Abstract
Pulmonary cavities are caused by bacterial pneumonia, fungal diseases, lung cancer, and tuberculosis (TB). However, in Korea, patients with cavitary lung lesions are generally considered to have pulmonary TB, where the incidence of TB is approximately 70/100,000 per year. We report a case of chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis that was obscured by multidrug-resistant pulmonary TB.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Initial CT shows cavitary lesion with air space consolidation, left. Follow-up CT after 2 months of anti-tuberculosis medication revealed aggravated lesion, right.
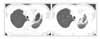
References
1. Chaudhuri MR. Primary pulmonary cavitating carcinomas. Thorax. 1973. 28:354–366.
2. Yang YW, Kang YA, Lee SH, Lee SM, Yoo CG, Kim YW, et al. Aetiologies and predictors of pulmonary cavities in South Korea. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007. 11:457–462.
3. Gefter WB, Weingrad TR, Epstein DM, Ochs RH, Miller WT. "Semi-invasive" pulmonary aspergillosis: a new look at the spectrum of aspergillus infections of the lung. Radiology. 1981. 140:313–321.
4. Gefter WB. The spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. J Thorac Imaging. 1992. 7:56–74.
5. Saraceno JL, Phelps DT, Ferro TJ, Futerfas R, Schwartz DB. Chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis: approach to management. Chest. 1997. 112:541–548.
6. Kim SY, Lee KS, Han J, Kim J, Kim TS, Choo SW, et al. Semiinvasive pulmonary aspergillosis: CT and pathologic findings in six patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:795–798.
7. Chatzimichalis A, Massard G, Kessler R, Barsotti P, Claudon B, Ojard-Chillet J, et al. Bronchopulmonary aspergilloma: a reappraisal. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998. 65:927–929.
8. Kawamura S, Maesaki S, Noda T, Hirakata Y, Tomono K, Tashiro T, et al. Comparison between PCR and detection of antigen in sera for diagnosis of pulmonary aspergillosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. 37:218–220.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download