Abstract
– Abstract – Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, resistant to at least isoniazid and rifampicin, continues to present a serious challenge to human health. However, there are no reports addressing multidrug-resistant tuberculous spondylitis in Korea. We report a case of multidrug-resistant tuberculous spondylitis at L2-L3 in a 30-year-old woman.
REFERENCES
1). Br Med Res Counc. Treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis with streptomycin and paraaminosalicylic acid. Br Med J. 1950; 2:1073–1085.
2). Bai GH. Anti-tuberculosis drug resistance in Korea. CDMR. 2005; 16:101–107.
3). Chaulet P, Boulahbal F, Grosset J. Surveillance of drug resistance for tuberculosis control: why and how? Tuber Lung Dis. 1995; 76:487–492.

4). Ahn JI, Oh HY, Rah JH, Kang KS. A clinical study of tuberculous spondylitis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1981; 16:300–310.

5). Pablos-Mendez A, Raviglione MC, Laszlo A, et al. World Health Organization-International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease Working Group on Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Resistance Surveillance. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:1641–1649.
6). Kim BJ, Lee HI, Lee DH, et al. The current status for Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis in Korea. J of Tuberculosis and respiratory disease. 2006; 60:404–411.
7). Ahn JS, Lee JK, Jeon TS, Kwon YS, Kwak SK. Changes of kyphotic angle following operative treatment of tuberculous spondylitis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001; 8:148–155.

8). Martin NS. Tuberculosis of the spine. A study of the results of treatment during the last twenty-five years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970; 52:613–628.
Fig. 1.
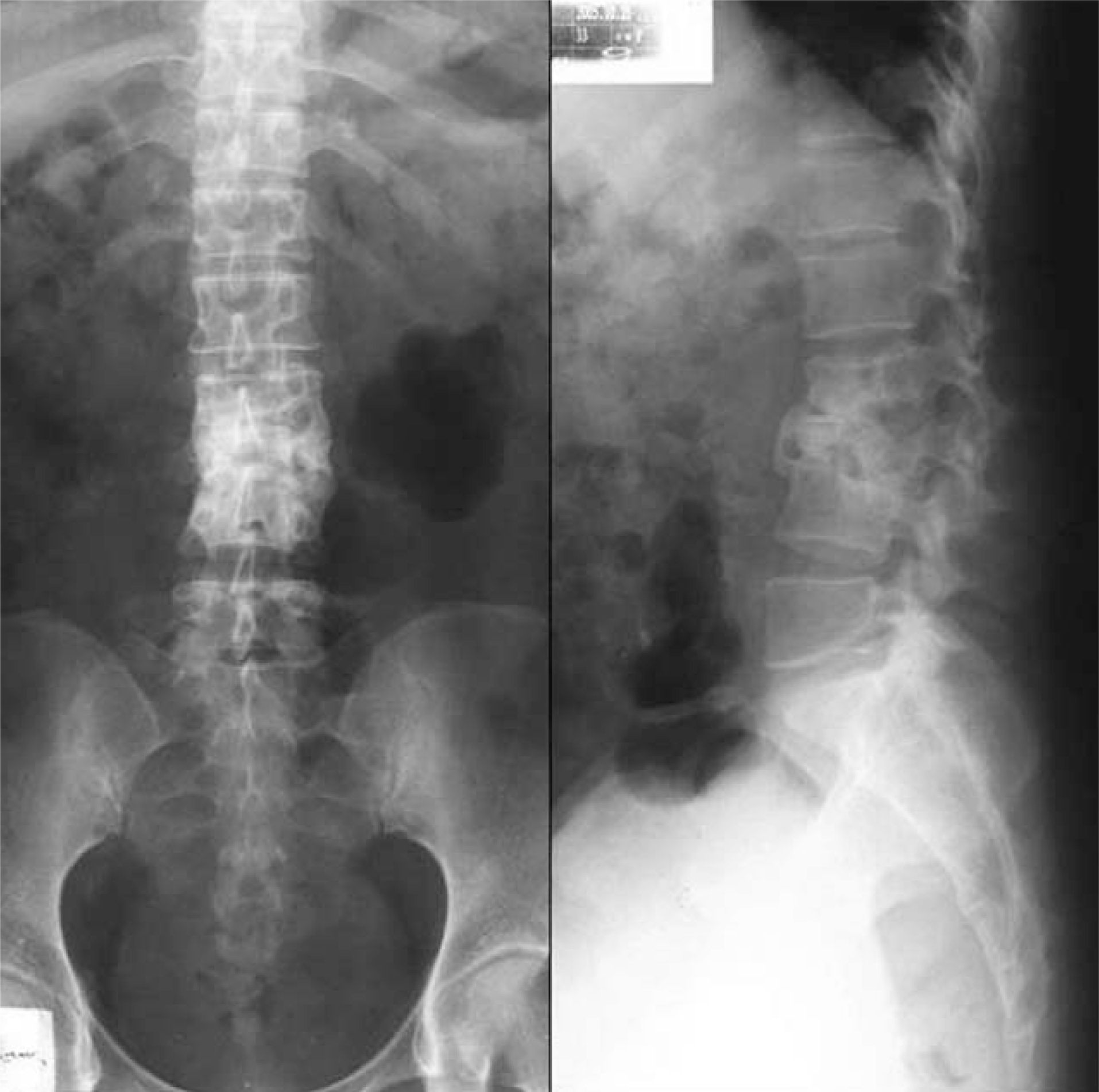
Preoperative radiographs and MR Imaging. (A) Radiographs show destruction of vertebral body and kyphotic deformity (Sagittal index: 40 degrees) at L2-3. (B) Sagittal T1 and T2-weighted imaging of L2-3 demonstrate destruction of vertebral bodies and compression of dural sacs. Axial T2-weighted images show the abscess formation at psoas muscle, right.
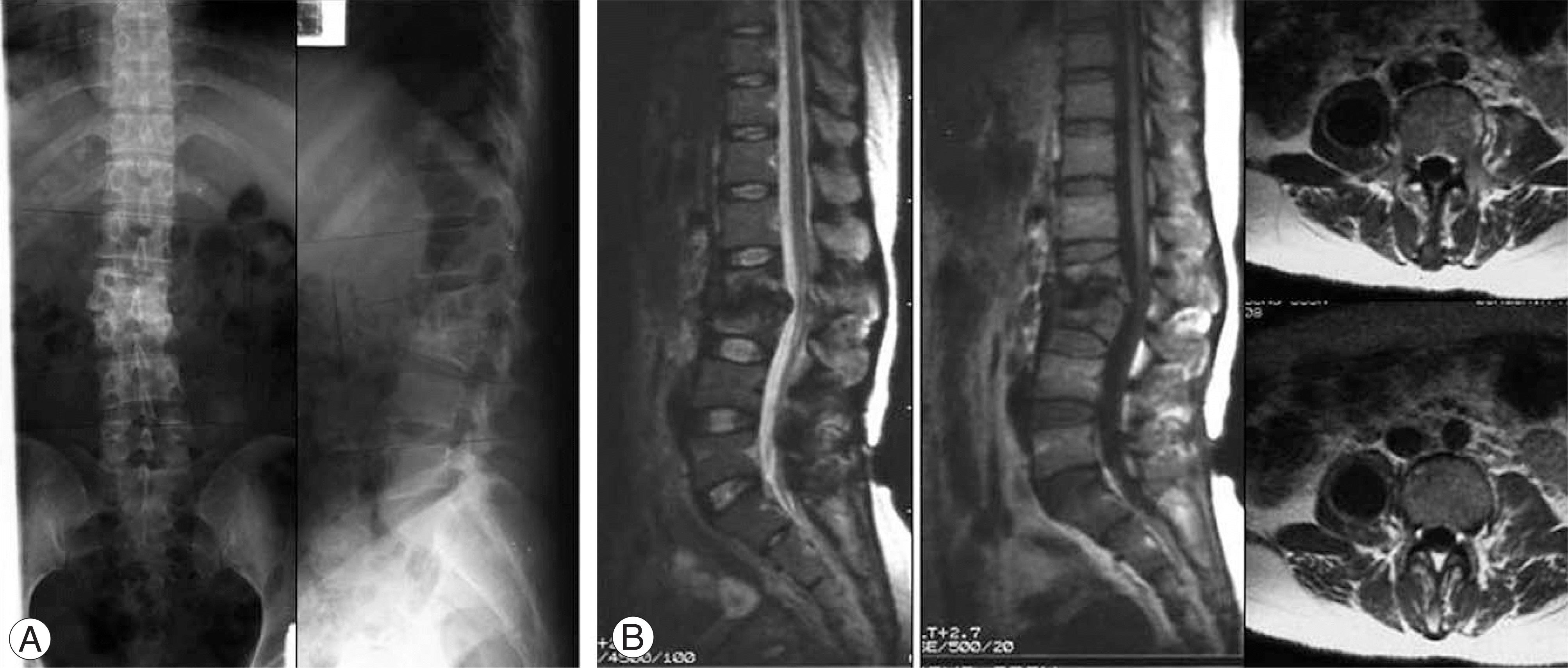
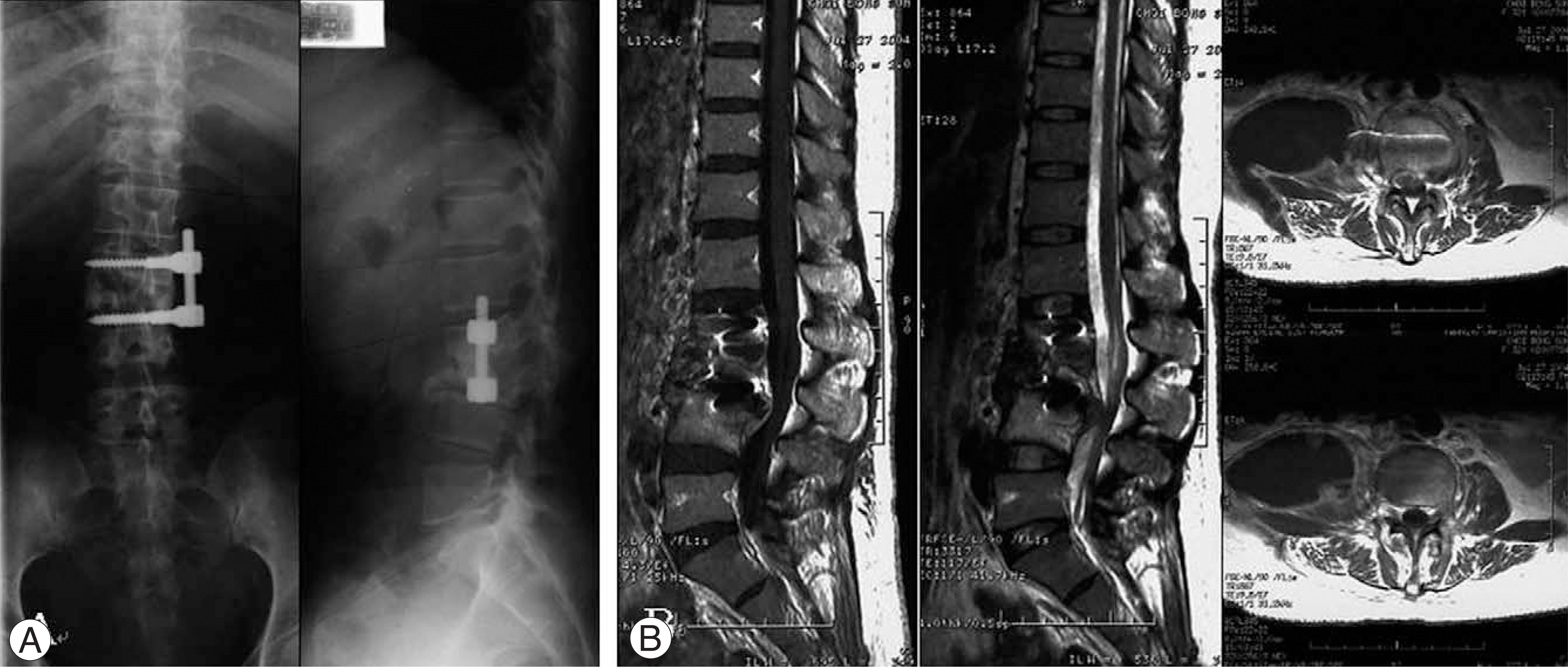
Fig. 3.
Radiographs and MR Imaging at 26months after the operation. (A) Radiographs show collapse of grafted bone, destruction of vertebral bodies and kyphotic deformity at L2-4. (B) Sagittal T1 and T2-weighted imaging of L2-4 demonstrate destruction of vertebral bodies and severe compression of dural sacs. Axial T2-weighted images show the large abscess formation at psoas muscle and fistula formation, right.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download