Abstract
Behcet's disease is a systemic vasculitis of an unknown etiology involving the arteries and veins of all sizes. There are reports showing that a pulmonary artery aneurysm or thromboembolism and superior vena cava thrombosis are present in 5-10% of patients with Behcet's disease and that lung parenchymal lesions are mainly airway consolidations resulting from hemorrhage or infarction. We encountered a patient with increasing pulmonary cavitary changes and localized aspergilloma. The patient was a 43-year-old man diagnosed with Behcet's disease with a history of recurrent oro-genital ulceration and uveitis, and who was administered methotrexate, colchicines, prednisolone. During the follow up he developed progressive dyspnea upon exertion and finger clubbing. Therefore further evaluations were performed. Chest computed tomography showed more advanced consolidations and cavitations than the previous film with the previously known aspergilloma still observable. An open lung biopsy was carried out to determine the presence of malignant changes, which revealed nonspecific vasculitis. Azathioprine was added resultion in an improvement of symptoms.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
On chest radiography A, there is cavitary consolidative mass-like lesion at left upper lung field. On chest radiography B, there is more increased size of cystic lesion with air fluid level in both upper lung field and newly developed cystic lesion in right lower lung field and increased ill defined haziness in lower lung field
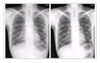
Figure 2
At initial chest CT (A) shows multifocal consolidation with ground glass haziness and some cavitary change in subpleural area of both lung. After 16 months chest CT (B) shows newly developed cavitary lesion is at both lower lung field and the cavity of left lower lung field was more greater than before. The small mass like lesion is in the center of cavity on left lower lobe. It is suggesting aspergilloma. A: 2003/10/17 chest CT, B: 2005/01/20 chest CT

References
1. Sakane T, Takeno M, Susuki N, Inaba G. Behcet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999. 341:1284–1291.
2. Jegal YJ, Chang HK, Ryu DS, Won KS. A case of Behcet's disease with pulmonary infarction. Korean J Med. 2000. 59:535–539.
3. Raz I, Okon E, Chajek-Shaul T. Pulmonary manifestations in Behcet's syndrome. Chest. 1989. 95:585–589.
4. Kim YJ, Lee SM, Ahn Y. A case of Behcet's disese with superior vena cava syndrome. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2004. 56:657–663.
5. Erkan F, Gul A, Tasali E. Pulmonary manifestation of Behcet's disease. Thorax. 2001. 56:572–578.
6. Park KJ, Park SH, Kim SJ, Kim HJ, Chang J, Ahn CM, et al. Clinical manifestations of the lung involvement in Behcet's syndrome. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1996. 43:763–773.
7. Kim HS, Cho JH, Yang MH, Kim HJ, Park BJ, Kim YS, et al. A case of suspected Behcet's disease diagnosed by manifestation of pulmonary artery aneurysm. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2002. 52:405–410.
8. Yoo DH, Jung SS, Choi YC, Lee J, Ahn JH, Kim SY, et al. A case of Behcet's disease with pulmonary arteritis manifestaed as multiple pulmonary nodules. Korean J Med. 1989. 36:695–700.
9. Aydintug AO, Tokhoz G, D'Cruz DP, Gurler A, ervera R, Duzgun N, et al. Antibodies to endotherlial cells in patients with Behcet's disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993. 67:157–162.
10. Haznedaroglu IC, Celik I, Buyukasik Y, Kosar A, Kirasli S, Kundar SV. Haemostasis, thrombosis, and endothelium in Behcet's disease. Acta Haematol. 1998. 99:236–237.
11. Cervera R, Navarro M, Lopez-Soto A, Cid MC, Font J, Esparrza J, et al. Antibodies to endothelial cells in Behcet's disease: cell-binding heterogeneity and association with clinical activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994. 53:265–267.
12. Han SW, Kang YM, Kim YW, Lee JT. Cardiovascular involvement in Behcet's disease. Korean J Med. 2003. 64:542–551.
13. Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, et al. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998. 91:3527–3561.
14. Broze GJ Jr. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor and the current concept of blood coagulation. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1995. 6:Suppl. S7–S13.
15. Greenberger PA, Patterson R. Diagnosis and management of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann Allergy. 1986. 56:444–448.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download