Abstract
Hyperlipidemia and hypertension are among the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and they often co-exist within a single patient. Recently, many studies published results regarding the potential role of statins in decreasing blood pressure (BP) however there is still a controversy over the efficacy of statin therapy on BP. This study aimed to investigate the potential role of rosuvastatin in BP lowering properties in Korean population. Data were taken from three randomized, multiple-dose cross over studies for rosuvastatin, angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) and metformin monotherapies and the combined therapy of rosuvastatin and ARB, in total of 91 healthy male normotensive subjects. Measurements of systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) at the baseline before treatment begins and for 24 hours after the last dose were used in the analysis. The analysis variables used were (i) the mean change in steady-state BP from the baseline, symbolized as ΔBP, and (ii) the difference in ΔBP between the ARB monotherapy and the combined therapy, symbolized as ΔBP,d. The △BP and ΔBP,d for SBP from each study varied in -0.1 ~ -1.3 mmHg and 1.2 ~ 1.6 mmHg, respectively, and were not significantly different from zero. The △BP and ΔBP,d for DBP from each study varied in -2.8 ~ -1.4 mmHg and -2.9 ~ -1.8, respectively, which were statistically significant for △BP (p < 0.05) but was not for ΔBP,d (p > 0.05). These results indicated that the rosuvastatin monotherapy may produce small blood pressure lowing effect in DBP.
REFERENCES
1.Jang JY., Lee SH., Kim BS., Seo HS., Kim WS., Ahn Y, et al. Additive beneficial effects of valsartan combined with rosuvastatin in the treatment of hypercholesterolemic hypertensive patients. Korean Circ J. 2015. 45:225–233. DOI: doi: 10.4070/kcj.2015.45.3.225.

2.Banach M., Nikfar S., Rahimi R., Bielecka-Dabrowa A., Pencina MJ., Mikhailidis DP, et al. The effects of statins on blood pressure in normotensive or hypertensive subjects—a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Cardiol. 2013. 168:2816–2824. DOI: doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.03.068.
3.Borghi C., Prandin M., Costa F., Bacchelli S., Degli Esposti D., Ambrosioni E. Use of statins and blood pressure control in treated hypertensive patients with hypercholesterolemia. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2000. 35:549–555.

4.Briasoulis A., Agarwal V., Valachis A., Messerli FH. Antihypertensive effects of statins: a meta-analysis of prospective controlled studies. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2013. 15:310–320. DOI: doi: 10.1111/jch.12081.

5.Golomb BA., Dimsdale JE., White HL., Ritchie JB., Criqui MH. Reduction in blood pressure with statins: results from the UCSD Statin Study, a randomized trial. Arch Intern Med. 2008. 168:721–727. DOI: doi: 10.1001/archinte.168. 7.721.
6.Aydin U., Ugurlucan M., Gungor F., Ziyade S., Inan B., Banach M, et al. Effects of atorvastatin on vascular intimal hyperplasia: an experimental rodent model. Angiology. 2009. 60:370–377. DOI: doi: 10.1177/0003319708321102.

7.John S., Schneider MP., Delles C., Jacobi J., Schmieder RE. Lipid-independent effects of statins on endothelial function and bioavailability of nitric oxide in hypercholesterolemic patients. Am Heart J. 2005. 149:473.

8.Katsiki N., Mikhailidis DP., Banach M. Effects of statin treatment on endothelial function, oxidative stress and inflammation in patients with arterial hypertension and normal cholesterol levels. J Hypertens. 2011. 29:2493–2494. author reply 4.DOI: doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32834c7bc9.

9.Stepien M., Banach M., Mikhailidis DP., Gluba A., Kjeldsen SE., Rysz J. Role and significance of statins in the treatment of hypertensive patients. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. 25:1995–2005. DOI: doi: 10.1185/03007990903098081.

10.Osende JI., Ruiz-Ortega M., Blanco-Colio LM., Egido J. Statins to prevent cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients. The ASCOT-LLA study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004. 19:528–531.

11.Strazzullo P., Kerry SM., Barbato A., Versiero M., D'Elia L., Cappuccio FP. Do statins reduce blood pressure? A meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension. 2007. 49:792–798.
12.Lee D., Roh H., Son H., Jang SB., Lee S., Nam SY, et al. Pharmacokinetic interaction between rosuvastatin and metformin in healthy Korean male volunteers: a randomized, open-label, 3-period, crossover, multiple-dose study. Clin Ther. 2014. 36:1171–1181. DOI: doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.06.004.

13.Roh H., Son H., Lee D., Chang H., Yun C., Park K. Pharmacokinetic interaction between rosuvastatin and olmesartan: a randomized, open-label, 3-period, multiple-dose crossover study in healthy Korean male subjects. Clin Ther. 2014. 36:1159–1170. DOI: doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.06.022.

14.Son M., Kim Y., Lee D., Roh H., Son H., Guk J, et al. Pharmacokinetic interaction between rosuvastatin and telmisartan in healthy Korean male volunteers: a randomized, open-label, two-period, crossover, multiple-dose study. Clin Ther. 2014. 36:1147–1158. DOI: doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.06.007.

Figure 1.
Mean (SD) BP profile at baseline and for 24 hours after the last dose for SBP (a) and DBP (b) for rosuvastatin monotherapy
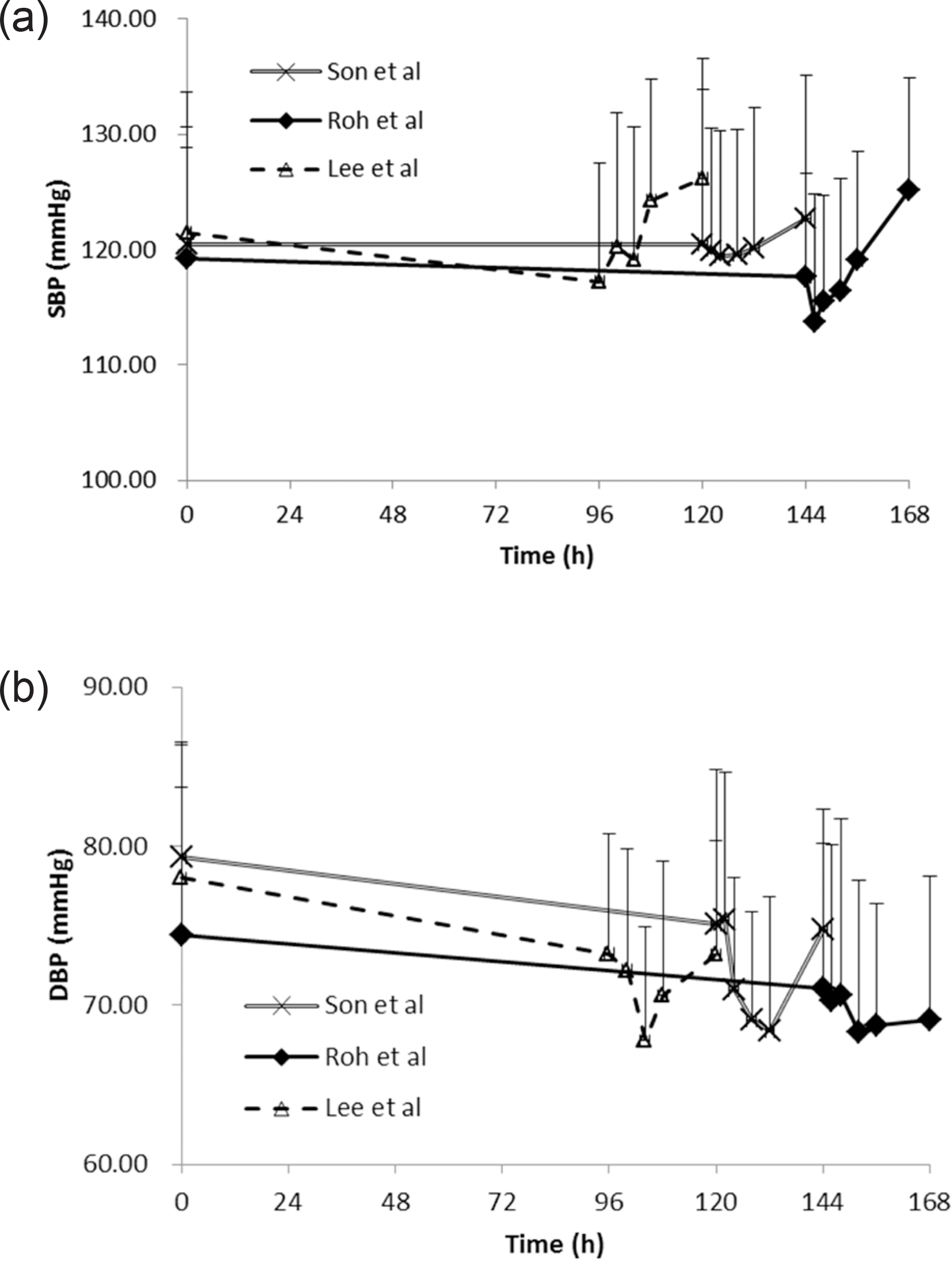
Figure 2.
Mean (SD) BP profile at baseline and for 24 hours after the last dose for SBP (a) and DBP (b) for combination therapy of rosuvastatin and olmesartan (upper) and rosuvastatin and telmisartan (lower)
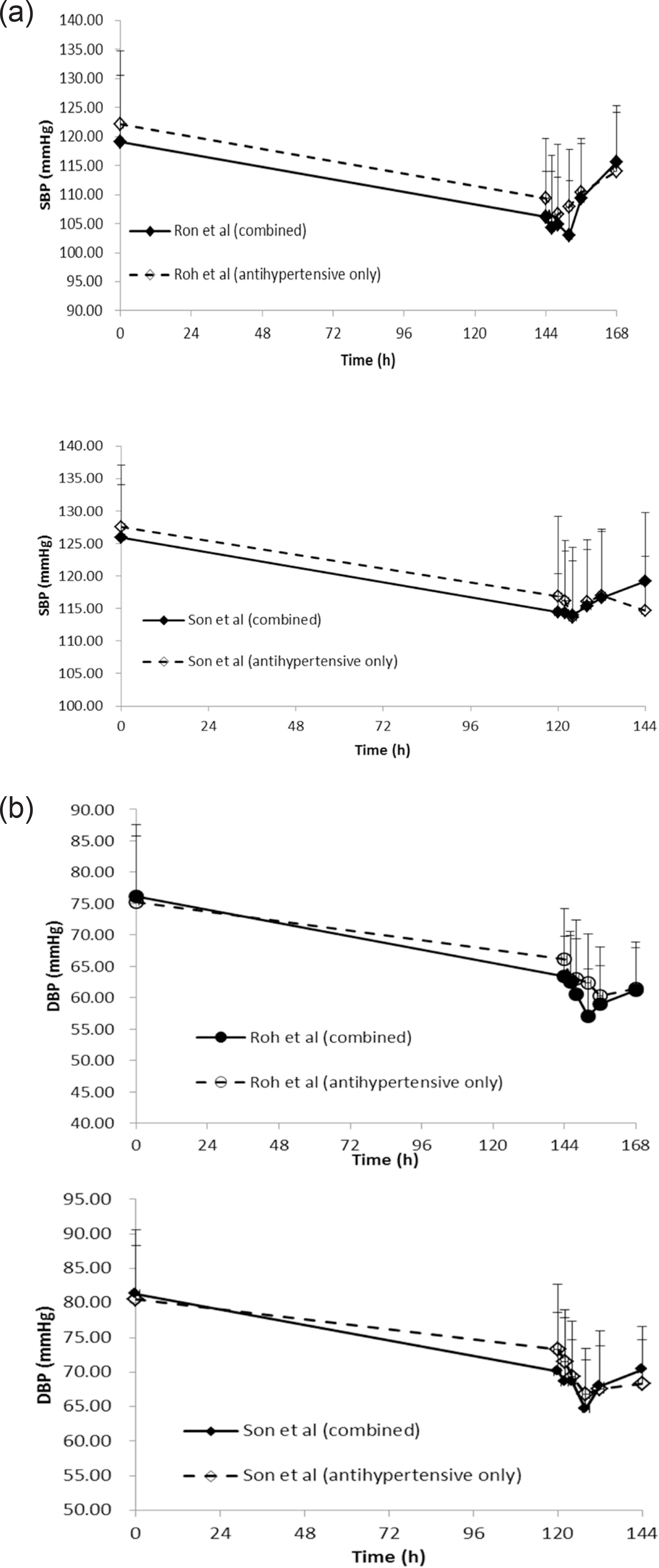
Table 1.
Characteristics of clinical trials included in the analysis
Table 2.
T-test results for rosuvastatin monotherapy
Table 3.
T-test results for combination therapy of rosuvastatin and olmesartan (Roh et al) or telmisartan (Son et al)
| △BP,d for SBP (mmHg) | △BP,d for DBP (mmHg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μ | CI | p-value | μ | CI | p-value | |
| Roh et al[13] | 1.2 | -3.2 ~ 5.6 | 0.6799 | -2.9 | -6.1 ~ 0.3 | 0.0655 |
| Son et al[14] | 1.6 | -4.9 ~ 7.4 | 0.4623 | -1.8 | -7.3 ~ 3.7 | 0.2868 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download