1. Abdel-Hamid KM. Jost BC, Friedman E, Abdel-Hamid KM, Jani AL, editors. Atopic dermatitis. The Washington Manual Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology Subspecialty Consult. 2003. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;66–73.
2. Akihisa T, Yasukawa K, Oinuma H, Kasahara Y, Yamanouchi S, Takido M, Kumaki K, Tamura T. Triterpene alcohols from the flowers of compositae and their anti-inflammatory effects. Phytochemistry. 1996. 43:1255–1260.

3. Bardana EJ Jr. Immunoglobulin E-(IgE) and non-IgE-mediated reactions in the pathogenesis of atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome (AEDS). Allergy. 2004. 59:Suppl 78. 25–29.

4. Boguniewicz M, Beltrani VS. Adelman DC, Casale TB, Corren J, editors. Atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis. Manual of Allergy and Immunology. 2002. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia;165–186.
5. Buckle J. The role of aromatherapy in nursing care. Nurs Clin North Am. 2001. 36:57–72.
6. Carle R, Gomaa K. The medicinal use of Matricaria flos. Br J Phytother. 1992. 2:147–153.
7. Cerrato P. Aromatherapy: Is it for real? Regist Nurse. 1998. 61:51–52.
8. Chan LS, Robinson N, Xu L. Expression of interleukin-4 in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in a pruritic inflammatory skin disease: an experimental animal model to study atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2001. 117:977–983.

9. Del Rosso J, Friedlander SF. Corticosteroids: options in the era of steroid-sparing therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005. 53:Suppl 1. S50–S58.

10. Duda D, Lorenz W, Dick W, Celik I, Black A, Healy MJR, Black JW. Can clinically relevant histamine release be accurately diagnosed in anaesthetised patients without plasma histamine measurements? Randomised study with nested sampling aimed to change paradigms. Inflamm Res. 1998. 47:Suppl 1. S73–S74.

11. Fiorentino DF, Bond MW, Mosmann TR. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J Exp Med. 1989. 170:2081–2095.

12. Hartman D, Coetzee JC. Two US practitioners' experience of using essential oils for wound care. J Wound Care. 2002. 11:317–320.

13. Heo Y. In vitro model for modulation of helper T cell differentiation and activation. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2005. Suppl 24:18.9.1–18.9.10.
14. Heo Y, Mondal TK, Gao D, Kasten-Jolly J, Kishikawa H, Lawrence DA. Posttranscriptional inhibition of interferon-gamma production by lead. Toxicol Sci. 2007. 96:92–100.

15. Heo Y, Parsons PJ, Lawrence DA. Lead differentially modifies cytokine production in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996. 138:149–157.
16. Heo Y, Saxon A, Hankinson O. Effect of diesel exhaust particles and their components on the allergen-specific IgE and IgG1 response in mice. Toxicology. 2001. 159:143–158.

17. Kapp A. The role of eosinophils in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis - eosinophil granule proteins as markers of disease activity. Allergy. 1993. 48:1–5.

18. Kepron MR, Chen YW, Uhr JW, Vitetta ES. IL-4 induces the specific rearrangement of gamma 1 genes on the expressed and unexpressed chromosomes of lipopolysaccharide-activated normal murine B cells. J Immunol. 1989. 143:334–339.
19. Kobayashi Y, Nakano Y, Inayama K, Sakai A, Kamiya T. Dietary intake of the flower extracts of German chamomile (
Matricaria recutita L.) inhibited compound 48/80-induced itch-scratch responses in mice. Phytomedicine. 2003. 10:657–664.

20. Kobayashi Y, Takahashi R, Ogino F. Antipruritic effect of the single oral administration of German chamomile flower extract and its combined effect with antiallergic agents in ddY mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005. 101:308–312.

21. Koblenzer CS. Itching and the atopic skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 104:S109–S113.

22. Kurt-Jones EA, Hamberg S, Ohara J, Paul WE, Abbas AK. Heterogeneity of helper/inducer T lymphocytes. I. Lymphokine production and lymphokine responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1987. 166:1774–1787.

23. Lawrence BM. Progress in essential oil. Perfumer & Flavorist. 1996. 21:55–68.
24. Lee SH, Baek SJ, Kim HA, Heo Y. 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis like immune alteration in mice. J Toxicol Public Health. 2006. 22:357–364.
25. Lester MR, Hofer MF, Gately M, Trumble A, Leung DYM. Down-regulating effects of IL-4 and IL-10 on the IFN-gamma response in atopic dermatitis. J Immunol. 1995. 154:6174–6181.
26. Matsumoto M, Ra C, Kawamoto K, Sato H, Itakura A, Sawada J, Ushio H, Suto H, Mitsuishi K, Hikasa Y, Matsuda H. IgE hyperproduction through enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of Janus kinase 3 in NC/Nga mice, a model for human atopic dermatitis. J Immunol. 1999. 162:1056–1063.
27. Moss M, Cook J, Wesnes K, Duckett P. Aromas of rosemary and lavender essential oils differentially affect cognition and mood in healthy adults. Int J Neurosci. 2003. 113:15–38.

28. Norris DA. Mechanisms of action of topical therapies and the rationale for combination therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005. 53:Suppl 1. S17–S25.

29. Sanderson CJ, Strath M, Warren DJ, O'garra A, Kirkwood TB. The production of lymphokines by primary alloreactive T-cell clones: a co-ordinate analysis of 233 clones in seven lymphokine assays. Immunology. 1985. 56:575–584.
30. Simon D, Braathen LR, Simon HU. Eosinophils and atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2004. 59:561–570.

31. Snapper CM, Paul WE. Interferon-γ and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987. 236:944–947.

32. Standen MD, Myers SP. The roles of essential oils in the modulation of immune function and inflammation: survey of aromatherapy educators. Int J Aromather. 2004. 14:150–161.

33. Takakura M, Takeshita F, Aihara M, Xin KQ, Ichino M, Okuda K, Ikezawa Z. Hyperproduction of IFN-γ by CpG oligodeoxynucleotide-induce exacerbation of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion in some NC/Nga mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2005. 125:1156–1162.

34. Tamura T, Amano T, Ohmori K, Manabe H. The effects of olopatadine hydrochloride on the number of scratching induced by repeated application of oxazolone in mice. Eur J pharmacol. 2005. 524:149–154.

35. Wahlgren CF. Itch and atopic dermatitis: an overview. J Dermatol. 1999. 26:770–779.

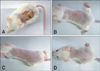
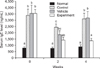
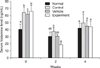
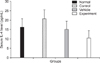





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download