP, DuBose RF, et al. Cloning and characterization of TRAIL-R3, a novel member of the emerging TRAIL receptor family. J Exp Med. 1997. 186:1165–1170.
16. Mongkolsapaya J, Cowper AE, Xu XN, Morris G, McMichael AJ, Bell JI, et al. Lymphocyte inhibitor of TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand): a new receptor protecting lymphocytes from the death ligand TRAIL. J Immunol. 1998. 160:3–6.
17. Kastan M. On the TRAIL from p53 to apoptosis? Nat Genet. 1997. 17:130–131.
18. Beg AA, Baltimore D. An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α induced cell death. Science. 1996. 274:782–784.
19. Wang CY, Mayo MW, Baldwin AS Jr. TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-κB. Science. 1996. 274:784–787.
20. Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM. Suppression of TNF-α-induced apoptosis by NF-κB. Science. 1996. 274:787–789.
21. Griffith TS, Rauch CT, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, Lynch DH, et al. Functional analysis of TRAIL receptors using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1999. 162:2597–2605.
22. Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-κB activity through induction of IκB synthesis. Science. 1995. 270:286–290.
23. Schreck R, Rieber P, Baeuerle PA. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of NF-κB transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991. 10:2247–2258.
24. Satake H, Suzuki K, Aoki T, Otsuka M, Sugiura Y, Yamamoto T, et al. Cupric ion blocks NF-κB activation through inhibiting the signal-induced phosphorylation of IκBα. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995. 216:568–573.
25. Thanos D, Maniatis T. NF-κB: A lesson in family values. Cell. 1995. 80:529–532.
26. Delic J, Masdehors P, Omura S, Cosset JM, Dumont J, Binet JL, et al. The proteasome inhibitor lactacystin induces apoptosis and sensitizes chemo and radioresistant human chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes to TNF-α initiated apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 1998. 77:1103–1107.
27. Fiedler MA, Wernke-Dollries K, Stark JM. Inhibition of TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation and IL-8 release in A549 cells with proteasome inhibitor MG132. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998. 19:259–268.
28. Jeremias I, Kupatt C, Baumann B, Herr I, Wirth T, Debatin KM. Inhibition of nuclear factor kB activation attenuates apoptosis resistance in lymphoid cells. Blood. 1998. 91:4624–4631.
29. Michalek MT, Grant EP, Gramm C, Goldberg AL, Rock KL. A role for the ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic pathway in MHC class I-restricted antigen presentation. Nature. 1993. 363:552–554.
30. Sherwood SW, Kung AL, Roitelman J, Simoni RD, Schimke RT. In vivo inhibition of cyclin B degradation and induction of cell-cycle arrest in mammalian cells by the neutral cysteine protease inhibitor N-acetylleucylleucylnorleucinal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. 90:3353–3357.
31. Rothe M, Pan MG, Henzel WJ, Ayres TM, Goeddel DV. The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell. 1995. 83:1243–1252.
32. Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ, Malim MH, Ballard DW. Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-κB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. 94:10057–10062.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download