Abstract
Background
MMPs and TIMPs are important factors for abnormal remodeling the pulmonary parenchyme in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia(IIP) This study evaluated the expression of MMPs and TIMPs in the tissue of IPF, NSIP and normal control subjects.
Methods
The MMP-2 and -9 activity in the lung tissue was studied by gelatin zymography, and the expression of MMP-1, -2 ,-9, TIMP-1 and -2 in the lung tissue was measured by immunohistochemistry. Thirty five patients, who were diagnosed with IIP (UIP ; 22, NSIP ; 13), were enrolled in the immunohistochemical study. Thirteen patients with IIP (UIP ; 9, NSIP ; 4) and five patients with lung cancer were enrolled in the zymographic assay.
Results
(1) The immunohistochemistry for MMP-1,-2,-9, TIMP-1 and-2 ; MMP-1,-9 and TIMP-2 were stained stronger in the UIP subjects than NSIP and the normal control. TIMP-2 was strongly stained in the UIP tissue. particularly the fibroblasts in the fibroblastic foci. (2) Zymography for MMP-2 and MMP-9 revealed MMP-2 to have prominent expression in the UIP tissue than in the NSIP tissue.
Figures and Tables
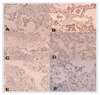 | Figure 1Immunohistochemical detection of MMP-1 in lung tissue with UIP (A), MMP-1 with NSIP (B), TIMP-1 with UIP (C), TIMP-1 with NSIP (D), TIMP-2 with UIP (E), TIMP-2 with NSIP (F). Immunoreactive MMP-1(collagenase-1) for UIP (A) and MMP-1 for NSIP (B) is noticed in reactive alveolar and bronchiolar epithelial cells and in clusters of alveolar macrophages (× 400). Fibroblasts/myofibroblasts show a weak reaction for TIMP-1(C) (× 400). The TIMP-1 immunoreactivity of the epithelial cells lining the alveolar space are little. Macrophages show only a minimal increase in reactivity(D) (× 400). TIMP-2 is intensely stained in the interstitial cells located in subepithelial fibroblasts/myofibroblast foci(E) (× 400). Most areas of NSIP are negative for TIMP-2. Rare foci of myofibroblastic cells in NSIP show positive reaction of TIMP-2(F) (× 400). |
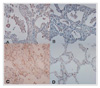 | Figure 2Immunohistochemical detection of MMP-2 in lung tissue with UIP (A), MMP-2 with NSIP (B), MMP-9 with UIP(C), MMP-9 with NSIP(D). MMP-2 for UIP(A), MMP-2 for NSIP(B) is stained in the interstitial cells located in subepithelial fibroblast/myofibroblast foci (× 400). Fibroblast/myofibroblst in UIP show moderate reaction for MMP-9(C). Also MMP-9 for UIP(C), MMP-9 for NSIP(D) is moderate to stong stained in the neutrophils and lymphocytes (× 400). |
 | Figure 3Gelatin zymograms of lung tissue from UIP, NSIP and normal controls. Gelatinolytic bands of 92 kD (proMMP-9), 85 kD (active MMP-9), 72 kD (proMMP-2), 66 kD (active MMP-2) are detected. Intense lytic bands corresponding to the MMP-9, and MMP-2 are visible in UIP. the bands of MMP-2 and -9 in NSIP and normal control were more less expressed than that UIP. |
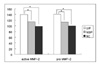 | Figure 4Densitometric analysis of gelatinolytic bands for MMP-2 in lungs from UIP, NSIP, Normal control (NC).
*p<0.05
Densitometric analysis of gelatinolytic bands for active MMP-2 in lungs from UIP is higher than that of NSIP and NC. Also densitometric analysis of gelatinolyic bands for pro MMP-2 in lungs from UIP is higher than that of NSIP and NC.
|
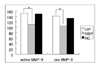 | Figure 5Densitometric analysis of gelatinolytic bands for MMP-9 in lungs from UIP, NSIP, Normal control (NC).
*p<0.05
Densitometric analysis of gelatinolytic bands for active MMP-9 in lungs from UIP is higher than that of NSIP. Also densitometric analysis of gelatinolyic bands for pro MMP-9 in lungs from UIP is higher than that of NSIP.
|
References
1. American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 165:277–304.
2. Gross TJ, Hunninhake GW. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:517–525.
3. Katzenstein AL, Fiorelli RF. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia/fibrosis: histologic features and clinical significance. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994. 18:136–147.
4. Leslie KO. Historical perspictive: a pathologic approach to the classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Chest. 2005. 128:513S–519S.
5. Kim DS. An CM, editor. idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Respiratory diseases. 2004. Seoul: Koonja publishing Inc;457–467.
6. Hayashi T, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Fleming MV, Fishback N, Koss MN, Liotta LA, et al. Immunohistochemical study of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the lungs of patients with diffuse alveolar damage and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 1996. 149:1241–1256.
7. Murphy G, Docherty AJ. The matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992. 7:120–125.
8. Selman M, Ruiz V, Cabrea S, Segura L, Ramirez R, Barrios R, et al. TIMP-1, -2, -3, and -4 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: aprevailing nondegradative lung microenvironment? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000. 279:L562–L574.
9. Fukuda Y, Ishizake M, Kudoh S, Kitaichi M, Yamanaka N. Localization of matrix metalloproteinases-1, -2, and -9, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in interstitial lung diseases. Lab invest. 1998. 78:687–698.
10. Madtes DK, Eliston AL, Kaback LA, Clark JG. Selective induction of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001. 24:599–607.
11. Choi KH, Lee HB, Jeong MY, Rhee YK, Chung MJ, Kwak YG, et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Chest. 2002. 121:1478–1485.
12. Suga M, Iyonaga K, Okamoto T, Gushima Y, Miyakawa H, Akaike T, et al. Characteristic elevation of matrix metalloproteinase activity in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:1949–1956.
13. Park JH, Shim TS, Lim CM, Koh YS, Lee SD, Kim WS, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2001. 51:303–314.
14. Kyung SY, Lim YH, An CH, Park JW, Jeong SH, Shin EK, et al. Immunohistochemical study of metalloproteinase-1 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1, -2 in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Korean J Med. 2003. 65:196–204.
15. Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications fortherapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001. 134:136–151.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download