Abstract
Background
Recently, there have been several studies showing that irinotecan hydrochloride, a topoisomerase I inhibitor, is effective against extensive disease(ED) small cell lung cancer (SCLC). We conducted a phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of irinotecan plus cisplatin as a 1st line therapy for both limited and extensive disease SCLC.
Methods
The study was conducted between January 2002 and June 2004. Patients were treated with 60mg/m2 irinotecan on day 1, 8, 15 and 60mg/m2 cisplatin on day 1, every 4 weeks. During concurrent thoracic irradiation for limited disease (LD)-SCLC patients, dose of irinotecan was reduced to 40mg/m2. Prophylactic cranial irradiation was given to patients with complete remission (CR) after chemotherapy.
Results
Median ages of LD- and ED-SCLC were 64 years and performance status (PS) was 0-2. In patients with LD-SCLC, the response rate after concurrent chemoradiotherapy was 85% (CR, 6; Partial response[PR], 11). The median survival was 20 months (95% CIs, 15.6 to 24.4) with 1-and 2-year survival rates of 85% and 35%, respectively. Median progression free survival (PFS) was 12 months (95% CIs, 6.2 to 18.1) with 1-year PFS of 36%. In ED-SCLC, the response rate was 83.4% (CR, 1; PR, 14). The median survival was 14.5 months (95% CIs, 8.8 to 20.1) with 1-year survival rates of 75%. Median PFS was 6.3 months (95% CIs, 5.6 to 7.1) with 1-year PFS of 20%. The major toxicities (grade 3 or 4) of this regimen included leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, nausea/vomiting, and diarrhea without life threatening complication.
Figures and Tables
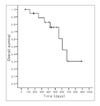 | Figure 1Kaplan-Meier Survival Curve of patients with LD-SCLC. Median survival of LD-SCLC was 20 months (95% CIs; 15.6 to 24.4) with 1- & 2-year survival rates of 85% and 35%, respectIvely. |
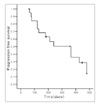 | Figure 2Progression Free Survival (PFS) of patients with LD-SCLC. Median PFS was 12 months (95% CIs; 6.2 to 18.1) with 1 year PFS of 36%. |
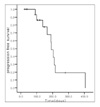 | Figure 3Kaplan-Meier Survival Curve of patients with ED-SCLC. Median survival of ED-SCLC was 14.5 months (95% CIs; 8.8 to 20.1) with 1 year survival rate of 75%. |
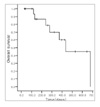 | Figure 4Progression Free Survival (PFS) of patients with ED-SCLC. Median PFS was 6.3 months (95% CIs; 5.6 to 7.1) with 1 year PFS of 20% |
References
1. Simon M, Argiris A, Murren JR. Progress in the therapy of small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2004. 49:119–133.
2. Chua YJ, Steer C, Yip D. Recent advances in management of small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004. 30:521–543.
3. Kudoh S, Fujiwara Y, Takada Y, Yamamoto H, Kinoshita A, Ariyoshi Y, et al. West Japan Lung Cancer Group. Phase II study of irinotecan combined with cisplatin in patients with previously untreated small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998. 16:1068–1074.
4. Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, Negoro S, Sugiura T, Yokoyama A, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:85–91.
5. World Health Organization. WHO Handbook for Results of Cancer Treatment: WHO offset Publication No. 48. 1979. Geneva, Switzerland: Word Health Organization.
6. Tobinai K, Kohno A, Shimada Y, Watanabe T, Tamura T, Takeyama T, et al. Toxicity grading criteria of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group. The Clinical Trial Review Committee of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1993. 23:250–257.
7. Oka M, Fukuda M, Kuba M, Ichiki M, Rikimaru T, Soda H, et al. Phase I study of irinotecan and cisplatin with concurrent split-course radiotherapy in limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2002. 38:1998–2004.
8. Fried DB, Morris DE, Poole C, Rosenman JG, Halle JS, Detterbeck FC, et al. Systematic review evaluating the timing of thoracic radiation therapy in combined modality therapy for limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:4785–4793.
9. Stuschke M, Pottgen C. Localized small-cell lung cancer: which type of thoracic radiotherapy and which time schedule. Lung Cancer. 2004. 45:133–137.
10. Mitsuoka S, Kudoh S, Takada Y. Phase II study of cisplatin, etoposide and concurrent thoracic radiotherapy (TRT) followed by irinotecan and cisplatin in patients with limited stage small-cell lung cancer (SCLC); updated results of WJTOG 9902. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2004. 23:624a.
11. Han JY, Cho KH, Lee DH, Kim HY, Kim EA, Lee SY, et al. Phase II study of irinotecan plus cisplatin induction followed by concurrent twice-daily thoracic irradiation with etoposide plus cisplatin chemotherapy for limited-disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:3488–3494.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print







 XML Download
XML Download