Abstract
The typical radiographic findings of pulmonary edema from the increased hydrostatic pressure shows centrally localized consolidation, which is known as a "butterfly or bat's wing" pattern. These terms describe the anatomic distribution of edema that uniformly involve the hilum and medulla of the lung but not the peripheral region of the lung parenchyma (cortex). We present a case of butterfly wing-like pulmonary edema on a chest radiograph by mitral regurgitation due to an idiopathic chordal rupture.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
(A) Chest PA shows bilateral peribronchial consolidation more prominent in right lung with small amount of pleural effusion in both costophrenic angles. (B) Thin-section Chest CT demonstrates bilateral diffuse consolidation and ground glass opacities sparing subpleural lung zone.
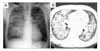
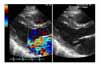
Figure 2
Long-axis parasternal view of two-dimensional echocardiogram during early systole demonstrates mitral regurgitant jet flow toward the left atrial appendage and mitral valve prolapse.
References
1. Ku JM, Chung JW. Lim JK, Lee KS, editors. Chapter 9 Pulmonary edema and hypertension. Thoracic radiology. 2000. Seoul: Ilchokak;303–316.
2. Fraser RS, Muller NL, Colman NC, Pare PD, editors. Chapter 51 Pulmonary edema. Fraser and Pare's diagnosis of diseases of the chest. 1999. 4th ed. Montreal: Saunders;1958–1973.
3. Gurney JW, Goodman LR. Pulmonary edema localized in the right upper lobe accompanying mitral regurgitation. Radiology. 1989. 171:397–399.
4. Schnyder PA, Sarraj AM, Duvoisin BE, Kapenberger L, Landry MJ. Pulmonary edema associated with mitral regurgitation: prevalence of predominant involvement of the right upper lobe. Am J Roentgenol. 1993. 161:33–36.
5. Young AL, Langston CS, Schiffman RL, Shortsleeve MJ. Mitral valve regurgitation causing right upper lobe pulmonary edema. Tex Heart Inst J. 2001. 28:53–56.
6. Grenon H, Bilodeau S. Pulmonary edema of the right upper lobe associated with acute mitral regurgitation. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1994. 45:97–100.
7. Alarcon JJ, Guembe P, de Miguel E, Gordillo I, Abellas A. Localized right upper lobe edema. Chest. 1995. 107:274–276.
8. Singh R, Schrank JP, Nolan SP, McGuire LB. Spontaneous rupture of mitral chordae tendinae. JAMA. 1972. 219:189–193.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download