Abstract
Leuconostoc species are Gram-positive coccobacilli and are used in dairy products and are intrinsically resistant to vancomycin. Leuconostoc infections are rare in humans, usually occurring in immune-compromised patients. We describe 6 patients with Leuconostoc bacteremia at Dong-A university hospital between 1990 and 2015. One isolate (L. lactis) was identified to species level using 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis. All patients had underlying diseases and 5 patients underwent procedures that interrupted the normal integumentary defense. Four patients died within 30 days after being identified as carrying Leuconostoc species.
REFERENCES
1.Templin KS., Crook T., Riley T 3rd., Whitener C., Aber RC. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and bacteremia due to Leuconostoc species in a patient with end-stage liver disease; a case report. J Infect. 2001. 43:155–7.

2.Handwerger S., Horowitz H., Coburn K., Kolokathis A., Wormser G. Infection due to Leuconostoc species: six cases and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990. 12:602–10.

3.Kim GY., Kim MH., Park SY., Park MJ., Suh JT., Lee HJ. A case of bacteremia caused by Leuconostoc lactis identified by 16S rRNA sequencing. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2006. 9:137–41.
4.Shin J., Her M., Moon C., Kim D., Lee S., Jung S. Leuconostoc bacteremia in a patient with amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis and tuberculosis arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2011. 21:691–5.
5.Shin KS., Han KD., Hong SB. Septicemia caused by Leuconostoc lactis with intrinsic toleranceto vancomycin in a patient with biliary stent. Korean Journal of Biomedical Laboratory Sciences. 2013. 19:280–3.
6.Lee MR., Huang YT., Lee PI., Liao CH., Lai CC., Lee LN, et al. Healthcare-associated bacteremia caused by Leuconostoc species at a university hospital in Taiwan between 1995 and 2008. J Hosp Infect. 2011. 78:45–9.
7.Moise-Broder PA., Sakoulas G., Eliopoulos GM., Schentag JJ., Forrest A., Moellering RC Jr. Accessory gene regulator group II polymorphism in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is predictive of failure of vancomycin therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 38:1700–5.

8.Coovadia YM., Solwa Z., van Den Ende J. Potential pathogenicity of Leuconostoc. Lancet. 1988. 1:306.

9.Swenson JM., Facklam RR., Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of vancomycin- resistant Leuconostoc, Pediococcus, and Lactobacillus species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990. 34:543–9.
Fig. 1.
The phylogenetic relationships of isolate DAU-03 with other related Leuconostoc strains based on 16S rRNA gene sequences
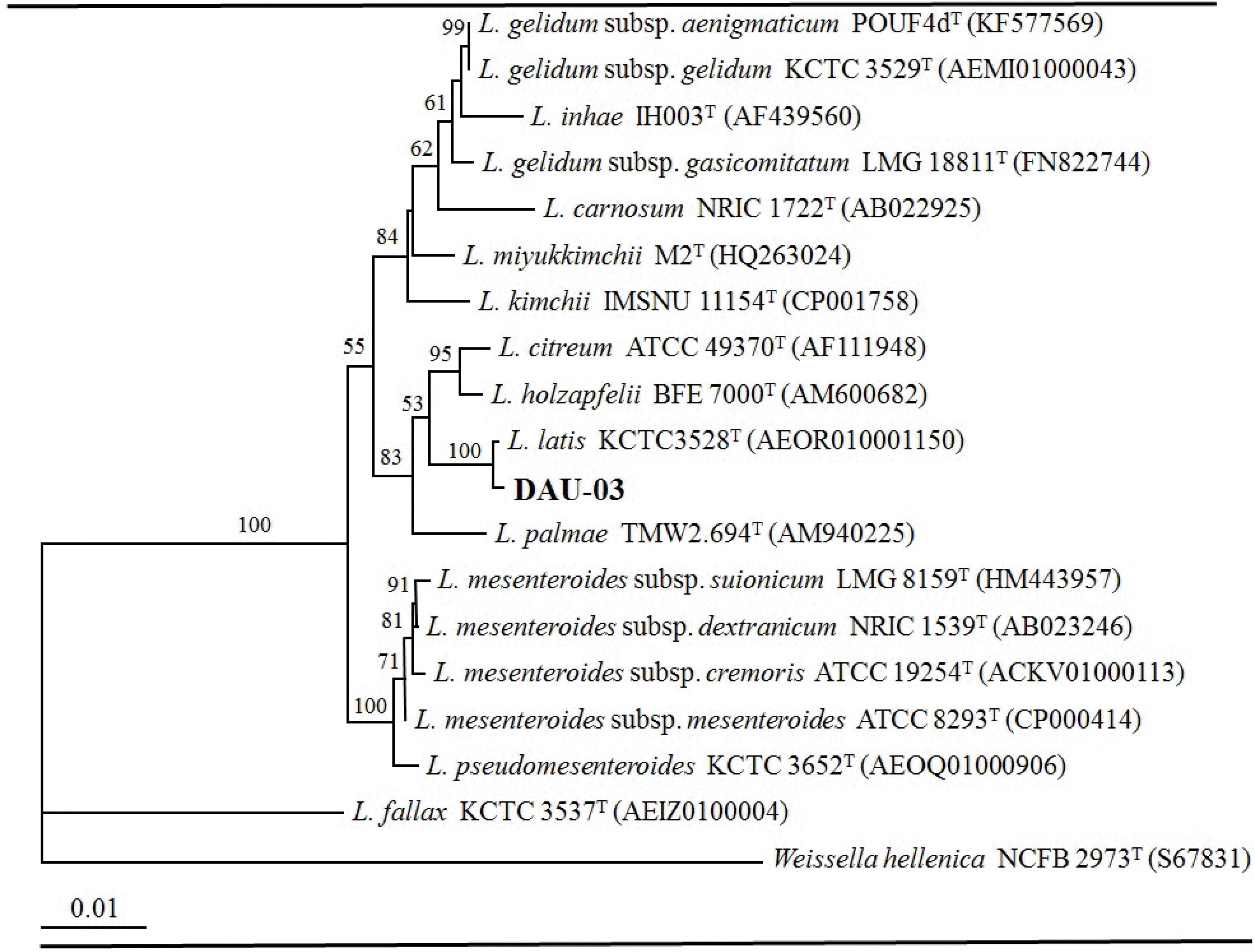
Table 1.
Clinical feature of 6 patients with L. species bacteremia
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organism | L. lactis | L. pseudomes-enteroides | L. pseudomes-enteroides | L. mesenteroides | L. citreum | L. citreum |
| Age/ Sex | 75/M | 56/M | 80F | 65M | 73F | 60M |
| Underlying disease | ||||||
| Malignancies | Pancreas cancer | External auricular cancer | Early gastric cancer | Cholangio-carcinoma, Adavanced gastric cancer | ||
| Diabetes | + | + | + | - | - | - |
| Others Indwelling venous catheter C | Cholecystitis Central catheter | Chronic hepatitis BVenous port | Congestive heart failure Atrial fibrillation | Venous port | Congestive heart failure Central catheter | Venous port |
| *WBC(/mm3) | 10,290 | 11,600 | 11,780 | 4,250 | 10,690 | 16,380 |
| *CRP(mg/dL) | 31.06 | 17.16 | 7.21 | 5.12 | 9.86 | 20.66 |
| †Antibiotics | Imipenem | Ticarcillin /clavulanate | Levofloxacin | Cefepime | Ceftriaxone | Teicoplanin, Meropenem |
| ‡All-cause mortality | Died | Died | Survived | Survived | Died | Died |
Table 2.
Antimicrobial susceptibility of isolates of L. isolates
| Patient 1 L. lactis | Patient 2 L. pseudomes-enteroides | Patient 3 L. pseudomes-enteroides | Patient 4 L. mesenteroides | Patient 5 L. citreum | Patient 6 L. citreum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin | I (4)* | S (< = 0.25) | I (0.5) | I (2) | S (< = 2) | I (4) |
| Imipenem | S (< = 1) | |||||
| Ciprofloxacin | S (1) | |||||
| Penicillin G | I (0.5) | I (0.25) | I (0.25) | I (1) | S (1) | I (2) |
| Vancomycin | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | R (>=8) | R (> = 32) | R (> = 8) |
| Clindamycin | I (0.5) | S (< = 0.25) | S (< = 0.25) | S (<=0.25) | S (< = 0.25) | S (< = 0.25) |
| Erythromycin | S (< = 0.12) | S (< = 0.12) | S (< = 0.12) | S (<=0.12) | S (< = 0.25) | S (< = 0.12) |
| Tetracyclin | S (2) | S (2) | S (2) | S (2) | S (4) | S (0.5) |
| Levofloxacin | S (1) | I (4) | S (1) | I (4) | I (4) | S (2) |
| Teicoplanin | R (> = 32) | |||||
| Norfloxacin | R (> = 16) | |||||
| Gentamicin | S (†SYN-S) | |||||
| Cefazolin | S (2) | |||||
| Ceftriaxone | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | |
| Cefotaxime | R (4) | R (4) | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | R (> = 8) | |
| Linezolid | S (< = 2) | S (< = 2) | S (< = 2) | S (< = 2) | S (< = 2) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download