Abstract
Background
LOH11A is a region with frequent allele loss (>75%) in lung cancer that is located on the centromeric part of chromosome 11p15.5. Clinical and cell biological studies suggest that this region contains a gene associated with metastatic tumor spread. RRM1 encoding the M1 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, which is an enzyme that catalyses the rate-limiting step in deoxyribonucleotide synthesis, is located in the LOH11A region.
Methods
Polymorphisms were found at nucleotide position (-)37 (C/A) and (-)524 (C/T) from the beginning of exon 1
of the RRM1 gene that might regulate the expression of RRM1. We studied the polymorphisms in 127 Korean
individuals (66 lung cancer and 61 normal controls) and compared with those of 140 American patients with lung cancer.
Results
CC, AC and AA were found at the (-)37 position in 64(50.4%), 55(43.3%), and 8(6.3%) out of 127 Korean individuals (66 cancer, 61 non-cancer patients), respectively. There was a similar frequency of allele A at (-)37 in the American(27.9%) and Korean population(28.0%). CC, CT and TT was found at the (-)524 position in 24(18.9%), 44(34.6%), and 59(46.5%) out of the 127 Korean individuals, respectively. There was a similar frequency of allele C at (-)524 in the American(34.6%) and Korean population(36.2%).
There was no difference in the frequency of the (-)37 and (-)524 genotypes between the cancer and non-cancer group. However there was a significant correlation of the genotypes between (-)37 and (-)524 (p<0.001), which suggests the possible coordination of these polymorphisms in the regulation of the promoter activity of the RRM1 gene.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Allelotyping of RRM1 (-)37 C/A polymorphism. Restriction enzyme BbSI cuts when (-)37 base is A. Homozygous A allelotype (lane 3 from left) shows complete digestion into 157 bp bands. Homozygous C allelotype (lane 4 and 7) have original 217 bp bands only without digestion.
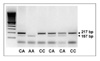
Figure 2
Allelotyping of RRM1 (-)524 C/A polymorphism. Restriction enzyme ApoI cuts when (-)524 base is T. Homozygous T allelotype (lane 2, 5 and 6 from left) shows complete digestion into 74 bp bands. Homozygous C allelotype (lane 3 and 4) have original 176 bp bands only without digestion.
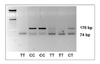
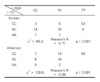
Table 2
Allele Frequency of RRM1 Gene (-)37 Polymorphism in Korean and American Population (χ2 = 1.21, p = 0.55)*

Table 3
Allele Frequency of RRM1 Gene (-)524 Polymorphism in Korean and American Population (χ2 = 2.26, p = 0.32)*

References
1. Bepler G, O'Briant KC, Kim YC, Schreiber G, Pitterle DM. A 1.4-Mb high-resolution physical map and contig of chromosome segment 11p15.5 and genes in the LOH11A metastasis suppressor region. Genomics. 1999. 55:164–175.
2. Schreiber G, Pitterle D, Kim YC, Bepler G. Molecular genetic analysis of primary lung cancer and cancer metastatic to the lung. Anticancer Res. 1999. 19:1109–1115.
3. O'Briant K, Jolicoeur E, Garst J, Campa M, Schreiber G, Bepler G. Growth inhibition of a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line by genetic complementation with chromosome 11. Anticancer Res. 1997. 17:3243–3251.
4. Fan H, Huang A, Villegas C, Wright JA. The R1 component of mammalian ribonucleotide reductase has malignancy-suppressing activity as demonstrated by gene transfer experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. 94:13181–13186.
5. Pitterle DM, Kim YC, Jolicoeur EM, Cao Y, O'Briant KC, Bepler G. Lung cancer and the human gene for ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1 (RRM1). Mamm Genome. 1999. 10:916–922.
6. Bepler G, Gautam A, McIntyre LM, Beck AF, Chervinsky DS, Kim YC, et al. Prognostic significance of molecular genetic aberrations on chromosome segment 11p15.5 in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:1353–1360.
7. Ueda T, Ugawa S, Ishida Y, Shibata Y, Murakami S, Shimada S. Identification of coding single-nucleotide polymorphisms in human taste receptor genes involving bitter tasting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. 285:147–151.
8. Filatov D, Ingemarson R, Johansson E, Rova U, Thelander L. Mouse ribonucleotide reductase: from genes to proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995. 23:903–905.
9. Stubbe J. Ribonucleotide reductases in the twenty-first century. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. 95:2723–2724.
10. Bepler G, Garcia-Blanco MA. Three tumor-suppressor regions on chromosome 11p identified by high-resolution deletion mapping in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. 91:5513–5517.
11. Kim YC, Cao Y, Pitterle DM, O'Briant KC, Bepler G. SSA/RO52gene and expressed sequence tags in an 85 kb region of chromosome segment 11p15.5. Int J Cancer. 2000. 87:61–67.
12. Bepler G, Fong KM, Johnson BE, O'Briant KC, Daly LA, Zimmerman PV, et al. Association of chromosome 11 locus D11S12 with histology, stage, and metastases in lung cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 1998. 22:14–19.
13. Bepler G, Koehler A. Multiple chromosomal aberrations and 11p allelotyping in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1995. 84:39–45.
14. Knudson AG. Hereditary cancer: two hits revisited. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1996. 122:135–140.
15. Venkatachalam S, Shi YP, Jones SN, Vogel H, Bradley A, Pinkel D, et al. Retention of wild-type p53 in tumors from p53 heterozygous mice: reduction of p53 dosage can promote cancer formation. EMBO J. 1998. 17:4657–4667.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download