Abstract
Purpose
Papillary carcinoma of the breast is a rare disease and accounts for 1-2% of all breast cancers. Because of its rarity, there have been no reports regarding prognostic factors of papillary carcinoma of the breast. The aim of this study was to review the clinicopathological factors and treatment modalities of papillary carcinoma of the breast and to evaluate the relationship between these factors and survival rates.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 31 patients diagnosed with papillary carcinoma of the breast from January 1986 to December 2005.
Results
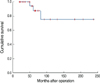
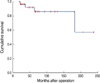
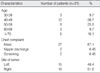
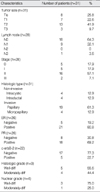
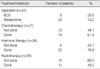
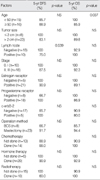
The mean age of the patients was 53.5 yr. The most common symptom was a palpable mass (n=27). The mean size of a tumor was 3.5 cm and 41.9% of the patients were categorized as T2. Eighteen patients had node negative breast cancer. According to the TNM stage, there were 5, 5, 16 and 2 patients with stage 0, I, II and III disease, respectively. Expression of estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor were positive in 80.8% and 69.2% of the patients, respectively. Twenty-three patients underwent mastectomy and eight patients underwent breast-conserving surgery. Fourteen patients received chemotherapy, 20 patients received hormone therapy, and 10 patients received radiotherapy. The 10-yr disease-free survival rate and 10-yr overall survival rate were 74.9% and 86.1%, respectively. Axillary lymph node negative and an age under 50 yr were statistically significant factors in 5-yr disease-free survival and in 5-yr overall survival, respectively.
Figures and Tables
Fig 1
Microscopic findings of papillary carcinoma of the breast. Papillary carcinoma demonstrates a monotonous cellular proliferation with papillary architecture and nuclear hyperchromasia. The inset is a higher power of the carcinoma and reveals cellular pleomorphism and numerous mitoses (H&E stain, ×100).

References
1. Fisher ER, Palekar AS, Redmond C, Barton B, Fisher B. Pathologic findings from the national surgical adjuvant breast project (Protocol No.4) VI. Invasive papillary cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980. 73:313–320.

2. Carter D. Intraductal papillary tumors of the breast. A study of 76 cases. Cancer. 1977. 39:1689–1692.

3. Devitt JE, Barr JR. The clinical recognition of cystic carcinoma of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1984. 159:130–132.
4. Carter D, Orr SL, Merino MJ. Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast after mastectomy, radiotherapy or excisional biopsy alone. Cancer. 1983. 52:14–19.

5. Bansidhar BJ, Garguilo GA. Papillary carcinoma of the breast: characteristics and classification. Am Surg. 2003. 69:400–403.
6. Masood S, Barwick KW. Estrogen receptor expression of the less common breast carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990. 93:437.
7. Kim DJ, Kim YS, Joo HC. Papillary carcinoma of the breast. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000. 59:8–14.
8. The Korean Breast Cancer Society. Survival analysis of Korean breast cancer patients diagnosed between 1993 and 2002 in Korea-a nationwide study of the cancer registry. J Breast Cancer. 2006. 9:214–229.
9. World Health Organization. Histological typing of breast tumors. Tumori. 1982. 68:181–198.
10. Czernobilsky B. Intracystic carcinoma of the female breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967. 124:93–98.
11. Kang HS, Kim YC, Noh DY, Park IA, Youn YK, Oh SK, et al. Histopathologic features of papillary cancer in breast. J Korean Surg Soc. 1998. 55:486–491.
12. Kim DJ, Kim YS, Joo HC. Papillary carcinoma of the breast. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000. 59:8–14.
13. Lefkowitz M, Lefkowitz W, Wargotz ES. Intraductal (intracystic) papillary carcinoma of the breast and its variants: a clinicopathologic study of 77 cases. Hum Pathol. 1994. 25:802–809.

14. Hunter CE Jr, Sawyers JL. Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast. South Med J. 1980. 73:1484–1486.

15. Rosen PP, Hoda SA. Rosen PP, Hoda SA, editors. Papillary carcinoma. Breast pathology diagnosis by needle core biopsy. 2006. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;135–146.
16. McCulloch GL, Evans AJ, Yeoman L, Wilson ARM, Pinder SE, Ellis IO, et al. Radiological features of papillary carcinoma of the breast. Clin Radiol. 1997. 52:865–868.

17. Lam WW, Tang AP, Tse G, Chu WC. Radiology-pathology conference: papillary carcinoma of the breast. Clin Imaging. 2005. 29:396–400.
19. Luna-More S, Gonzalez B, Acedo C, Rodrigo I, Luna C. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. A new special type of invasive mammary carcinoma. Path Res Pract. 1994. 190:668–674.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download