Abstract
Pain is the most common symptom of almost all rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, and others. In addition to commonly known peripheral or nociceptive pain mechanisms, central sensitization plays an essential and significant role as a cause of chronic pain in rheumatic diseases. Chronic pain is also associated with several psychiatric diseases such as depression and anxiety disorders and other various central pain maladies such as irritable bowel syndrome and temporomandibular joint disorder. Therefore, many researchers and clinicians have inferred that similar therapeutic strategies may be employed against this spectrum of disorders. Utilizing recently gained understanding of chronic pain mechanisms will allow a targeted therapeutic approach to individuals who have rheumatologic disease with different spectrum of symptomatic severity and disability.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Normal pain processing pathway. Modified from Ref. 6 with permission from Wolters Kluwer Health.
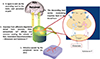
Table 1
Classification of pain in rheumatic diseases according to history taking and physical examination

References
1. Montecucco C, Cavagna L, Caporali R. Pain and rheumatology: an overview of the problem. Eur J Pain Suppl. 2009; 3:105–109.

4. Merskey H, Bogduk N. Classification of chronic pain: descriptions of chronic pain syndromes and definitions of pain terms. 2nd ed. Seattle: IASP Press;1994.
5. Gottschalk A, Smith DS. New concepts in acute pain therapy: preemptive analgesia. Am Fam Physician. 2001; 63:1979–1984.
6. Staud R, Rodriguez ME. Mechanisms of disease: pain in fibromyalgia syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006; 2:90–98.

7. Ki MY, Kim SM. Diagnosis and treatment of neuropathic pain. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:1139–1148.

8. Phillips K, Clauw DJ. Central pain mechanisms in the rheumatic diseases: future directions. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:291–302.
9. Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Gough J, MacKinnon A. Fibromyalgia is a major contributor to quality of life in lupus. J Rheumatol. 1997; 24:2145–2148.
10. Wolfe F, Hauser W, Hassett AL, Katz RS, Walitt BT. The development of fibromyalgia--I: examination of rates and predictors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Pain. 2011; 152:291–299.

11. Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Katz RS, Mease P, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010; 62:600–610.

12. Jones AK, Huneke NT, Lloyd DM, Brown CA, Watson A. Role of functional brain imaging in understanding rheumatic pain. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2012; 14:557–567.

13. Oh DH, Kim TH, Ji JD, Uhm WS, Jun JB, Bae SC, et al. Depression and its associated factors with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2000; 7:232–242.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download